WikiJournal Preprints/Planet Nine
Treedegateer
This article is an unpublished pre-print not yet undergoing peer review.
It is adapted from the Wikipedia page Planet Nine and contains some or all of that page's content licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution ShareAlike License and is intended to be used to update that page after peer review.
To submit this article for peer review, please:
Suggested (provisional) preprint citation format:
WikiJournal Preprints/Planet Nine, Wikidata Q22133699
Reviewers: (comments)
Article information
Abstract
This undiscovered super-Earth-sized planet would have a predicted mass of five to ten times that of the Earth, and an elongated orbit 400 to 800 times as far from the Sun as the Earth. Konstantin Batygin and Michael E. Brown suggest that Planet Nine could be the core of a giant planet that was ejected from its original orbit by Jupiter during the genesis of the Solar System. Others propose that the planet was captured from another star,[5] was once a rogue planet, or that it formed on a distant orbit and was pulled into an eccentric orbit by a passing star.[1]
As of September 2019[update] , no observation of Planet Nine had been announced.[6][7] While sky surveys such as Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) and Pan-STARRS did not detect Planet Nine, they have not ruled out the existence of a Neptune-diameter object in the outer Solar System.[8][9] The ability of these past sky surveys to detect Planet Nine were dependent on its location and characteristics. Further surveys of the remaining regions are ongoing using NEOWISE and the 8-meter Subaru Telescope.[6][10] Unless Planet Nine is observed, its existence is purely conjectural. Several alternative theories have been proposed to explain the observed clustering of TNOs.
History
[edit | edit source]Following the discovery of Neptune in 1846, there was considerable speculation that another planet might exist beyond its orbit. The best-known of these theories predicted the existence of a distant planet that was influencing the orbits of Uranus and Neptune. After extensive calculations Percival Lowell predicted the possible orbit and location of the hypothetical trans-Neptunian planet and began an extensive search for it in 1906. He called the hypothetical object Planet X, a name previously used by Gabriel Dallet.[11][12] Clyde Tombaugh continued Lowell's search and in 1930 discovered Pluto, but it was soon determined to be too small to qualify as Lowell's Planet X.[13] After Voyager 2's flyby of Neptune in 1989, the difference between Uranus' predicted and observed orbit was determined to have been due to the use of a previously inaccurate mass of Neptune.[14]
Attempts to detect planets beyond Neptune by indirect means such as orbital perturbation date back to before the discovery of Pluto. Among the first was George Forbes who postulated the existence of two trans-Neptunian planets in 1880. One would have an average distance from the Sun, or semi-major axis, of 100 astronomical units (AU), 100 times that of the Earth. The second would have a semimajor axis of 300 AU. His work is considered similar to more recent Planet Nine theories in that the planets would be responsible for a clustering of the orbits of several objects, in this case the aphelion distances of periodic comets similar to that of the Jupiter-family comets.[15][16]
The discovery of Sedna's peculiar orbit in 2004 led to speculation that it had encountered a massive body other than one of the known planets. Sedna's orbit is detached, with a perihelion distance of 76 AU that is too large to be due to gravitational interactions with Neptune. Several authors proposed that Sedna entered this orbit after encountering an unknown planet on a distant orbit, a member of the open cluster that formed with the Sun, or another star that later passed near the Solar System.[17][18] The announcement in March 2014 of the discovery of a second sednoid with a perihelion distance of 80 AU, 2012 VP113, in a similar orbit led to renewed speculation that an unknown super-Earth remained in the distant Solar System.[19][20]
At a conference in 2012, Rodney Gomes proposed that an undetected planet was responsible for the orbits of some eTNOs with detached orbits and the large semi-major axis Centaurs, small Solar System bodies that cross the orbits of the giant planets.[21][22] The proposed Neptune-massed planet would be in a distant (1500 AU), eccentric (eccentricity 0.4), and inclined (inclination 40°) orbit. Like Planet Nine it would cause the perihelia of objects with semi-major axes greater than 300 AU to oscillate, delivering some into planet-crossing orbits and others into detached orbits like that of Sedna. An article by Gomes, Soares, and Brasser was published in 2015, detailing their arguments.[23]
In 2014, astronomers Chad Trujillo and Scott S. Sheppard noted the similarities in the orbits of Sedna and 2012 VP113 and several other eTNOs. They proposed that an unknown planet in a circular orbit between 200 and 300 AU was perturbing their orbits. Later, in 2015, Raúl and Carlos de la Fuente Marco argued that two massive planets in orbital resonance were necessary to produce the similarities of so many orbits.[3]
Batygin and Brown hypothesis
[edit | edit source]
In early 2016, California Institute of Technology's Batygin and Brown described how the similar orbits of six eTNOs could be explained by Planet Nine and proposed a possible orbit for the planet.[1] This hypothesis could also explain eTNOs with orbits perpendicular to the inner planets[1] and others with extreme inclinations,[25] and had been offered as an explanation of the tilt of the Sun's axis.[26]
Orbit
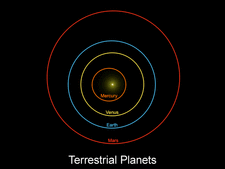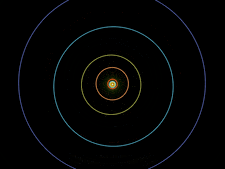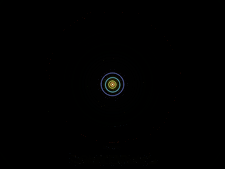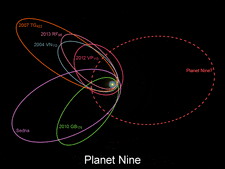
[edit | edit source]Planet Nine is hypothesized to follow an elliptical orbit around the Sun with an eccentricity of 0.2 to 0.5. The planet's semi-major axis is estimated to be 400 AU to 800 AU,[A] roughly 13 to 26 times the distance from Neptune to the Sun. It would take the planet between 10,000 and 20,000 years to make one full orbit around the Sun.[27] Its inclination to the ecliptic, the plane of the Earth's orbit, is projected to be 15 ° to 25 °.[2] [B] The aphelion, or farthest point from the Sun, would be in the general direction of the constellation of Taurus,[28] whereas the perihelion, the nearest point to the Sun, would be in the general direction of the southerly areas of Serpens (Caput), Ophiuchus, and Libra.[29][30] Brown thinks that if Planet Nine is confirmed to exist, a probe could reach it in as little as 20 years by using a powered slingshot trajectory around the Sun.[31]
Mass and radius
[edit | edit source]The planet is estimated to have 5 to 10 times the mass of Earth and a radius of 2 to 4 times Earth's.[2] Brown thinks that if Planet Nine exists, its mass is sufficient to clear its orbit of large bodies in 4.6 billion years, the age of the Solar System, and that its gravity dominates the outer edge of the Solar System, which is sufficient to make it a planet by current definitions.[32] Astronomer Jean-Luc Margot has also stated that Planet Nine satisfies his criteria and would qualify as a planet if and when it is detected.[33][34]
Origin
[edit | edit source]Several possible origins for Planet Nine have been examined including its ejection from the neighborhood of the known giant planets, capture from another star, and in situ formation. In their initial article, Batygin and Brown proposed that Planet Nine formed closer to the Sun and was ejected into a distant eccentric orbit following a close encounter with Jupiter or Saturn during the nebular epoch.[1] The gravity of a nearby star, or drag from the gaseous remnants of the Solar nebula,[35] then reduced the eccentricity of its orbit. This raised its perihelion, leaving it in a very wide but stable orbit beyond the influence of the other planets.[36][37] The odds of this occurring has been estimated at a few percent.[38] Had it not been flung into the Solar System's farthest reaches, Planet Nine could have accreted more mass from the proto-planetary disk and developed into the core of a gas giant.[32][39] Instead, its growth was halted early, leaving it with a lower mass than Uranus or Neptune.[40]
Dynamical friction from a massive belt of planetesimals could also enable Planet Nine's capture in a stable orbit. Recent models propose that a 60–130 Earth mass disk of planetesimals could have formed as the gas was cleared from the outer parts of the proto-planetary disk.[41] As Planet Nine passed through this disk its gravity would alter the paths of the individual objects in a way that reduced Planet Nine's velocity relative to it. This would lower the eccentricity of Planet Nine and stabilize its orbit. If this disk had a distant inner edge, 100–200 AU, a planet encountering Neptune would have a 20% chance of being captured in an orbit similar to that proposed for Planet Nine, with the observed clustering more likely if the inner edge is at 200 AU. Unlike the gas nebula, the planetesimal disk is likely to have been long lived, potentially allowing a later capture.[42]
Planet Nine could have been captured from outside the Solar System during a close encounter between the Sun and another star. If a planet was in a distant orbit around this star, three-body interactions during the encounter could alter the planet's path, leaving it in a stable orbit around the Sun. A planet originating in a system without Jupiter-massed planets could remain in a distant eccentric orbit for a longer time, increasing its chances of capture.[5] The wider range of possible orbits would reduce the odds of its capture in a relatively low inclination orbit to 1–2 percent.[43] This process could also occur with rogue planets, but the likelihood of their capture is much smaller, with only 0.05–0.10% being captured in orbits similar to that proposed for Planet Nine.[44]
An encounter with another star could also alter the orbit of a distant planet, shifting it from a circular to an eccentric orbit. The in situ formation of a planet at this distance would require a very massive and extensive disk,[1] or the outward drift of solids in a dissipating disk forming a narrow ring from which the planet accreted over a billion years.[45] If a planet formed at such a great distance while the Sun was in its original cluster, the probability of it remaining bound to the Sun in a highly eccentric orbit is roughly 10%.[43] A previous article reported that if the massive disk extended beyond 80 AU some objects scattered outward by Jupiter and Saturn would have been left in high inclination (inc > 50°), low eccentricity orbits which have not been observed.[46] An extended disk would also have been subject to gravitational disruption by passing stars and by mass loss due to photoevaporation while the Sun remained in the open cluster where it formed.[2]
Evidence
[edit | edit source]
|
|
‡ Trans-Neptunian dwarf planets are called "plutoids" |
The gravitational influence of Planet Nine would explain four peculiarities of the Solar System:[47]
- the clustering of the orbits of eTNOs;
- the high perihelia of objects like 90377 Sedna that are detached from Neptune's influence;
- the high inclinations of eTNOs with orbits roughly perpendicular to the orbits of the eight known planets;
- high-inclination trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs) with semi-major axis less than 100 AU.
Planet Nine was initially proposed to explain the clustering of orbits, via a mechanism that would also explain the high perihelia of objects like Sedna. The evolution of some of these objects into perpendicular orbits was unexpected, but found to match objects previously observed. The orbits of some objects with perpendicular orbits were later found to evolve toward smaller semi-major axes when the other planets were included in simulations. Although other mechanisms have been offered for many of these peculiarities, the gravitational influence of Planet Nine is the only one that explains all four. The gravity of Planet Nine would also increase the inclinations of other objects that cross its orbit, however, which could leave the scattered disk objects,[48] bodies orbiting beyond Neptune with semi-major axes greater than 50 AU, and short-period comets with a broader inclination distribution than is observed.[49] Previously Planet Nine was hypothesized to be responsible for the 6 degree tilt of the Sun's axis relative to the orbits of the planets,[50] but recent updates to its predicted orbit and mass limit this shift to ~1 degree.[2]
Observations: Orbital clustering of high perihelion objects
[edit | edit source]
The clustering of the orbits of TNOs with large semi-major axes was first described by Trujillo and Sheppard, who noted similarities between the orbits of Sedna and 2012 VP113. Without the presence of Planet Nine, these orbits should be distributed randomly, without preference for any direction. Upon further analysis, Trujillo and Sheppard observed that the arguments of perihelion of 12 TNOs with perihelia greater than 30 AU and semi-major axes greater than 150 AU were clustered near zero degrees, meaning that they rise through the ecliptic when they are closest to the Sun. Trujillo and Sheppard proposed that this alignment was caused by a massive unknown planet beyond Neptune via the Kozai mechanism.[3] For objects with similar semi-major axes the Kozai mechanism would confine their arguments of perihelion to near 0 or 180 degrees. This confinement allows objects with eccentric and inclined orbits to avoid close approaches to the planet because they would cross the plane of the planet's orbit at their closest and farthest points from the Sun, and cross the planet's orbit when they are well above or below its orbit.[51][52] Trujillo and Sheppard's hypothesis about how the objects would be aligned by the Kozai mechanism has been supplanted by further analysis and evidence.[1]
Batygin and Brown, looking to refute the mechanism proposed by Trujillo and Sheppard, also examined the orbits of the TNOs with large semi-major axes.[1] After eliminating the objects in Trujillo and Sheppard's original analysis that were unstable due to close approaches to Neptune or were affected by Neptune's mean-motion resonances, Batygin and Brown determined that the arguments of perihelion for the remaining six objects (Sedna, 2012 VP113, 2004 VN112, 2010 GB174, 2000 CR105, and 2010 VZ98) were clustered around 318±8 °. This finding did not agree with how the Kozai mechanism would tend to align orbits with arguments of perihelion at 0° or 180°.[1][C]
Batygin and Brown also found that the orbits of the six eTNOs with semi-major axes greater than 250 AU and perihelia beyond 30 AU (Sedna, 2012 VP113, 2004 VN112, 2010 GB174, 2007 TG422, and 2013 RF98) were aligned in space with their perihelia in roughly the same direction, resulting in a clustering of their longitudes of perihelion, the location where they make their closest approaches to the Sun. The orbits of the six objects were also tilted with respect to that of the ecliptic and approximately coplanar, producing a clustering of their longitudes of ascending nodes, the directions where they each rise through the ecliptic. They determined that there was only a 0.007% likelihood that this combination of alignments was due to chance.[1][53][54] These six objects had been discovered by six different surveys on six different telescopes. That made it less likely that the clumping might be due to an observation bias such as pointing a telescope at a particular part of the sky. The observed clustering should be smeared out in a few hundred million years due to the locations of the perihelia and the ascending nodes changing, or precessing, at differing rates due to their varied semi-major axes and eccentricities.[D] This indicates that the clustering could not be due to an event in the distant past,[1] for example a passing star,[55] and is most likely maintained by the gravitational field of an object orbiting the Sun.[1]
Two of the six objects (2013 RF98 and 2004 VN112) also have very similar orbits and spectra.[56][57] This has led to the suggestion that they were a binary object disrupted near aphelion during an encounter with a distant object. The disruption of a binary would require a relatively close encounter, which becomes less likely at large distances from the Sun.[58]
In a later article Trujillo and Sheppard noted a correlation between the longitude of perihelion and the argument of perihelion of the TNOs with semi-major axes greater than 150 AU. Those with a longitude of perihelion of 0–120° have arguments of perihelion between 280–360°, and those with longitude of perihelion between 180° and 340° have arguments of perihelion between 0° and 40°. The statistical significance of this correlation was 99.99%. They suggested that the correlation is due to the orbits of these objects avoiding close approaches to a massive planet by passing above or below its orbit.[59]
A 2017 article by Carlos and Raul de la Fuente Marcos noted that distribution of the distances to the ascending nodes of the eTNOs, and those of centaurs and comets with large semi-major axes, may be bimodal. They suggest it is due to the eTNOs avoiding close approaches to a planet with a semi-major axis of 300–400 AU.[60][61]
A) Six original and eight additional eTNO objects orbits with current positions near their perihelion in purple, with hypothetical Planet Nine orbit in green B) Close up view of 13 eTNO current positions
Simulations: Observed clustering reproduced
[edit | edit source]The clustering of the orbits of eTNOs and raising of their perihelia is reproduced in simulations that include Planet Nine. In simulations conducted by Batygin and Brown, swarms of scattered disk objects with semi-major axes up to 550 AU that began with random orientations were sculpted into roughly collinear and coplanar groups of spatially confined orbits by a massive distant planet in a highly eccentric orbit. This left most of the objects' perihelia pointed in similar directions and the objects' orbits with similar tilts. Many of these objects entered high-perihelion orbits like Sedna and, unexpectedly, some entered perpendicular orbits that Batygin and Brown later noticed had been previously observed.[1]
In their original analysis Batygin and Brown found that the distribution of the orbits of the first six eTNOs was best reproduced in simulations using a 10 Earth mass[E] planet in the following orbit:[F]
- semi-major axis a ≈ 700 AU (orbital period 7001.5=18,520 years)
- eccentricity e ≈ 0.6, (perihelion ≈ 280 AU, aphelion ≈ 1120 AU)
- inclination i ≈ 30° to the ecliptic
- longitude of the ascending node Ω ≈ 100 °.[G]
- argument of perihelion ω ≈ 140° and longitude of perihelion ϖ = 240 °[62]
These parameters for Planet Nine produce different simulated effects on TNOs. Objects with semi-major axis greater than 250 AU are strongly anti-aligned with Planet Nine, with perihelia opposite Planet Nine's perihelion. Objects with semi-major axes between 150 AU and 250 AU are weakly aligned with Planet Nine, with perihelia in the same direction as Planet Nine's perihelion. Little effect is found on objects with semi-major axes less than 150 AU.[8] The simulations also revealed that objects with semi-major axis greater than 250 AU could have stable, aligned orbits if they had lower eccentricities. These objects have yet to be observed.[1]
Other possible orbits for Planet Nine were also examined, with semi-major axes between 400 AU and 1500 AU, eccentricites up to 0.8, and a wide range of inclinations. These orbits yield varied results. Batygin and Brown found that orbits of the eTNOs were more likely to have similar tilts if Planet Nine had a higher inclination, but anti-alignment also decreased.[8] Simulations by Becker et al. showed that their orbits were more stable if Planet Nine had a smaller eccentricity, but that anti-alignment was more likely at higher eccentricities.[63] Lawler et al. found that the population captured in orbital resonances with Planet Nine was smaller if it had a circular orbit, and that fewer objects reached high inclination orbits.[64] Investigations by Cáceres et al. showed that the orbits of the eTNOs were better aligned if Planet Nine had a lower perihelion orbit, but its perihelion would need to be higher than 90 AU.[65] Later investigations by Batygin et al. found that higher eccentricity orbits reduced the average tilts of the eTNOs orbits.[2] While there are many possible combinations of orbital parameters and masses for Planet Nine, none of the alternative simulations have been better at predicting the observed alignment of objects in the Solar System. The discovery of additional distant Solar System objects would allow astronomers to make more accurate predictions about the orbit of the hypothesized planet. These may also provide further support for, or refutation of, the Planet Nine hypothesis.[66][67]
Simulations that included the migration of giant planets resulted in a weaker alignment of the eTNOs orbits.[49] The direction of alignment also switched, from more aligned to anti-aligned with increasing semi-major axis, and from anti-aligned to aligned with increasing perihelion distance. The latter would result in the sednoids' orbits being oriented opposite most of the other eTNOs.[48]
Dynamics: How Planet Nine modifies the orbits of eTNOs
[edit | edit source]
Planet Nine modifies the orbits of eTNOs via a combination of effects. On very long timescales Planet Nine exerts a torque on the orbits of the eTNOs that varies with the alignment of their orbits with Planet Nine's. The resulting exchanges of angular momentum cause the perihelia to rise, placing them in Sedna-like orbits, and later fall, returning them to their original orbits after several hundred million years. The motion of their directions of perihelion also reverses when their eccentricities are small, keeping the objects anti-aligned, see blue curves on diagram, or aligned, red curves. On shorter timescales mean-motion resonances with Planet Nine provides phase protection, which stabilizes their orbits by slightly altering the objects' semi-major axes, keeping their orbits synchronized with Planet Nine's and preventing close approaches. The gravity of Neptune and the other giant planets, and the inclination of Planet Nine's orbit, weaken this protection. This results in a chaotic variation of semi-major axes as objects hop between resonances, including high order resonances such as 27:17, on million-year timescales.[69] The mean-motion resonances may not be necessary for the survival of eTNOs if they and Planet Nine are both on inclined orbits.[70] The orbital poles of the objects precess around, or circle, the pole of the Solar System's Laplace plane. At large semi-major axes the Laplace plane is warped toward the plane of Planet Nine's orbit. This causes orbital poles of the eTNOs on average to be tilted toward one side and their longitudes of ascending nodes to be clustered.[69]
Objects in perpendicular orbits with large semi-major axis
[edit | edit source]
Planet Nine can deliver eTNOs into orbits roughly perpendicular to the ecliptic.[71][72] Several objects with high inclinations, greater than 50°, and large semi-major axes, above 250 AU, have been observed.[73] These orbits are produced when some low inclination eTNOs enter a secular resonance with Planet Nine upon reaching low eccentricity orbits. The resonance causes their eccentricities and inclinations to increase, delivering the eTNOs into perpendicular orbits with low perihelia where they are more readily observed. The eTNOs then evolve into retrograde orbits with lower eccentricities, after which they pass through a second phase of high eccentricity perpendicular orbits, before returning to low eccentricity and inclination orbits. The secular resonance with Planet Nine involves a linear combination of the orbit's arguments and longitudes of perihelion: Δϖ – 2ω. Unlike the Kozai mechanism this resonance causes objects to reach their maximum eccentricities when in nearly perpendicular orbits. In simulations conducted by Batygin and Morbidelli this evolution was relatively common, with 38% of stable objects undergoing it at least once.[69] The arguments of perihelion of these objects are clustered near or opposite Planet Nine's and their longitudes of ascending node are clustered around 90° in either direction from Planet Nine's when they reach low perihelia.[1][70] This is in rough agreement with observations with the differences attributed to distant encounters with the known giant planets.[1]
Orbits of high-inclination objects
[edit | edit source]A population of high-inclination TNOs with semi-major axes less than 100 AU may be generated by the combined effects of Planet Nine and the other giant planets. The eTNOs that enter perpendicular orbits have perihelia low enough for their orbits to intersect those of Neptune or the other giant planets. An encounter with one of these planets can lower an eTNO's semi-major axis to below 100 AU, where the object's orbits is no longer controlled by Planet Nine, leaving it in an orbit like 2008 KV42. The predicted orbital distribution of the longest lived of these objects is nonuniform. Most would have orbits with perihelia ranging from 5 AU to 35 AU and inclinations below 110 degree; beyond a gap with few objects are would be others with inclinations near 150 degrees and perihelia near 10 AU.[25] Previously it was proposed that these objects originated in the Oort Cloud,[74] a theoretical cloud of icy planetesimals surrounding the Sun at distances of 2,000 to 200,000 AU.[75] In simulations without Planet Nine an insufficient number are produced from the Oort cloud relative to observations, however.[48]
Oort cloud and comets
[edit | edit source]Planet Nine would alter the source regions and the inclination distribution of comets. In simulations of the migration of the giant planets described by the Nice model fewer objects are captured in the Oort cloud when Planet Nine is included. Other objects would be captured in a cloud of objects dynamically controlled by Planet Nine. This Planet Nine cloud, made up of the eTNOs and the perpendicular objects, would extend from semi-major axes of 200 AU to 3000 AU and contain roughly 0.3–0.4 Earth masses.[49][64] When the perihelia of objects in the Planet Nine cloud drop low enough for them to encounter the other planets some would be scattered into orbits that enter the inner Solar System where they could be observed as comets. If Planet Nine exists these would make up roughly one third of the Halley-type comets. Interactions with Planet Nine would also increase the inclinations of the scattered disk objects that cross its orbit. This could result in more with moderate inclinations of 15–30 degrees than are observed.[48] The inclinations of the Jupiter-family comets derived from that population would also have a broader inclination distribution than is observed.[49][76] Recent estimates of a smaller mass and eccentricity for Planet Nine would reduce its effect on these inclinations.[2]
Reception
[edit | edit source]Batygin was cautious in interpreting the results of the simulation developed for his and Brown's research article, saying, "Until Planet Nine is caught on camera it does not count as being real. All we have now is an echo."[77] Brown put the odds for the existence of Planet Nine at about 90%.[32] Greg Laughlin, one of the few researchers who knew in advance about this article, gives an estimate of 68.3%.[4] Other skeptical scientists demand more data in terms of additional KBOs to be analyzed or final evidence through photographic confirmation.[78][67][79] Brown, though conceding the skeptics' point, still thinks that there is enough data to mount a search for a new planet.[80]
The Planet Nine hypothesis is supported by several astronomers and academics. Jim Green, director of NASA's Science Mission Directorate, said, "the evidence is stronger now than it's been before".[81] But Green also cautioned about the possibility of other explanations for the observed motion of distant eTNOs and, quoting Carl Sagan, he said, "extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence."[32] Massachusetts Institute of Technology Professor Tom Levenson concluded that, for now, Planet Nine seems the only satisfactory explanation for everything now known about the outer regions of the Solar System.[77] Astronomer Alessandro Morbidelli, who reviewed the research article for The Astronomical Journal, concurred, saying, "I don't see any alternative explanation to that offered by Batygin and Brown."[4][32]
Astronomer Renu Malhotra remains agnostic about Planet Nine, but noted that she and her colleagues have found that the orbits of eTNOs seem tilted in a way that is difficult to otherwise explain. "The amount of warp we see is just crazy," she said. "To me, it's the most intriguing evidence for Planet Nine I've run across so far."[82]
Other authorities have varying degrees of skepticism. American astrophysicist Ethan Siegel, who previously speculated that planets may have been ejected from the Solar System during an early dynamical instability, is skeptical of the existence of an undiscovered planet in the Solar System.[72][83] In a 2018 article discussing a survey that did not find evidence of clustering of the eTNOs' orbits he suggests the previously observed clustering could have been the result of observing bias and claims most scientists think Planet Nine does not exist.[84] Planetary scientist Hal Levison thinks that the chance of an ejected object ending up in the inner Oort cloud is only about 2%, and speculates that many objects must have been thrown past the Oort cloud if one has entered a stable orbit.[85]
Alternative hypotheses
[edit | edit source]Temporary or coincidental clustering
[edit | edit source]The results of the Outer Solar System Survey (OSSOS) suggest that the observed clustering is the result of a combination of observing bias and small number statistics. OSSOS, a well-characterized survey of the outer Solar System with known biases, observed eight objects with semi-major axis > 150 AU with orbits oriented in a wide range of directions. After accounting for the observational biases of the survey, no evidence for the arguments of perihelion (ω) clustering identified by Trujillo and Sheppard was seen,[I] and the orientation of the orbits of the objects with the largest semi-major axis was statistically consistent with being random.[86][87] This result differed from an analysis of discovery biases in the previously observed eTNOs by Mike Brown. He found that after observation biases were accounted for, the clustering of longitudes of perihelion of 10 known eTNOs would be observed only 1.2% of the time if their actual distribution was uniform. When combined with the odds of the observed clustering of the arguments of perihelion, the probability was 0.025%.[88] A later analysis of the discovery biases of 14 eTNOs by Brown and Batygin determined the probability of the observed clustering of the longitudes of perihelion and the orbital pole locations to be 0.2%.[89]
Simulations of 15 known objects evolving under the influence of Planet Nine also revealed differences from observations. Cory Shankman and his colleagues included Planet Nine in a simulation of many clones (objects with similar orbits) of 15 objects with semi-major axis > 150 AU and perihelion > 30 AU.[J] While they observed alignment of the orbits opposite that of Planet Nine's for the objects with semi-major axis greater than 250 AU, clustering of the arguments of perihelion was not seen. Their simulations also showed that the perihelia of the eTNOs rose and fell smoothly, leaving many with perihelion distances between 50 AU and 70 AU where none had been observed, and predicted that there would be many other unobserved objects.[90] These included a large reservoir of high-inclination objects that would have been missed due to most observations being at small inclinations,[64] and a large population of objects with perihelia so distant that they would be too faint to observe. Many of the objects were also ejected from the Solar System after encountering the other giant planets. The large unobserved populations and the loss of many objects led Shankman et al. to estimate that the mass of the original population was tens of Earth masses, requiring that a much larger mass had been ejected during the early Solar System.[K] Shankman et al. concluded that the existence of Planet Nine is unlikely and that the currently observed alignment of the existing eTNOs is a temporary phenomenon that will disappear as more objects are detected.[82][90]
Inclination instability in a massive disk
[edit | edit source]Ann-Marie Madigan and Michael McCourt postulate that an inclination instability in a distant massive belt is responsible for the alignment of the arguments of perihelion of the eTNOs.[91] An inclination instability could occur in a disk of particles with high eccentricity orbits (e > 0.6) around a central body, such as the Sun. The self-gravity of this disk would cause its spontaneous organization, increasing the inclinations of the objects and aligning the arguments of perihelion, forming it into a cone above or below the original plane.[92] This process would require an extended time and significant mass of the disk, on the order of a billion years for a 1–10 Earth-mass disk.[91] While an inclination instability could align the arguments of perihelion and raise perihelia, producing detached objects, it would not align the longitudes of perihelion.[88] Mike Brown considers Planet Nine a more probable explanation, noting that current surveys have not revealed a large enough scattered-disk to produce an "inclination instability".[93][94] In Nice model simulations of the Solar System that included the self-gravity of the planetesimal disk an inclination instability did not occur. Instead, the simulation produced a rapid precession of the objects' orbits and most of the objects were ejected on too short of a timescale for an inclination instability to occur.[95]
Shepherding by a massive disk
[edit | edit source]Antranik Sefilian and Jihad Touma propose that a massive disk of moderately eccentric TNOs is responsible for the clustering of the longitudes of perihelion of the eTNOs. Their predicted 10 Earth-mass disk would contain TNOs with aligned orbits and eccentricities that increased with their semimajor axes ranging from zero to 0.165. The gravitational effects of this disk would offset the forward precession driven by the giant planets so that the orbital orientations of its individual objects are maintained. The orbits of objects with high eccentricities, such as the observed eTNOs, would be stable and have roughly fixed orientations, or longitudes of perihelion, if their orbits were anti-aligned with this disk.[96] Although Brown thinks the proposed disk could explain the observed clustering of the eTNOs, he finds it implausible that the disk could survive over the age of the Solar System.[97] Batygin thinks that there is insufficient mass in the Kuiper belt to explain the formation of the disk and asks "why would the protoplanetary disk end near 30 AU and restart beyond 100 AU?"[98]
Planet in lower eccentricity orbit
[edit | edit source]| Body | Barycentric period (years) |
Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 GP136 | 1,830 | 9:1 |
| 2000 CR105 | 3,304 | 5:1 |
| 2012 VP113 | 4,300 | 4:1 |
| 2004 VN112 | 5,900 | 3:1 |
| 2010 GB174 | 6,600 | 5:2 |
| 90377 Sedna | ≈ 11,400 | 3:2 |
| Hypothetical planet | ≈ 17,000 | 1:1 |
The Planet Nine hypothesis includes a set of predictions about the mass and orbit of the planet. An alternative theory predicts a planet with different orbital parameters. Malhotra, Kathryn Volk, and Xianyu Wang have proposed that the four detached objects with the longest orbital periods, those with perihelia beyond 40 AU and semi-major axes greater than 250 AU, are in n:1 or n:2 mean-motion resonances with a hypothetical planet. Two other objects with semi-major axes greater than 150 AU are also potentially in resonance with this planet. Their proposed planet could be on a lower eccentricity, low inclination orbit, with eccentricity e < 0.18 and inclination i ≈ 11°. The eccentricity is limited in this case by the requirement that close approaches of 2010 GB174 to the planet are avoided. If the eTNOs are in periodic orbits of the third kind,[L] with their stability enhanced by the libration of their arguments of perihelion, the planet could be in a higher inclination orbit, with i ≈ 48°. Unlike Batygin and Brown, Malhotra, Volk and Wang do not specify that most of the distant detached objects would have orbits anti-aligned with the massive planet.[99][101]
Alignment due to the Kozai mechanism
[edit | edit source]Trujillo and Sheppard argued in 2014 that a massive planet in a circular orbit with an average distance between 200 AU and 300 AU was responsible for the clustering of the arguments of perihelion of twelve TNOs with large semi-major axes. Trujillo and Sheppard identified a clustering near zero degrees of the arguments of perihelion of the orbits of twelve TNOs with perihelia greater than 30 AU and semi-major axes greater than 150 AU.[1][3] After numerical simulations showed that the arguments of perihelion should circulate at varying rates, leaving them randomized after billions of years, they suggested that a massive planet in a circular orbit at a few hundred astronomical units was responsible for this clustering.[3][102] This massive planet would cause the arguments of perihelion of the TNOs to librate about 0° or 180° via the Kozai mechanism so that their orbits crossed the plane of the planet's orbit near perihelion and aphelion, the closest and farthest points from the planet.[3][51] In numerical simulations including a 2–15 Earth mass body in a circular low-inclination orbit between 200 AU and 300 AU the arguments of perihelia of Sedna and 2012 VP113 librated around 0° for billions of years (although the lower perihelion objects did not) and underwent periods of libration with a Neptune mass object in a high inclination orbit at 1,500 AU.[3] Another process such as a passing star would be required to account for the absence of objects with arguments of perihelion near 180°.[1][M]
These simulations showed the basic idea of how a single large planet can shepherd the smaller TNOs into similar types of orbits. They were basic proof of concept simulations that did not obtain a unique orbit for the planet as they state there are many possible orbital configurations the planet could have.[102] Thus they did not fully formulate a model that successfully incorporated all the clustering of the eTNOs with an orbit for the planet.[1] But they were the first to notice there was a clustering in the orbits of TNOs and that the most likely reason was from an unknown massive distant planet. Their work is very similar to how Alexis Bouvard noticed Uranus' motion was peculiar and suggested that it was likely gravitational forces from an unknown 8th planet, which led to the discovery of Neptune.[105]
Raúl and Carlos de la Fuente Marcos proposed a similar model but with two distant planets in resonance.[51][106] An analysis by Carlos and Raúl de la Fuente Marcos with Sverre J. Aarseth confirmed that the observed alignment of the arguments of perihelion could not be due to observational bias. They speculated that instead it was caused by an object with a mass between that of Mars and Saturn that orbited at some 200 AU from the Sun. Like Trujillo and Sheppard they theorized that the TNOs are kept bunched together by a Kozai mechanism and compared their behavior to that of Comet 96P/Machholz under the influence of Jupiter.[107] They also struggled to explain the orbital alignment using a model with only one unknown planet, and therefore suggested that this planet is itself in resonance with a more-massive world about 250 AU from the Sun.[102][108] In their article, Brown and Batygin noted that alignment of arguments of perihelion near 0° or 180° via the Kozai mechanism requires a ratio of the semi-major axes nearly equal to one, indicating that multiple planets with orbits tuned to the data set would be required, making this explanation too unwieldy.[1]
Detection attempts
[edit | edit source]Visibility and location
[edit | edit source]Due to its extreme distance from the Sun, Planet Nine would reflect little sunlight, potentially evading telescope sightings.[32] It is expected to have an apparent magnitude fainter than 22, making it at least 600 times fainter than Pluto.[8][N] If Planet Nine exists and is close to perihelion, astronomers could identify it based on existing images. At aphelion, the largest telescopes would be required, but if the planet is currently located in between, many observatories could spot Planet Nine.[112] Statistically, the planet is more likely to be close to its aphelion at a distance greater than 600 AU.[113] This is because objects move more slowly when near their aphelion, in accordance with Kepler's second law. A 2019 study estimated that Planet Nine, if it exists, may be smaller and closer than originally thought. This would make the hypothetical planet brighter and easier to spot, with an apparent magnitude of 21–22.[2][114] According to University of Michigan professor Fred Adams, within the next 10 to 15 years, Planet Nine will either be observable or enough data will have been gathered to rule out its existence.[115][116]
Searches of existing data
[edit | edit source]The search of databases of stellar objects by Batygin and Brown has already excluded much of the sky along Planet Nine's predicted orbit. The remaining regions include the direction of its aphelion, where it would be too faint to be spotted by these surveys, and near the plane of the Milky Way, where it would be difficult to distinguish from the numerous stars.[29] This search included the archival data from the Catalina Sky Survey to magnitude c. 19, Pan-STARRS to magnitude 21.5, and infrared data from the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) satellite.[8][29] They have more recently also searched the first year data release from the Zwicky Transient Facility without identifying Planet Nine.[117]
Other researchers have been conducting searches of existing data. David Gerdes, who helped develop the camera used in the Dark Energy Survey, claims that software designed to identify distant Solar System objects such as 2014 UZ224 could find Planet Nine if it was imaged as part of that survey, which covered a quarter of the southern sky.[118][119] Michael Medford and Danny Goldstein, graduate students at the University of California, Berkeley, are also examining archived data using a technique that combines images taken at different times. Using a supercomputer they will offset the images to account for the calculated motion of Planet Nine, allowing many faint images of a faint moving object to be combined to produce a brighter image.[76] A search combining multiple images collected by WISE and NEOWISE data has also been conducted without detecting Planet Nine. This search covered regions of the sky away from the galactic plane at the "W1" wavelength (the 3.4 μm wavelength used by WISE) and is estimated to be able to detect a 10-Earth mass object out to 800–900 AU.[6][120]
Ongoing searches
[edit | edit source]Because the planet is predicted to be visible in the Northern Hemisphere, the primary search is expected to be carried out using the Subaru Telescope, which has both an aperture large enough to see faint objects and a wide field of view to shorten the search.[20] Two teams of astronomers—Batygin and Brown, as well as Trujillo and Sheppard—are undertaking this search together, and both teams expect the search to take up to five years.[10][121] Brown and Batygin initially narrowed the search for Planet Nine down to roughly 2,000 square degrees of sky near Orion, a swath of space that Batygin thinks could be covered in about 20 nights by the Subaru Telescope.[122] Subsequent refinements by Batygin and Brown have reduced the search space to 600–800 square degrees of sky.[123] In December 2018, they spent 4 half–nights and 3 full nights observing with the Subaru Telescope.[124]
Radiation
[edit | edit source]Although a distant planet such as Planet Nine would reflect little light, due to its large mass it would still be radiating the heat from its formation as it cools. At its estimated temperature of 47 K (−226.2 °C) the peak of its emissions would be at infrared wavelengths.[125] This radiation signature could be detected by Earth-based submillimeter telescopes, such as ALMA,[126] and a search could be conducted by cosmic microwave background experiments operating at mm wavelengths.[127][128][129][O] Jim Green of NASA's Science Mission Directorate is optimistic that it could be observed by the James Webb Space Telescope, the successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, that is expected to be launched in 2021.[81]
Citizen science
[edit | edit source]The Zooniverse Backyard Worlds project, started in February 2017, is using archival data from the WISE spacecraft to search for Planet Nine. The project will also search for substellar objects like brown dwarfs in the neighborhood of the Solar System.[131][132] 32,000 animations of four images each, which constitute 3 per cent of the WISE data, have been uploaded to the Backyard Worlds website. By looking for moving objects in the animations, citizen scientists might find Planet Nine.[133]
In April 2017,[134] using data from the SkyMapper telescope at Siding Spring Observatory, citizen scientists on the Zooniverse platform reported four candidates for Planet Nine. These candidates will be followed up on by astronomers to determine their viability.[135] The project, which started on 28 March 2017, completed their goals in less than three days with around five million classifications by more than 60,000 individuals.[135]
Attempts to predict location
[edit | edit source]Cassini measurements of Saturn's orbit
[edit | edit source]Precise observations of Saturn's orbit using data from Cassini suggest that Planet Nine could not be in certain sections of its proposed orbit because its gravity would cause a noticeable effect on Saturn's position. This data neither proves nor disproves that Planet Nine exists.[136]
An initial analysis by Fienga, Laskar, Manche, and Gastineau using Cassini data to search for Saturn's orbital residuals, small differences with its predicted orbit due to the Sun and the known planets, was inconsistent with Planet Nine being located with a true anomaly, the location along its orbit relative to perihelion, of −130° to −110° or −65° to 85°. The analysis, using Batygin and Brown's orbital parameters for Planet Nine, suggests that the lack of perturbations to Saturn's orbit is best explained if Planet Nine is located at a true anomaly of 117.8++11
−10 deg. At this location, Planet Nine would be approximately 630 AU from the Sun,[136] with right ascension close to 2h and declination close to −20°, in Cetus.[137] In contrast, if the putative planet is near aphelion it would be located near right ascension 3.0h to 5.5h and declination −1° to 6°.[138]
A later analysis of Cassini data by astrophysicists Matthew Holman and Matthew Payne tightened the constraints on possible locations of Planet Nine. Holman and Payne developed a more efficient model that allowed them to explore a broader range of parameters than the previous analysis. The parameters identified using this technique to analyze the Cassini data was then intersected with Batygin and Brown's dynamical constraints on Planet Nine's orbit. Holman and Payne concluded that Planet Nine is most likely to be located within 20° of RA = 40°, Dec = −15°, in an area of the sky near the constellation Cetus.[119][139]
William Folkner, a planetary scientist at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), has stated that the Cassini spacecraft is not experiencing unexplained deviations in its orbit around Saturn. An undiscovered planet would affect the orbit of Saturn, not Cassini. This could produce a signature in the measurements of Cassini, but JPL has seen no unexplained signatures in Cassini data.[140]
Analysis of Pluto's orbit
[edit | edit source]An analysis in 2016 of Pluto's orbit by Holman and Payne found perturbations much larger than predicted by Batygin and Brown's proposed orbit for Planet Nine. Holman and Payne suggested three possible explanations: systematic errors in the measurements of Pluto's orbit; an unmodeled mass in the Solar System, such as a small planet in the range of 60–100 AU (potentially explaining the Kuiper cliff); or a planet more massive or closer to the Sun instead of the planet predicted by Batygin and Brown.[82][141]
Orbits of nearly parabolic comets
[edit | edit source]An analysis of the orbits of comets with nearly parabolic orbits identifies five new comets with hyperbolic orbits that approach the nominal orbit of Planet Nine described in Batygin and Brown's initial article. If these orbits are hyperbolic due to close encounters with Planet Nine the analysis estimates that Planet Nine is currently near aphelion with a right ascension of 83–90° and a declination of 8–10°.[142] Scott Sheppard, who is skeptical of this analysis, notes that many different forces influence the orbits of comets.[82]
Occultations by Jupiter Trojans
[edit | edit source]Malena Rice and Gregory Laughlin have proposed that a network of telescopes be built to detect occultations by Jupiter Trojans. The timing of these occultations would provide precise astrometry of these objects enabling their orbits to be monitored for variations due to the tide from Planet Nine.[143]
Attempts to predict semimajor axis
[edit | edit source]An analysis by Sarah Millholland and Gregory Laughlin identified a pattern of commensurabilities (ratios between orbital periods of pairs of objects consistent with both being in resonance with another object) of the eTNOs. They identify five objects that would be near resonances with Planet Nine if had a semi-major axis of 654 AU: Sedna (3:2), 2004 VN112 (3:1), 2012 VP113 (4:1), 2000 CR105 (5:1), and 2001 FP185 (5:1). They identify this planet as Planet Nine but propose a different orbit with an eccentricity e ≈ 0.5, inclination i ≈ 30°, argument of perihelion ω ≈ 150°, and longitude of ascending node Ω ≈ 50° (the last differs from Brown and Batygin's value of 90°).[15][P]
Carlos and Raul de la Fuente Marcos also note commensurabilities among the known eTNOs similar to that of the Kuiper belt, where accidental commensurabilities occur due to objects in resonances with Neptune. They find that some of these objects would be in 5:3 and 3:1 resonances with a planet that had a semi-major axis of ≈700 AU.[145]
Three objects with smaller semi-major axes near 172 AU (2013 UH15, 2016 QV89 and 2016 QU89) have also been proposed to be in resonance with Planet Nine. These objects would be in resonance and anti-aligned with Planet Nine if it had a semi-major axis of 315 AU, below the range proposed by Batygin and Brown. Alternatively, they could be in resonance with Planet Nine, but have orbital orientations that circulate instead of being confined by Planet Nine if it had a semi-major axis of 505 AU.[146]
A later analysis by Elizabeth Bailey, Michael Brown and Konstantin Batygin found that if Planet Nine is in an eccentric and inclined orbit the capture of many of the eTNOs in higher order resonances and their chaotic transfer between resonances prevent the identification of Planet Nine's semi-major axis using current observations. They also determined that the odds of the first six objects observed being in N/1 or N/2 period ratios with Planet Nine are less than 5% if it has an eccentric orbit.[147]
Naming
[edit | edit source]Planet Nine does not have an official name and will not receive one unless its existence is confirmed via imaging. Only two planets, Uranus and Neptune, have been discovered in recorded history. However, many minor planets, including dwarf planets, asteroids, and comets have been discovered and named. Consequently, there is a well-established process for naming newly discovered solar system objects. If Planet Nine is observed, the International Astronomical Union will certify a name, with priority usually given to a name proposed by its discoverers.[148] It is likely to be a name chosen from Roman or Greek mythology.[149]
In their original article, Batygin and Brown simply referred to the object as "perturber",[1] and only in later press releases did they use "Planet Nine".[150] They have also used the names "Jehoshaphat" and "George" for Planet Nine. Brown has stated: "We actually call it Phattie[Q] when we're just talking to each other."[4] In a 2019 interview with Derek Muller for the YouTube channel Veritasium, Batygin also suggested, based on an online petition, to name the planet after singer David Bowie, and to name any potential moons of the planet after characters from Bowie's song catalogue, such as Ziggy Stardust or Starman.[151]
In 2018, planetary scientist Alan Stern objected to the name Planet Nine, saying, "It is an effort to erase Clyde Tombaugh's legacy and it's frankly insulting", suggesting the name Planet X until its discovery.[152] He signed a statement with 34 other scientists saying, "We further believe the use of this term [Planet Nine] should be discontinued in favor of culturally and taxonomically neutral terms for such planets, such as Planet X, Planet Next, or Giant Planet Five."[153] According to Brown, "'Planet X' is not a generic reference to some unknown planet, but a specific prediction of Lowell's which led to the (accidental) discovery of Pluto. Our prediction is not related to this prediction."[152]
Notes
[edit | edit source]- ↑ A range of semi-major axes extending from 400 AU to 1000 AU produce the observed clustering in simulations.[8]
- ↑ The New Yorker put the average orbital distance of Planet Nine into perspective with an apparent allusion to one of the magazine's most famous cartoons, View of the World from 9th Avenue: "If the Sun were on Fifth Avenue and Earth were one block west, Jupiter would be on the West Side Highway, Pluto would be in Montclair, New Jersey, and the new planet would be somewhere near Cleveland.[4] "
- ↑ Two types of protection mechanisms are possible:[52]
- For bodies whose values of a and e are such that they could encounter the planets only near perihelion (or aphelion), such encounters may be prevented by the high inclination and the libration of ω about 90° or 270° (even when the encounters occur, they do not affect much the minor planet's orbit due to comparatively high relative velocities).
- Another mechanism is viable when at low inclinations when ω oscillates around 0° or 180° and the minor planet's semi-major axis is close to that of the perturbing planet: in this case the °node crossing occurs always near perihelion and aphelion, far from the planet itself, provided the eccentricity is high enough and the orbit of the planet is almost circular.
- ↑ The precession rate is slower for objects with larger semi-major axes and inclinations and with smaller eccentricities: where are the masses and semi-major axes of the planets Jupiter through Neptune.
- ↑ Batygin and Brown provide an order of magnitude estimate for the mass.
- If M were equal to 0.1 Earth mass, then the dynamical evolution would proceed at an exceptionally slow rate, and the lifetime of the Solar System would likely be insufficient for the required orbital sculpting to transpire.
- If M were equal to 1 Earth mass, then long-lived apsidally anti-aligned orbits would indeed occur, but removal of unstable orbits would happen on a much longer timescale than the current evolution of the Solar System. Hence, even though they would show preference for a particular apsidal direction, they would not exhibit true confinement like the data.
- They also note that M greater than 10 Earth mass would imply a longer semi-major axis.
- ↑ calculated values in parentheses.
- ↑ The average of longitude of the ascending node for the 6 objects is about 102°. In a blog published later, Batygin and Brown constrained their estimate of the longitude of the ascending node to 94 °.
- ↑ Similar figures in articles by Beust[68] and Batygin and Morbidelli[69] are plots of the Hamiltonian, showing combinations of orbital eccentricities and orientations that have equal energy. If there are no close encounters with Planet Nine, which would change the energy of the orbit, the object's orbital elements remain on one of these curves as the orbits evolve.
- ↑ Of the eight objects with a semi-major axis > 150 AU, OSSOS found three with arguments of perihelion (ω) outside the cluster previously identified by Trujillo and Sheppard (2014):[3] 2015 GT50, 2015 KH163, and 2013 UT15.[86]
- ↑ A link to the plots of the orbital evolution of all 15 is included in the arxiv version of the article.
- ↑ Shankman et al. estimated the mass of this population at tens of Earth masses, and that hundreds to thousands of Earth masses would need to be ejected from the vicinity of the giant planets for this mass to have remained. In the Nice model 20–50 Earth masses is estimated to have been ejected, a significant mass is also ejected from the neighborhoods of the giant planets during their formation.
- ↑ This is often referred (perhaps erroneously) to as Kozai within mean-motion resonance.[100]
- ↑ Assuming that the orbital elements of these objects have not changed, Jílková et al. proposed an encounter with a passing star might have helped acquire these objects – dubbed sednitos (eTNOs with q > 30 and a > 150) by them. They also predicted that the sednitos region is populated by 930 planetesimals and the inner Oort Cloud acquired ∼440 planetesimals through the same encounter.[103][104]
- ↑ The 8 meter Subaru Telescope has achieved a 27.7 magnitude photographic limit with a ten-hour exposure,[109] which is about 100 times dimmer than Planet Nine is expected to be. For comparison, the Hubble Space Telescope has detected objects as faint as 31st magnitude with an exposure of about 2 million seconds (555 hours) during Hubble Ultra Deep Field photography.[110] Hubble’s field of view is very narrow, as is the Keck Observatory’s Large Binocular Telescope.[10] Brown hopes to make a request for use of the Hubble Space Telescope the day the planet is spotted.[111]
- ↑ It is estimated that to find Planet Nine, telescopes that can resolve a 30 mJy point source are needed, and that can also resolve an annual parallax motion of ~5 arcminutes.[130]
- ↑ A 3-D version of the image of the orbit and those of several eTNOs shown in figure 14 of "Constraints on Planet Nine's Orbit and Sky Position within a Framework of Mean-motion Resonances" is available.[144]
- ↑ Most news outlets reported the name as Phattie (a slang term for "cool" or "awesome"; also, a marijuana cigarette)[10] but The New Yorker quote cited above uses "fatty" in what appears to be a nearly unique variation. The apparently correct spelling has been substituted.
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 Batygin, Konstantin; Brown, Michael E. (2016). "Evidence for a Distant Giant Planet in the Solar System". The Astronomical Journal 151 (2): 22. doi:10.3847/0004-6256/151/2/22.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Batygin, Konstantin; Adams, Fred C.; Brown, Michael E.; Becker, Juliette C. (2019). "The Planet Nine Hypothesis". Physics Reports 805: 1–53. doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2019.01.009.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 Trujillo, Chadwick A.; Sheppard, Scott S. (2014). "A Sedna-like Body with a Perihelion of 80 Astronomical Units". Nature 507 (7493): 471–474. doi:10.1038/nature13156. PMID 24670765. Archived from the original on 16 December 2014. http://home.dtm.ciw.edu/users/sheppard/pub/TrujilloSheppard2014.pdf. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Burdick, Alan (20 January 2016). "Discovering Planet Nine". The New Yorker. Archived from the original on 21 January 2016. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Mustill, Alexander J.; Raymond, Sean N.; Davies, Melvyn B. (21 July 2016). "Is there an exoplanet in the Solar System?". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters 460 (1): L109–L113. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slw075.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Meisner, A.M.; Bromley, B.C.; Kenyon, S.J.; Anderson, T.E. (2017). "A 3π Search for Planet Nine at 3.4μm with WISE and NEOWISE". The Astronomical Journal 155 (4): 166. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aaae70.
- ↑ Perdelwitz, V.M.; Völschow, M.V.; Müller, H.M. (2018). "A New Approach to Distant Solar System Object Detection in Large Survey Data Sets". Astronomy & Astrophysics 615 (159): A159. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201732254.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 Brown, Michael E.; Batygin, Konstantin (2016). "Observational Constraints on the Orbit and Location of Planet Nine in the Outer Solar System". The Astrophysical Journal Letters 824 (2): L23. doi:10.3847/2041-8205/824/2/L23.
- ↑ Luhman, Kevin L. (2014). "A Search for a Distant Companion to the Sun with the Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer". The Astrophysical Journal 781 (4): 4. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/781/1/4.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 Hand, Eric (20 January 2016). "Astronomers say a Neptune-sized planet lurks beyond Pluto". Science. doi:10.1126/science.aae0237. Archived from the original on 20 January 2016. http://www.sciencemag.org/news/2016/01/feature-astronomers-say-neptune-sized-planet-lurks-unseen-solar-system. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- ↑ Morton Grosser (1964). "The Search For A Planet Beyond Neptune". Isis 55 (2): 163–183. doi:10.1086/349825.
- ↑ Tombaugh, Clyde W. (1946). "The Search for the Ninth Planet, Pluto". Astronomical Society of the Pacific Leaflets 5 (209): 73–80.
- ↑ Ken Croswell (1997). Planet Quest: The Epic Discovery of Alien Solar Systems. New York: The Free Press. pp. 57–58. ISBN 978-0-684-83252-4.
- ↑ Browne, Malcolm W. (1 June 1993). "Evidence for Planet X Evaporates in Spotlight of New Research". New York Times. Retrieved 9 February 2019.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Millholland, Sarah; Laughlin, Gregory (2017). "Constraints on Planet Nine's Orbit and Sky Position within a Framework of Mean-Motion Resonances". The Astronomical Journal 153 (3): 91. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/153/3/91.
- ↑ Kirkwood, D. (1880). "On Comets and Ultra-Neptunian Planets". The Observatory 3: 439–447. http://adsbit.harvard.edu/full/seri/Obs../0003//0000439.000.html.
- ↑ Wall, Mike (24 August 2011). "A Conversation With Pluto's Killer: Q & A With Astronomer Mike Brown". Space.com. Archived from the original on 2 February 2016. Retrieved 7 February 2016.
- ↑ Brown, Michael E.; Trujillo, Chadwick; Rabinowitz, David (2004). "Discovery of a Candidate Inner Oort Cloud Planetoid". The Astrophysical Journal 617 (1): 645–649. doi:10.1086/422095.
- ↑ Sample, Ian (26 March 2014). "Dwarf Planet Discovery Hints at a Hidden Super Earth in Solar System". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 29 April 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Mortillaro, Nicole (9 February 2016). "Meet Mike Brown: Pluto Killer and the Man Who Brought Us Planet 9". Global News. Archived from the original on 10 February 2016. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
'It was that search for more objects like Sedna ... led to the realization ... that they're all being pulled off in one direction by something. And that's what finally led us down the hole that there must be a big planet out there.' —Mike Brown
- ↑ Wolchover, Natalie (25 May 2012). "Planet X? New Evidence of an Unseen Planet at Solar System's Edge". LiveScience. Archived from the original on 30 January 2016. Retrieved 7 February 2016.
More work is needed to determine whether Sedna and the other scattered disc objects were sent on their circuitous trips round the Sun by a star that passed by long ago, or by an unseen planet that exists in the solar system right now. Finding and observing the orbits of other distant objects similar to Sedna will add more data points to astronomers' computer models.
- ↑ Lovett, Richard A. (12 May 2012). "New Planet Found in Our Solar System?". National Geographic News. Archived from the original on 10 July 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ Gomes, Rodney (2015). "The Observation of Large Semi-Major Axis Centaurs: Testing for the Signature of a Planetary-Mass Solar Companion". Icarus 258: 37–49. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2015.06.020.
- ↑ "Where is Planet Nine?". The Search for Planet Nine (Blog). 20 January 2016. Archived from the original on 30 January 2016.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Batygin, Konstantin; Brown, Michael E. (2016). "Generation of Highly Inclined Trans-Neptunian Objects by Planet Nine". The Astrophysical Journal Letters 833 (1): L3. doi:10.3847/2041-8205/833/1/L3.
- ↑ Gomes, Rodney; Deienno, Rogerio; Morbidelli, Alessandro (2016). "The Inclination of the Planetary System Relative to the Solar Equator May Be Explained by the Presence of Planet 9". The Astronomical Journal 153 (1): 27. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/153/1/27.
- ↑ "Planet X". NASA Solar System Exploration. Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- ↑ Michael E. Brown (3 March 2017). "Planet Nine". YouTube. 19:06. Archived from the original on 6 April 2017. Retrieved 15 March 2017.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 29.2 Batygin, Konstantin; Brown, Mike (20 January 2016). "Where is Planet Nine?". The Search for Planet Nine. Michael E. Brown and Konstantin Batygin. RA/Dec chart. Archived from the original on 30 January 2016. Retrieved 24 January 2016.
- ↑ Lemonick, Michael D. (20 January 2016). "Strong Evidence Suggests a Super Earth Lies beyond Pluto". Scientific American. video. Archived from the original on 22 January 2016. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ↑ Becker, Adam; Grossman, Lisa; Aron, Jacob (22 January 2016). "How Planet Nine May Have Been Exiled to Solar System's Edge". New Scientist. Archived from the original on 24 January 2016. Retrieved 25 January 2016.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 32.3 32.4 32.5 Achenbach, Joel; Feltman, Rachel (20 January 2016). "New Evidence Suggests a Ninth Planet Lurking at the Edge of the Solar System". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 20 January 2016. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- ↑ Margot, Jean-Luc (22 January 2016). "Would Planet Nine Pass the Planet Test?". University of California at Los Angeles. Archived from the original on 1 April 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ Margot, Jean-Luc (2015). "A Quantitative Criterion for Defining Planets". The Astronomical Journal 150 (6): 185. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/150/6/185.
- ↑ Bromley, Benjamin C.; Kenyon, Scott J. (22 July 2016). "Making Planet Nine: A Scattered Giant in the Outer Solar System". The Astrophysical Journal 826 (1): 64. doi:10.3847/0004-637X/826/1/64.
- ↑ Chang, Kenneth (20 January 2016). "Ninth Planet May Exist Beyond Pluto, Scientists Report". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 24 January 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ Totten, Sanden (20 January 2016). "Caltech Researchers Answer Skeptics' Questions about Planet 9". 89.3 KPCC. Archived from the original on 6 July 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ Bailey, Nora; Fabrycky, Daniel (2018). "Stellar Flybys Interrupting Planet-Planet Scattering Generates Oort Planets". arXiv:1905.07044 [astro-ph.EP].
- ↑ D'Angelo, G.; Lissauer, J.J. (2018). "Formation of Giant Planets". In Deeg H., Belmonte J.. Handbook of Exoplanets. Springer International Publishing AG. pp. 2319–2343. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-55333-7_140. ISBN 978-3-319-55332-0. Bibcode: 2018haex.bookE.140D.
- ↑ Izidoro, André; Morbidelli, Alessandro; Raymond, Sean N.; Hersant, Franck; Pierens, Arnaud (2015). "Accretion of Uranus and Neptune from Inward-Migrating Planetary Embryos Blocked by Jupiter and Saturn". Astronomy & Astrophysics 582: A99. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201425525.
- ↑ Carrera, Daniel; Gorti, Uma; Johansen, Anders; Davies, Melvyn B. (2017). "Planetesimal Formation by the Streaming Instability in a Photoevaporating Disk". The Astrophysical Journal 839 (1): 16. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aa6932.
- ↑ Eriksson, Linn E.J.; Mustill, Alexander J.; Johansen, Anders (2017). "Circularizing Planet Nine through Dynamical Friction with an Extended, Cold Planetesimal Belt". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 475 (4): 4609. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty111.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 Li, Gongjie; Adams, Fred C. (2016). "Interaction Cross Sections and Survival Rates for Proposed Solar System Member Planet Nine". The Astrophysical Journal Letters 823 (1): L3. doi:10.3847/2041-8205/823/1/L3.
- ↑ Parker, Richard J.; Lichtenberg, Tim; Quanz, Sascha P. (2017). "Was Planet 9 Captured in the Sun's Natal Star-Forming Region?". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters 472 (1): L75–L79. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slx141.
- ↑ Kenyon, Scott J.; Bromley, Benjamin C. (2016). "Making Planet Nine: Pebble Accretion at 250–750 AU in a Gravitationally Unstable Ring". The Astrophysical Journal 825 (1): 33. doi:10.3847/0004-637X/825/1/33.
- ↑ Kretke, K.A.; Levison, H.F.; Buie, M.W.; Morbidelli, A. (2012). "A Method to Constrain the Size of the Protosolar Nebula". The Astronomical Journal 143 (4): 91. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/143/4/91.
- ↑ Brennan, Pat. "The Super-Earth that Came Home for Dinner". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Archived from the original on 16 October 2017. Retrieved 13 October 2017.
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 48.2 48.3 Kaib, Nathan A.; Pike, Rosemary; Lawler, Samantha; Kovalik, Maya; Brown, Christopher; Alexandersen, Mike; Bannister, Michele T.; Gladman, Brett J. et al. (2019). OSSOS XVII: Probing the Distant Solar System with Observed Scattering TNOs. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ab2383.
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 49.2 49.3 Nesvorny, D.; Vokrouhlicky, D.; Dones, L.; Levison, H.F.; Kaib, N.; Morbidelli, A. (2017). "Origin and Evolution of Short-Period Comets". The Astrophysical Journal 845 (1): 27. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aa7cf6.
- ↑ Stirone, Shannon. "Planet Nine May Be Responsible for Tilting the Sun". Astronomy. Archived from the original on 10 August 2017. Retrieved 29 July 2017.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 51.2 de la Fuente Marcos, Carlos; de la Fuente Marcos, Raúl (2014). "Extreme Trans-Neptunian Objects and the Kozai Mechanism: Signalling the Presence of Trans-Plutonian Planets". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Letters 443 (1): L59–L63. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slu084.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 Koponyás, Barbara (10 April 2010). "Near-Earth Asteroids and the Kozai-Mechanism" (PDF). 5th Austrian Hungarian Workshop in Vienna. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 March 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ McDonald, Bob (24 January 2016). "How Did We Miss Planet 9?". CBC News. Archived from the original on 5 February 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
It's like seeing a disturbance on the surface of water but not knowing what caused it. Perhaps it was a jumping fish, a whale or a seal. Even though you didn't actually see it, you could make an informed guess about the size of the object and its location by the nature of the ripples in the water.
- ↑ Lakdawalla, Emily (20 January 2016). "Theoretical Evidence for an Undiscovered Super-Earth at the Edge of Our Solar System". The Planetary Society. Archived from the original on 23 April 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ Hands, T. O.; Dehnen, W.; Gration, A.; Stadel, J.; Moore, B. (2019). "The fate of planetesimal discs in young open clusters: implications for 1I/'Oumuamua, the Kuiper belt, the Oort cloud and more". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: 1064. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz1069.
- ↑ de León, Julia; de la Fuente Marcos, Carlos; de la Fuente Marcos, Raúl (2017). "Visible Spectra of (474640) 2004 VN112-2013 RF98 with OSIRIS at the 10.4 M GTC: Evidence for Binary Dissociation near Aphelion Among the Extreme Trans-Neptunian Objects". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters 467 (1): L66–L70. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slx003.
- ↑ Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC). "New Data About Two Distant Asteroids Give a Clue to the Possible 'Planet Nine'". ScienceDaily. Archived from the original on 29 July 2017. Retrieved 29 July 2017.
- ↑ de la Fuente Marcos, C.; de la Fuente Marcos, R.; Aarseth, S.J. (1 November 2017). "Binary Stripping as a Plausible Origin of Correlated Pairs of Extreme Trans-Neptunian Objects". Astrophysics and Space Science 362 (11): 198. doi:10.1007/s10509-017-3181-1.
- ↑ Sheppard, Scott S., Scott S.; Trujillo, Chadwick (2016). "New Extreme Trans-Neptunian Objects: Toward a Super-Earth in the Outer Solar System". The Astronomical Journal 152 (6): 221. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/152/6/221.
- ↑ de la Fuente Marcos, Carlos; de la Fuente Marcos, Raúl (2017). "Evidence for a Possible Bimodal Distribution of the Nodal Distances of the Extreme Trans-Neptunian Objects: Avoiding a Trans-Plutonian Planet or Just Plain Bias?". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Letters 471 (1): L61–L65. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slx106.
- ↑ Spanish Foundation for Science and Technology (FECYT). "New Evidence in Support of the Planet Nine Hypothesis". phys.org. Archived from the original on 30 July 2017. Retrieved 29 July 2017.
- ↑ Brown, Michael E. "Planet Nine: Where Are You? (Part 1)". The Search for Planet Nine. Michael E. Brown and Konstantin Batygin. Archived from the original on 20 October 2017. Retrieved 19 October 2017.
- ↑ Becker, Juliette C.; Adams, Fred C.; Khain, Tali; Hamilton, Stephanie J.; Gerdes, David (2017). "Evaluating the Dynamical Stability of Outer Solar System Objects in the Presence of Planet Nine". The Astronomical Journal 154 (2): 61. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aa7aa2.
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 64.2 Lawler, S.M.; Shankman, C.; Kaib, N.; Bannister, M.T.; Gladman, B.; Kavelaars, J.J. (29 December 2016) [21 May 2016]. "Observational Signatures of a Massive Distant Planet on the Scattering Disk". The Astronomical Journal 153 (1): 33. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/153/1/33.
- ↑ Cáceres, Jessica; Gomes, Rodney (2018). "The Influence of Planet 9 on the Orbits of Distant TNOs: The Case for a Low Perihelion Planet". The Astronomical Journal 156 (4): 157. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aad77a.
- ↑ Scharping, Nathaniel (20 January 2016). "Planet Nine: A New Addition to the Solar System?". Discover. Archived from the original on 16 July 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ 67.0 67.1 Allen, Kate (20 January 2016). "Is a Real Ninth Planet out There Beyond Pluto?". The Toronto Star. Archived from the original on 17 April 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 Beust, H. (2016). "Orbital Clustering of Distant Kuiper Belt Objects by Hypothetical Planet 9. Secular or Resonant?". Astronomy & Astrophysics 590: L2. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201628638.
- ↑ 69.0 69.1 69.2 69.3 69.4 Batygin, Konstantin; Morbidelli, Alessandro (2017). "Dynamical Evolution Induced by Planet Nine". The Astronomical Journal 154 (6): 229. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aa937c.
- ↑ 70.0 70.1 Li, Gongjie; Hadden, Samuel; Payne, Matthew; Holman, Matthew J. (2018). "The Secular Dynamics of TNOs and Planet Nine Interactions". The Astronomical Journal 156 (6): 263. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aae83b.
- ↑ Hruska, Joel (20 January 2016). "Our Solar System May Contain a Ninth Planet, Far beyond Pluto". ExtremeTech. Archived from the original on 28 July 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 Siegel, Ethan (20 January 2016). "Not So Fast: Why There Likely Isn't A Large Planet Beyond Pluto". Forbes. Archived from the original on 14 October 2017. Retrieved 22 January 2016.
- ↑ "MPC list of a > 250, i > 40, and q > 6". Minor Planet Center. Archived from the original on 2 August 2017. Retrieved 4 February 2016.
- ↑ Brasser, R.; Schwamb, M.E.; Lykawka, P.S.; Gomes, R.S. (2012). "An Oort Cloud Origin for the High-Inclination, High-Perihelion Centaurs". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 420 (4): 3396–3402. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.20264.x.
- ↑ Williams, Matt (10 August 2015). "What is the Oort Cloud?". Universe Today. Retrieved 25 February 2019.
- ↑ 76.0 76.1 Gibbs, W. Wayt. "Is There a Giant Planet Lurking Beyond Pluto?". IEEE Spectrum. Archived from the original on 1 August 2017. Retrieved 1 August 2017.
- ↑ 77.0 77.1 Levenson, Thomas (25 January 2016). "A New Planet or a Red Herring?". The Atlantic. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
'We plotted the real data on top of the model' Batyagin recalls, and they fell 'exactly where they were supposed to be.' That was, he said, the epiphany. 'It was a dramatic moment. This thing I thought could disprove it turned out to be the strongest evidence for Planet Nine.'
- ↑ Grush, Loren (20 January 2016). "Our Solar System May Have a Ninth Planet After All – but Not All Evidence Is in (We Still Haven't Seen It Yet)". The Verge. Archived from the original on 29 July 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
The statistics do sound promising, at first. The researchers say there's a 1 in 15,000 chance that the movements of these objects are coincidental and don't indicate a planetary presence at all. ... 'When we usually consider something as clinched and air tight, it usually has odds with a much lower probability of failure than what they have,' says Sara Seager, a planetary scientist at MIT. For a study to be a slam dunk, the odds of failure are usually 1 in 1,744,278. ... But researchers often publish before they get the slam-dunk odds, in order to avoid getting scooped by a competing team, Seager says. Most outside experts agree that the researchers' models are strong. And Neptune was originally detected in a similar fashion—by researching observed anomalies in the movement of Uranus. Additionally, the idea of a large planet at such a distance from the Sun isn't actually that unlikely, according to Bruce Macintosh, a planetary scientist at Stanford University.
- ↑ Crocket, Christopher (31 January 2016). "Computer Simulations Heat up Hunt for Planet Nine". Science News. Archived from the original on 6 February 2016. Retrieved 7 February 2016.
'It's exciting and very compelling work,' says Meg Schwamb, a planetary scientist at Academia Sinica in Taipei, Taiwan. But only six bodies lead the way to the putative planet. 'Whether that's enough is still a question.'
- ↑ "We Can't See This Possible 9th Planet, but We Feel Its Presence". PBS NewsHour. 22 January 2016. Archived from the original on 22 July 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
'Right now, any good scientist is going to be skeptical, because it's a pretty big claim. And without the final evidence that it's real, there is always that chance that it's not. So, everybody should be skeptical. But I think it's time to mount this search. I mean, we like to think of it as, we have provided the treasure map of where this ninth planet is, and we have done the starting gun, and now it's a race to actually point your telescope at the right spot in the sky and make that discovery of planet nine.' —Mike Brown
- ↑ 81.0 81.1 Fecht, Sarah (22 January 2016). "Can There Really Be a Planet in Our Solar System That We Don't Know About?". Popular Science. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ 82.0 82.1 82.2 82.3 Choi, Charles Q. (25 October 2016). "Closing in on a Giant Ghost Planet". Scientific American. Archived from the original on 28 July 2017. Retrieved 21 March 2017.
- ↑ Siegel, Ethan (3 November 2015). "Jupiter May Have Ejected a Planet from Our Solar System". Forbes. Archived from the original on 28 January 2016. Retrieved 22 January 2016.
- ↑ Siegel, Ethan (14 September 2018). "This Is Why Most Scientists Think Planet Nine Doesn't Exist". Forbes.
- ↑ Beatty, Kelly (26 March 2014). "New Object Offers Hint of "Planet X"". Sky & Telescope. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ 86.0 86.1 Shankman, Cory (2017). "OSSOS. VI. Striking Biases in the Detection of Large Semimajor Axis Trans-Neptunian Objects". The Astronomical Journal 154 (2): 50. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aa7aed. https://pure.qub.ac.uk/portal/en/publications/ossos-vi-striking-biases-in-the-detection-of-large-semimajor-axis-transneptunian-objects(027b7a9c-a171-42b4-9449-9355b0a255d4).html.
- ↑ Siegel, Ethan. "This Is Why Most Scientists Think Planet Nine Doesn't Exist". Starts With A Bang. Forbes. Archived from the original on 18 September 2018. Retrieved 17 September 2018.
- ↑ 88.0 88.1 Brown, Michael E. (2017). "Observational Bias and the Clustering of Distant Eccentric Kuiper Belt Objects". The Astronomical Journal 154 (2): 65. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aa79f4.
- ↑ Brown, Michael E.; Batygin, Konstantin (2019). "Orbital Clustering in the Distant Solar System". The Astronomical Journal 157 (2): 62. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aaf051. http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/papers/ps/clustering.pdf.
- ↑ 90.0 90.1 Shankman, Cory; Kavelaars, J.J.; Lawler, Samantha; Bannister, Michelle (2017). "Consequences of a Distant Massive Planet on the Large Semi-Major Axis Trans-Neptunian Objects". The Astronomical Journal 153 (2): 63. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/153/2/63. https://pure.qub.ac.uk/portal/en/publications/consequences-of-a-distant-massive-planet-on-the-large-semimajor-axis-transneptunian-objects(f94859e2-eab4-46de-8b90-d7028d7bccdd).html.
- ↑ 91.0 91.1 Madigan, Ane-Marie; McCourt, Michael (2016). "A New Inclination Instability Reshapes Keplerian Discs into Cones: Application to the Outer Solar System". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters 457 (1): L89–93. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slv203.
- ↑ Madigan, Ann-Marie; Zderic, Alexander; McCourt, Michael; Fleisig, Jacob (2018). "On the Dynamics of the Inclination Instability". The Astronomical Journal 156 (4): 141. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aad95c.
- ↑ Wall, Mike (4 February 2016). "'Planet Nine'? Cosmic objects' strange orbits may have a different explanation". Space.com. Archived from the original on 8 February 2016. Retrieved 8 February 2016.
We need more mass in the outer solar system," she (Madigan) said. "So it can either come from having more minor planets, and their self-gravity will do this to themselves naturally, or it could be in the form of one single massive planet—a Planet Nine. So it's a really exciting time, and we're going to discover one or the other.
- ↑ Snell, Jason (5 February 2016). "This Week in Space: Weird Pluto and No Plan for Mars". Yahoo! Tech. Archived from the original on 18 August 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ Fan, Siteng; Batygin, Konstantin (2017). "Simulations of the Solar System's early dynamical evolution with a self-gravitating planetesimal disk". The Astrophysical Journal 851 (2): L37. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa9f0b.
- ↑ Sefilian, Antranik A.; Touma, Jihad R. (2019). "Shepherding in a Self-gravitating Disk of Trans-Neptunian Objects". The Astronomical Journal 157 (2): 59. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aaf0fc.
- ↑ Patel, Neel V. (21 January 2019). "Planet Nine Might Not Actually Be a Planet". Popular Science. Retrieved 21 January 2019.
- ↑ Dvorsky, George (22 January 2019). "Is the Elusive 'Planet Nine' Actually a Massive Ring of Debris in the Outer Solar System?". Gizmodo. Retrieved 23 January 2019.
- ↑ 99.0 99.1 Malhotra, Renu; Volk, Kathryn; Wang, Xianyu (2016). "Corralling a distant planet with extreme resonant Kuiper belt objects". The Astrophysical Journal Letters 824 (2): L22. doi:10.3847/2041-8205/824/2/L22.
- ↑ Malhotra, Renu (2017). "Prospects for Unseen Planets Beyond Neptune". ASP Conference Series 513: 45.
- ↑ Malhotra, Renu (15 April 2018). "The search for Planet Nine". YouTube. Retrieved 18 January 2019.
- ↑ 102.0 102.1 102.2 Crocket, Christopher (14 November 2014). "A Distant Planet May Lurk Far Beyond Neptune". Science News. Archived from the original on 15 April 2015. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- ↑ Jílková, Lucie; Portegies Zwart, Simon; Pijloo, Tjibaria; Hammer, Michael (2015). "How Sedna and Family Were Captured in a Close Encounter with a Solar Sibling". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 453 (3): 3157–3162. doi:10.1093/mnras/stv1803.
- ↑ Dickinson, David (6 August 2015). "Stealing Sedna". Universe Today. Archived from the original on 7 February 2016. Retrieved 7 February 2016.
- ↑ O'Connor, J.J.; Robertson, E.F. "Alexis Bouvard". MacTutor History of Mathematics archive. Archived from the original on 25 October 2017. Retrieved 20 October 2017.
- ↑ Lemonick, Michael D. (19 January 2015). "There May Be 'Super Earths' at the Edge of Our Solar System". Time. Archived from the original on 28 January 2016. Retrieved 7 February 2016.
- ↑ de la Fuente Marcos, Carlos; de la Fuente Marcos, Raúl; Aarseth, Sverre J. (2015). "Flipping Minor Bodies: What Comet 96P/Machholz 1 Can Tell Us About the Orbital Evolution of Extreme Trans-Neptunian Objects and the Production of Near-Earth Objects on Retrograde Orbits". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 446 (2): 1867–187. doi:10.1093/mnras/stu2230.
- ↑ Atkinson, Nancy (15 January 2015). "Astronomers Are Predicting at Least Two More Large Planets in the Solar System". Universe Today. Archived from the original on 6 February 2016. Retrieved 7 February 2016.
- ↑ "What is the faintest object imaged by ground-based telescopes?". Sky & Telescope. 24 July 2006. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ Illingworth, G.; Magee, D.; Oesch, P.; Bouwens, R. (25 September 2012). "Hubble goes to the extreme to assemble the deepest ever view of the universe". Hubble Space Telescope. Archived from the original on 1 February 2016. Retrieved 7 February 2016.
- ↑ Deep Astronomy (19 February 2016). "Ninth Planet Beyond Neptune?". YouTube. 46:57.
- ↑ Fesenmaier, Kimm (20 January 2016). "Caltech Researchers Find Evidence of a Real Ninth Planet". Caltech. Archived from the original on 20 January 2016. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- ↑ Drake, Nadia (20 January 2016). "Scientists Find Evidence for Ninth Planet in Solar System". National Geographic. Archived from the original on 29 June 2016. Retrieved 15 July 2016.
- ↑ "More support for Planet Nine". Phys.org. 27 February 2019. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- ↑ Carter, Jamie (25 March 2019). "Are we getting closer to finding 'Planet Nine'?". Future tech. TechRadar. Retrieved 14 May 2019.
- ↑ Paul Scott Anderson (3 March 2019). "Planet 9 hypothesis gets a boost". EarthSky. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- ↑ Brown, Michael. "@plutokiller". Twitter. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- ↑ Palka, Joe. "A Friend For Pluto: Astronomers Find New Dwarf Planet In Our Solar System". NPR. Archived from the original on 5 April 2018. Retrieved 5 April 2018.
- ↑ 119.0 119.1 Hall, Shannon (20 April 2016). "We Are Closing in on Possible Whereabouts of Planet Nine". New Scientist. Archived from the original on 17 June 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ Meisner, Aaron M.; Bromley, Benjamin B.; Nugent, Peter E.; Schlegel, David J; Kenyon, Scott J.; Schlafly, Edward F.; Dawson, Kyle S. (2016). "Searching for Planet Nine with Coadded WISE and NEOWISE-Reactivation Images". The Astronomical Journal 153 (2): 65. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/153/2/65.
- ↑ Wall, Mike (21 January 2016). "How Astronomers Could Actually See 'Planet Nine'". Space.com. Archived from the original on 23 January 2016. Retrieved 24 January 2016.
- ↑ Crockett, Christopher (5 July 2016). "New Clues in Search for Planet Nine". Science News. Archived from the original on 5 July 2016. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
- ↑ Choi, Charles C. (25 October 2016). "Closing in on a Giant Ghost Planet". Scientific American. Archived from the original on 26 October 2016. Retrieved 26 October 2016.
- ↑ Stirone, Shannon (22 January 2019). "The Hunt for Planet Nine". Longreads. Retrieved 22 January 2019.
- ↑ Linder, Esther F.; Mordasini, Christoph (2016). "Evolution and Magnitudes of Candidate Planet Nine". Astronomy & Astrophysics 589 (134): A134. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201628350.
- ↑ Powel, Corey S. (22 January 2016). "A Little Perspective on the New "9th Planet" (and the 10th, and the 11th)". Discover. Archived from the original on 14 July 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- ↑ Cowan, Nicolas B.; Holder, Gil; Kaib, Nathan A. (2016). "Cosmologists in Search of Planet Nine: the Case for CMB Experiments". The Astrophysical Journal Letters 822 (1): L2. doi:10.3847/2041-8205/822/1/L2.
- ↑ Aron, Jacob (24 February 2016). "Planet Nine Hunters Enlist Big Bang Telescopes and Saturn Probe". New Scientist. Archived from the original on 25 February 2016. Retrieved 27 February 2016.
- ↑ Wood, Charlie (2 September 2018). "Is there a mysterious Planet Nine lurking in our Solar system beyond Neptune?". Washington Post. Archived from the original on 2 September 2018. Retrieved 17 January 2019.
- ↑ Kohler, Susanna (25 April 2016). "Can CMB experiments find Planet Nine?". AAS Nova. American Astronomical Society. Archived from the original on 31 May 2016. Retrieved 29 April 2016.
- ↑ Byrd, Deborah; Imster, Eleanor (20 February 2017). "Help Astronomers Look for Planet 9". EarthSky. Archived from the original on 10 April 2017. Retrieved 9 April 2017.
- ↑ Hinckley, Story (17 February 2017). "Hunt for Planet 9: How You Can Help NASA Search for Brown Dwarfs and Low-Mass Stars". The Christian Science Monitor. Archived from the original on 8 April 2017. Retrieved 9 April 2017.
- ↑ Strom, Marcus (16 February 2017). "You Can Help Find Planet Nine from Outer Space Through Citizen Science". The Sydney Morning Herald. Archived from the original on 18 June 2018. Retrieved 12 November 2018.
- ↑ Byrd, Deborah (27 March 2017). "Another Planet 9 Search! You Can Help". EarthSky. Archived from the original on 9 April 2017. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ↑ 135.0 135.1 Wall, Mike (3 April 2017). "Where's Planet Nine? Citizen Scientists Spot 4 Possible Candidates". Space.com. Archived from the original on 9 April 2017. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ↑ 136.0 136.1 Fienga, A.; Laskar, J.; Manche, H.; Gastineau, M. (2016). "Constraints on the Location of a Possible 9th Planet Derived from the Cassini Data". Astronomy and Astrophysics 587 (1): L8. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201628227.
- ↑ de la Fuente Marcos, Carlos; de la Fuente Marcos, Raúl (2016). "Finding Planet Nine: a Monte Carlo Approach". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Letters 459 (1): L66–L70. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slw049.
- ↑ de la Fuente Marcos, Carlos; de la Fuente Marcos, Raúl (2016). "Finding Planet Nine: Apsidal Anti-Alignment Monte Carlo Results". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 462 (2): 1972–1977. doi:10.1093/mnras/stw1778.
- ↑ Holman, Matthew J.; Payne, Matthew J. (2016). "Observational Constraints on Planet Nine: Cassini Range Observations". The Astronomical Journal 152 (4): 94. doi:10.3847/0004-6256/152/4/94.
- ↑ "Saturn Spacecraft Not Affected by Hypothetical Planet 9". NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory. 8 April 2016. Archived from the original on 16 April 2016. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ↑ Holman, Matthew J.; Payne, Matthew J. (9 September 2016). "Observational Constraints on Planet Nine: Astrometry of Pluto and Other Trans-Neptunian Objects". The Astronomical Journal 152 (4): 80. doi:10.3847/0004-6256/152/4/80.
- ↑ Medvedev, Yu D.; Vavilov, D.E.; Bondarenko, Yu S.; Bulekbaev, D.A.; Kunturova, N.B. (2017). "Improvement of the Position of Planet X Based on the Motion of Nearly Parabolic Comets". Astronomy Letters 42 (2): 120–125. doi:10.1134/S1063773717020037.
- ↑ Rice, Malena; Laughlin, Gregory (2019). "The Case for a Large-Scale Occultation Network". The Astronomical Journal 158 (1): 19. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ab21df.
- ↑ Millholland, Sarah; Laughlin, Gregory (2017). "Constraints on Planet Nine's Orbit and Sky Position within a Framework of Mean-Motion Resonances". The Astronomical Journal 153 (3): 91. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/153/3/91. supplemented by Millholland, Sarah. "Planet Nine's Orbit in Space". GitHub. Archived from the original on 21 February 2017. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
- ↑ de la Fuente Marcos, Carlos; de la Fuente Marcos, Raúl (2016). "Commensurabilities between ETNOs: a Monte Carlo survey". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Letters 460 (1): L64–L68. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slw077.
- ↑ Kaine, T. (2018). "Dynamical Analysis of Three Distant Trans-Neptunian Objects with Similar Orbits". The Astronomical Journal 156 (6): 273. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aaeb2a.
- ↑ Bailey, Elizabeth; Brown, Michael E.; Batygin, Konstantin (2018). "Feasibility of a Resonance-Based Planet Nine Search". The Astronomical Journal 156 (2): 74. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aaccf4.
- ↑ "Naming of Astronomical Objects". International Astronomical Union. Archived from the original on 17 June 2016. Retrieved 25 February 2016.
- ↑ Totten, Sanden (22 January 2016). "Planet 9: What Should Its Name Be If It's Found?". 89.3 KPCC. Archived from the original on 7 February 2016. Retrieved 7 February 2016.
'We like to be consistent,' said Rosaly Lopes, a senior research scientist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and a member of the IAU's Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature. ... For a planet in our solar system, being consistent means sticking to the theme of giving them names from Greek and Roman mythology.
- ↑ Fesenmaier, Kimm (20 Jan 2016). "Caltech Researchers Find Evidence of a Real Ninth Planet". Caltech. Retrieved 15 January 2019.
- ↑ "Does Planet 9 Exist?". YouTube.com. 13 September 2019. Retrieved 13 September 2019.
- ↑ 152.0 152.1 Mosher, Dave (7 June 2018). "Is It Planet 9 or Planet X? Scientists Spar over What to Call the Solar System's Hypothetical Missing World". Business Insider. Archived from the original on 8 June 2018. Retrieved 9 June 2018.
- ↑ Paul Abell (29 July 2018). "On The Insensitive Use of the Term 'Planet 9' for Objects Beyond Pluto". Planetary Exploration Newsletter 12 (31). http://planetarynews.org/archive18/pen_v12_n31_180729.txt. Retrieved 2019-01-15.