Quizbank/College Physics Sem 1

- Quizbank now resides on MyOpenMath at https://www.myopenmath.com (although I hope Wikiversity can play an important role in helping students and teachers use these questions!)
- At the moment, most of the physics questions have already been transferred. To see them, join myopenmath.com as a student, and "enroll" in one or both of the following courses:
- Quizbank physics 1 (id 60675)
- Quizbank physics 2 (id 61712)
- Quizbank astronomy (id 63705)
The enrollment key for each course is 123. They are all is set to practice mode, giving students unlimited attempts at each question. Instructors can also print out copies of the quiz for classroom use. If you have any problems leave a message at user talk:Guy vandegrift.
- Latest essay: MyOpenMath/Pulling loose threads
- Latest lesson: Phasor algebra
College Physics Sem 1
[edit | edit source]This unit has 5 exams (tests) that can viewed by clicking the links (e.g., T1). They are classroom-ready exams based on the collection of quizzes shown below each exam. The fraction indicates the ratio of the number of questions randomly selected to the number of questions on each quiz. Students can access these quizzes using either the (uneditable) permalink or directly via links to subpages of QB. Students and instructors can also view all at /All. Ideas for use by instructors can be found at Quizbank/Instructions.
- Test is Wed 17 Sep 2018
2/4 from Special:Permalink/1828918 to QB/a02_1Dkinem_definitions
3/4 from Special:Permalink/1863423 to QB/a02_1Dkinem_equations
5/12 from Special:Permalink/1863384 to QB/b_motionSimpleArithmetic
3/4 from Special:Permalink/1863096 to QB/a03_2Dkinem_2dmotion
2/4 from Special:Permalink/1863115 to QB/a03_2Dkinem_smithtrain
00-Mathematics_for_this_course


Measured in radians, defines angle (in radians), where s is arclength and r is radius. The circumference of a circle is and the circle's area is is its area. The surface area of a sphere is and sphere's volume is
A vector can be expressed as, , where , and are the x and y components. Alternative notation for the unit vectors include and . An important vector is the displacement from the origin, with components are typically written without subscripts: . The magnitude (or absolute value or norm) of a vector is is , where the angle (or phase), , obeys , or (almost) equivalently, . As with any function/inverse function pair, the tangent and arctangent are related by where . The arctangent is not a true function because it is multivalued, with .

The geometric interpretations of and are shown in the figure. Vector addition and subtraction can also be defined through the components: AND
01-Introduction
|
- 1 kilometer = .621 miles and 1 MPH = 1 mi/hr ≈ .447 m/s
- Typically air density is 1.2kg/m3, with pressure 105Pa. The density of water is 1000kg/m3.
- Earth's mean radius ≈ 6371km, mass ≈ 6×1024
kg, and gravitational acceleration = g ≈ 9.8m/s2 - Universal gravitational constant = G ≈ 6.67×10−11
m3·kg−1·s−2 - Speed of sound ≈ 340m/s and the speed of light = c ≈ 3×108m/s
- One light-year ≈ 9.5×1015m ≈ 63240AU (Astronomical unit)
- The electron has charge, e ≈ 1.6 × 10−19C and mass ≈ 9.11 × 10-31kg. 1eV = 1.602 × 10-19J is a unit of energy, defined as the work associated with moving one electron through a potential difference of one volt.
- 1 amu = 1 u ≈ 1.66 × 10-27 kg is the approximate mass of a proton or neutron.
- Boltzmann's constant = kB≈ 1.38 × 10-23 J K−1 , and the gas constant is R = NAkB≈8.314 J K−1 mol−1, where NA≈ 6.02 × 1023 is the Avogadro number.
- ≈ 8.987× 109 N·m²·C−2 is a fundamental constant of electricity; also ≈ 8.854 × 10−12 F·m−1 is the vacuum permittivity or the electric constant.
- = 4π × 10−7 NA ≈ 1.257 × 10−6 N A (magnetic permeability) is the fundamental constant of magnetism: .
- = h/(2π) ≈ 1.054×10−34 J·s the reduced Planck constant, and ≈ .526 × 10−10 m is the Bohr radius.
Two dimensional kinematics
Difference is denoted by , , or the Delta. or . Average, or mean, is denoted by , where is number and are probabilities. The average velocity is , and the average acceleration is , where denotes position. In CALCULUS, instantaneous values are denoted by v(t)=dx/dt and a=dv/dt=d2x/dt2.
The equations of motion for uniform acceleration are: , and, . Also, , and, . Note that only if the acceleration is uniform.
03-Two-Dimensional_Kinematics

...in advanced notation this becomes .
In free fall we often set, ax=0 and ay= -g. If angle is measured with respect to the x axis:
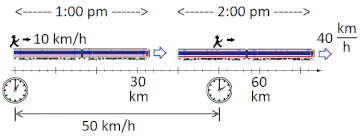
The figure shows a Man moving relative to Train with velocity, , where the velocity of the train relative to Earth is, is the velocity of the Train relative to Earth. The velocity of the Man relative to Earth is,
If the speeds are relativistic, define u=v/c where c is the speed of light, and this formula must be modified to:
7/19 from Special:Permalink/1863392 to QB/b_velocityAcceleration
1/4 from Special:Permalink/1863116 to QB/a04DynForce Newton_forces
2/4 from Special:Permalink/1863117 to QB/a04DynForce Newton_sled
2/5 from Special:Permalink/1863118 to QB/a04DynForce Newton_tensions
1/5 from Special:Permalink/1863119 to QB/a05frictDragElast_3rdLaw
2/5 from Special:Permalink/1863120 to QB/a06uniformCircMotGravitation_friction
2/14 from Special:Permalink/1828920 to QB/a06uniformCircMotGravitation_proof
1/3 from Special:Permalink/1828921 to QB/a07energy_cart1
2/3 from Special:Permalink/1863130 to QB/a07energy_cart2
2/3 from Special:Permalink/1863132 to QB/a08linearMomentumCollisions
3/5 from Special:Permalink/1863453 to QB/a09staticsTorques_torque
2/4 from Special:Permalink/1863455 to QB/a10rotationalMotionAngMom_dynamics
2/4 from Special:Permalink/1863294 to QB/a11fluidStatics_buoyantForce
1/4 from Special:Permalink/1863299 to QB/a12fluidDynamics_pipeDiameter
1/3 from Special:Permalink/1863303 to QB/a13TemperatureKineticTheoGasLaw
2/4 from Special:Permalink/1863314 to QB/a14HeatTransfer_specifHeatConduct
2/4 from Special:Permalink/1863334 to QB/a15Thermodynamics_heatEngine
1/4 from Special:Permalink/1863423 to QB/a02_1Dkinem_equations
1/12 from Special:Permalink/1863384 to QB/b_motionSimpleArithmetic
1/4 from Special:Permalink/1863096 to QB/a03_2Dkinem_2dmotion
1/19 from Special:Permalink/1863392 to QB/b_velocityAcceleration
1/4 from Special:Permalink/1863116 to QB/a04DynForce Newton_forces
1/4 from Special:Permalink/1863117 to QB/a04DynForce Newton_sled
1/5 from Special:Permalink/1863118 to QB/a04DynForce Newton_tensions
1/3 from Special:Permalink/1863130 to QB/a07energy_cart2
1/3 from Special:Permalink/1863132 to QB/a08linearMomentumCollisions
1/5 from Special:Permalink/1863453 to QB/a09staticsTorques_torque
1/4 from Special:Permalink/1863455 to QB/a10rotationalMotionAngMom_dynamics
1/4 from Special:Permalink/1863294 to QB/a11fluidStatics_buoyantForce
1/4 from Special:Permalink/1863299 to QB/a12fluidDynamics_pipeDiameter
1/3 from Special:Permalink/1863303 to QB/a13TemperatureKineticTheoGasLaw
1/4 from Special:Permalink/1863314 to QB/a14HeatTransfer_specifHeatConduct
1/4 from Special:Permalink/1863334 to QB/a15Thermodynamics_heatEngine
Links
[edit | edit source]- Questions list (useful for students as they prepare for the tests)
- All a variation of the previous link
- Quizbank/Instructions (classroom use suggestions)
- Subpages





























































