Motivation and emotion/Book/2014/Social media motivation
What motivates social media usage?
Overview
[edit | edit source]
The Internet has made it possible to surpass time differences and locations to reach anyone at any given time, it has also made large varieties of information accessible. Social media is the umbrella term used to describe the many platforms which are websites and applications available on electronic devices that enable social interaction. In an online and offline fashion, users are able to share and create content and participate in social networking sites.
Usage of social media can be explained by several factors. Psychologists have suggested that humans are motivated by the seek to fulfil their needs, and that a person will continue their actions if they feel rewarded for doing so. Research has shown social media to be a tool for people to develop and achieve their desires. Personality traits contribute to these human desires which can reflect through their social media usage.
This chapter aims to expand on the Online Social Networking chapter and answer what drives motivation for people to use social media? and why? Using psychological theory and research, this chapter will provide the reader with an understanding of how to use social media and the motivation that drives it so they will be able to apply this to their personal life. The reader will be presented with explanations to answer the two presented case studies highlighted in green following this overview.
|
Case Study 1 As an older man with a family, Donald owned and managed a shop selling scuba diving gear and had lived through passing phases and fads over his time, he was so sure the social media sites would be one of them. "What are these invites I keep getting? for Facebook? and LinkedIn? What do they do? and why would they be useful for me?" Question: Does Donald have a use for social media? What could he use it for? |
|
Case Study 2 The mother of a young teenage girl was starting to feel concerned. Her daughter was diagnosed with social anxiety that did not permit her to be part of most social situations which caused her to be a loner. Recently, she had become less interested in trying to involve herself in real world activities and instead used her time to constantly be online on these social media websites the mother knew nothing about. If she wasn't on the computer at home, she would be using her phone and hardly ever looking up because she was furiously typing. "I'm very worried for my daughter, it appears that she is becoming more introverted. She's starting to spend more time online and seems less interested in anything related to the real world. What motivates her to use the computer and phone so much?" Question: What could be motivating the daughter to use these social media websites so much? |
What is social media?
[edit | edit source]Forms of electronic communication that can be broadcasted via the internet to large audiences and allows users to interact with each other and become part of online communities to exchange information, ideas, personal messages, and other content (Kane, Alavi, Labianca & Borgatti, 2014). The asynchronous style of how consumers use the web sites add to accessibility of each experience and is how people are able to communicate intermittently in varied locations and times (Hardt, 2002). Social media comprises of internet websites that can either be used for blogging, social networking, collaborative learning, specific content searches and gaming. There is an extensive and growing list of platforms that can be accessed on any device that has a connection to the internet such as computers, tablets and phones.
| Platform | Used for |
|---|---|
| Social Networking: To see what our network is doing in their day to day activities | |
| Micro blogging: Connect with social network and niche content that interests us | |
| Visual discovery: An online pinboard to be inspired and get ideas for style, cooking, decorating, words of wisdom etc. | |
| Google+ | Social networking: Sharing and consuming information in business and tech industries |
| Wikipedia | Content driven community: Sharing information that can be edited to enhance content or dispute inaccuracies |
| Professional networking: Look for jobs and connect with other business professionals | |
| Visual discovery: See interesting images and videos from friends and public figures |
Note. Reprinted from “Social Media Powerful Tools for SH&E Professionals,” by Walaski, P, 2013, Professional Safety, 58(4), p. 40.
Psychological theories
[edit | edit source]Several psychological theories exist in explaining the motivation to use social media. Most of these theories are based on the human needs such as connection, that we can not satisfy in our real world and use social media and online resources to fulfil them.
Uses and gratifications theory
[edit | edit source]Blumler and Katz developed a theory known as the uses and gratifications theory which suggests that media users choose their form of media based on their motivation to fulfill goals, and attempts to explain why. Whiting and Williams (2013) suggest that the usage occurs because of the instant rewards gained by using it. The motivation to use social media will increase if these gratifications are met and because social media usage offers instant rewards, gratification is instantly felt by the person every time they exhibit that behaviour to achieve their goals.
Stafford and Schkade (2004) found that the five goals for social media use is:
- To gain knowledge and information
- Entertainment
- Escape from reality
- Enhance social connections
- Identify with others
Information seeking
[edit | edit source]People who value the process of finding information finds pleasure through attaining and sharing information. Sites such as Wikipedia enable learning and sharing of information and interests on particular topics. The Internet and social media websites can provide constant up to date information on real world events or on specific interests and share with entire communities (Dholakia, Bagozzi & Pearo 2004). The varied tools available on social media have transformed everyday problems into answer equippable resources via the use of ebooks, blog articles, slide shows and videos. E.g someone wanting to learn how to live a healthy life style can watch videos on how to do exercises and learn about healthy eating through ebooks.
Entertainment
[edit | edit source]
Users of social media have found fun and relaxation out of the ability to gain information and interact with others in an online world. The expansive range and current games, music and videos which circulate the internet can all be accessed through social media websites and enhance our learning or personal entertainment (Dholakia et al., 2004).
Gaming
[edit | edit source]Connecting with other gamers in an alternate reality through the use of games available on social media websites have enhanced story lines and challenges which the user seeks. Shin and Shin (2011) found that users enjoyed the competition that came from sharing scores with another through the social media websites and accessing forums that provides assistance to the game. Interacting with other users within the games was also a motivator to play online games.
Boredom
[edit | edit source]Logging on to social media websites have shown to be of great use to users that are bored or have time to kill. Attention and interest levels do not need to be high for the reader to understand their chosen topic. When a person lacks self observation, social media users often do not realise that they are spending an excessive amount of time logged on to these platforms which with repeated use develops into a habit. Spending repeated time on these entertaining sites is a contributing factor to procrastination and how procrastination happens.
Communication
[edit | edit source]
Communication through social media can be done via multiple media, places and times. The cheap and easiness of message conveying has increased it's popularity. Depending on the platform, a message can be short or long and have the ability to become global (Musial & Kazienko, 2013). Some modes of communication are: live chat videos, pictures, multiple people or single person messages, audio calls, private text messages.
Real world connection
[edit | edit source]If a goal is to make more social connections this can be done via social media as it leads to the real world connections. Meet ups are often the result of connections that occur in regards to a mutual interest discovered online with each other (Ross, Orr, Orr, Sisic, Arseneault & Simmering, 2009). Real world connections that begin online already have a sense of whether or not you’re going to like the other person based on online interaction. This is potentially why online dating is popular, and an increase in the number of marriages that began as Internet relationships.
Virtual communities
[edit | edit source]
Social media websites are designed to be widely accessible and attract the general population despite personal interests. Segregated groups have identified themselves by distinguishing factors such as an interest or an age group (Scheepers, Scheepers, Stockdale & Nurdin, 2014). The human desire to belong and become part of a group is why we join clubs and organisations (Scheepers et al., 2014). Social media allows people to become part of a generally unrestricted community. There is also potential to become part of multiple communities that might be hard to do in the real world. By using social media we have the capability of sustaining a connection to our involved communities without being physically together. Our real world communities that exist online enable us to continue interacting with them at times other than the usual allocated time and place together. Being able to interact with a community enables us to fulfill this extension (Scheepers et al., 2014).
Maslow's hierarchy of needs
[edit | edit source]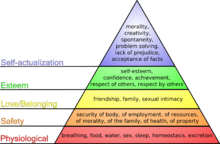
A theory proposed by Abraham Maslow about his observations of motivation in people. The theory states that a person possesses needs for:
- Physiological
- Safety
- Love and Belonging
- Esteem
- Self-Actualisation
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs are ordered from the most basic (1) to their full potential (5) and are required to have each stage first met before the person will desire for more stages. Depending on which need a person is motivated to achieve, people can find social media a useful way to meet them (Cao, Jiang, Oh, Li, Liao & Chen, 2013).
Social connectivity
[edit | edit source]Social networking websites provides a way for people to connect with each other and fulfil the need for love and belongingness. The accessibility of communicating through the social platforms makes it possible to talk to a number of people at the same time from any location. Kim, Shim and Ahn (2011) found the main use for social networking sites is the ability to keep in touch with friends and share information about events. Whether there's a time and location difference between people and groups, these sites enable various modes of social interaction to happen. As well as keeping in contact with current friends, it enables the opportunity to meet and interact with new and different people and communities from all over the world and build on these relationships in a faster and easier way (Kim et al., 2011; Ross et al., 2009).

Friends
[edit | edit source]With online social networks, such as Facebook, you can get in touch with old friends and make new ones. Most social networking web sites have tools that enable you to track down people from your past such as childhood friends or previous work colleagues. You can also use an online social network to make new friends with similar interests (Ross et al., 2009). Users are able to keep in contact with several friends at the same time, close friends and acquaintences on new levels through the sharing of their stories, news and pictures. According to the Social Comparison and Motivation chapter, social network users often compare themselves socially using this function.
Business
[edit | edit source]Pliska (2012) states that decision making and hard work starts with a google search. This is an acknowledgment of the highest need to achieve according to Maslow's theory, self actualisation is to realise one's full potential. The person will be able express creatively, pursue knowledge and give to society. Similarly, businesses have embraced social media to gain and give knowledge of their business. Through social media, businesses have been able to advertise to their potential customers new products and deals to attract them for their store or brand. They also use it as a promotion of their selves and their products and as a form of communication to their consumers. It is useful to address mass amounts of people and give a more human element to their companies. Using sites that allows customers to review and contact them directly has shown to increase their reputation by giving quick responses to the information they need (Aral & Dellarocas, 2013; Pliska, 2012). This is done by having a dedicated online team in charge of customer service and in marketing and advertisement. As well as the business to customer relationship, social media can be used for communicating with their employees, enabling them to participate on gaining knowledge enhancement information, discuss upcoming news, or products and accelerate work innovation through collaboration (Aral & Dellarocas, 2013; Pliska, 2012).
Self completion theory
[edit | edit source]Self completion theory was formulated by Wicklund and Gollwitzer. It proposes that individuals participate in activities, such as reading about fishing gear when they identify themselves as a fisherman, to define themselves when they feel they are uncertain or threatened known as the compensation hypothesis (Wagner, Wicklund & Shaigan, 1990). This has been utilised through social media websites when people try to compensate for their lost sense of self identity by interacting with topics that they deem they should be interacting with and affirming this or using it as an outlet to state their identity's opinion.
Identity
[edit | edit source]Social media allows it’s consumers to present literary descriptions of their selves instead of having a physical visual. The interactions that occurs between the entities finds this of use when the superficial appearances or status hold no meaning unlike the influence it can have in reality (Cover, 2012). For example, businesses that are likely to treat potential customers in varying ways based on their appearance, is less likely to happen online (Cover, 2012; Khaldi, 2014). Within the online community, the portrayal of self image is relatively similar to an ideal self image in their real world. People are more likely to exaggerate their best deemed qualities within this virtual community, and accordingly, this virtual self image usually leaves out the most unfavorable qualities which are inevitable in physical reality interactions (Khaldi, 2014). The ability to be a person's honest self online allows their freedom of individuality and opinions.
Opinions
[edit | edit source]
A function of social media is the availability to declare personal opinions usually expressed through blogging and microblogging sites. Gernsbacher (2014) proposes that the Internet has become less formal and more opinionated through effortless communication. People are able to convey their personal opinions indirectly through the preferences within websites and declare interests in the their photo or video albums, and posts, instead of an explicit self description (Gernsbacher, 2014). There is also the opportunity for people to be instantly heard and explicitly express these thoughts and opinions anonymously or with identification when in reality they could be voiceless, such as a customer unhappy with the service of a restaurant able to blog about this on their food blogging site (Musial & Kazienko, 2013; Walaski, 2013). A disadvantage to the use of social media for voicing opinions is that there is no control of the messages, people are able to attack people or organisations by devaluing and providing false accusations and criticisms (Walaski, 2013).
Quiz
[edit | edit source]Here is a short quiz to test your learning on the theories that motivate social media.
Personality
[edit | edit source]
Personality is explained by the Five Factor Model (“Big Five”). Universally suggests that the big five personality traits seen in people are extraversion, agreeableness, openness, neuroticism and conscientiousness (Ozguven & Mucan, 2013; Seidman, 2013). The varied traits influence the usage of social media in frequency and the typical use.
- Extraversion: Those high on the trait of Extraversion may utilise social media as a social tool but not to replace the social interactions. Introverts will feel able to express hidden self-aspects online as do individuals high in social anxiety, a trait positively correlated with introversion.
- Agreeableness: A tendency to be compassionate. Agreeable individuals present a more consistent and authentic version of themselves, and have greater perceived control over their online self-presentation. Thus, they may use social media to present actual self traits and refrain from attention-seeking.
- Openness: Reflects the degree of intellectual curiosity and is correlated with greater social media use. In their online self-presentation, open individuals are more self-disclosing. They are more likely to blog and reveal personal information in their profiles.
- Neuroticism: Relates to their belongingness needs. Neurotic individuals are less satisfied with romantic partners and more sensitive to rejection and may seek acceptance and social contact through social media. This also suggests they are more likely to present their ideal self online instead of their real self.
- Conscientiousness: Is the trait of being careful and thorough. Individuals high on the trait of conscientiousness are cautious online and are the least common to use social media sites.
The excessive use of social media can be explained by the need for attention in person with narcissistic personality disorder, as he or she will do anything to obtain that attention through whatever means.
Demographics
[edit | edit source]In conjunction with traits, this Social Media Motivation and Gender chapter has shown similarities and traditional gender role differences with social media use. While both genders utilise social media for their values and entertainment, males show more enjoyment in using social media for sporting themes and females using sites that allow for sentiment or friendship. Another predictor for the use of social media concluded by Coleman, Chandler and Gu (2013) found that young age[clarification needed] is the most consistent determinant for social media use. It was found that users of social media were predominately highly educated young males, and within this dimension, social networking sites were reported as being used by people of lower education and income levels.
Conclusion
[edit | edit source]According to psychological theories, usage of social media results in instant gratification from attaining our needs or goals which is influenced by our personality, gender and age and is what motivates us. Our motivation for social media use depends on the need or goal we are trying to fulfill, these can be met through the various platforms on social media. It is possible for anyone to create an identity and interact with other people, groups or communities they would otherwise not be able to. By doing this, a person's identity can have an opinion or preference and is able to voice that through the easy access of communication that social media tools provide. It enables anyone to publish or access information to a small or large audience. As social media is distinctly inexpensive and accessible compared to other forms of communication, the ability to connect and keep in contact with friends has been made easier. Promotion is used for the self and for the groups interacted with. Businesses have recently used this mode of marketing to reach their target audiences, this is also how people easily collect information and find entertainment.
Take home messages
[edit | edit source]- It improves our lives with minimal effort.
- It assists us in achieving our goals.
- People gain instant rewards and gratification with use.
- Factors such as our age, gender and personality affect our goals and needs thus influencing our motivation.
- We use it as a tool to fulfil our human needs that we can't do in real life.
|
Case Study 1 Possible Answer: Donald learns that he can use social media for personal use to keep in contact with family members and to further his business and expand his customer client base as well as interact with his employees through social networking sites. His scuba diving gear shop has received positive reviews from clients on social media sites and he has been able to extend his existing knowledge on scuba diving gear through content driven community sites which he has been able to collaboratively contribute to as well. |
|
Case Study 2 Possible Answer: After learning the uses of social media and speaking with her daughter, the mother has learned that her daughter spends most of her time online, as she found it is a way to connect with others without her social anxiety interfering. Online, she has joined many communities that consist of existing and new friends and has becoming part of a fan group for elephants and their welfare rights where she regularly expresses her opinion in ways that she feels she cannot in reality. |
See also
[edit | edit source]- Internet
- Social media
- Online and offline
- Online social networking (2011 Book chapter)
- Motivation
- Blog
- Social network
- Collaborative learning
- Online game
- Wikipedia
- Uses and gratifications theory
- Procrastination
- Procrastination (2011 Book chapter)
- Internet relationships and motivation (2014 Book chapter)
- Abraham Maslow
- Maslow's hierarchy of needs
- Social comparison and motivation (2014 Book chapter)
- Peter Gollwitzer
- Personality
- Big five personality traits
- Social media motivation and gender (2014 Book chapter)
References
[edit | edit source]Cao, H., Jiang, J., Oh, L., Li, H., Liao, X., & Chen, Z. (2013). A maslow's hierarchy of needs analysis of social networking services continuance. Journal of Service Management, 24(2), 170-190. doi:10.1108/09564231311323953
Coleman, L. J., Chandler, K., & Gu, J. (2013). Social media - A moving target. Journal of Marketing Development and Competitiveness, 7(1), 73.
Dholakia, U. M., Bagozzi, R. P., & Pearo, L. K. (2004). A social influence model of consumer participation in network- and small-group-based virtual communities. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 21(3), 241-263. doi:10.1016/j.ijresmar.2003.12.004
Gernsbacher, M. A. (2014). Internet-based communication. Discourse Processes, 51(5-6), 359. doi:10.1080/0163853X.2014.916174
Hardt, H. (2002). The reality of the mass media. Journal of Communication Inquiry, 26(1), 96-97. doi:10.1177/019685990202600108
Kane, G. C., Alavi, M., Labianca, G., & Borgatti, S. P. (2014). What's different about social media networks?: A framework and research agenda. Management Information Systems, 38(1), 275-304.
Khaldi, A. (2014). The Effect of Virtual Self Congruency on Consumer's Involvement in Social Media and the Motivation to Consume Social Media. Journal Of Business Studies Quarterly, 6(1), 184-190.
Kim, J. Y., Shim, J. P., & Ahn, K. M. (2011). Social networking service: Motivation, pleasure, and behavioral intention to use. The Journal of Computer Information Systems, 51(4), 92.
Musial, K., & Kazienko, P. (2013). Social networks on the internet. World Wide Web, 16(1), 31-72. doi:10.1007/s11280-011-0155-z
Ozguven, N., & Mucan, B. (2013). The relationship between personality traits and social media use. Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal, 41(3), 517.
Pliska, R. J. (2012). Social media: Identifying the business opportunities: The personal experiences of a social media user. Real Estate Issues, 37(1), 48.
Ross, C., Orr, R. R., Orr, E. S., Sisic, M., Arseneault, J. M., & Simmering, M. G. (2009). Personality and motivations associated with facebook use. Computers in Human Behavior, 25(2), 578-586. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2008.12.024
Scheepers, H., Scheepers, R., Stockdale, R., & Nurdin, N. (2014). The dependent variable in social media use. The Journal of Computer Information Systems, 54(2), 25.
Seidman, G. (2013). Self-presentation and belonging on facebook: How personality influences social media use and motivations. Personality and Individual Differences, 54(3), 402.
Shin, Y., & Shin, D. (2011). Why do people play social network games? Computers in Human Behavior, 27(2), 852-861. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2010.11.010
Stafford, T. F., Stafford, M. R., & Schkade, L. L. (2004). Determining uses and gratifications for the internet. Decision Sciences, 35(2), 259-288. doi:10.1111/j.00117315.2004.02524.x
Wagner, U., Wicklund, R. A., & Shaigan, S. (1990). Open devaluation and rejection of a fellow student: The impact of threat to a self-definition. Basic and Applied Social Psychology, 11(1), 61-76. doi:10.1207/s15324834basp1101_5
Walaski, P. (2013). Social media. Professional Safety, 58(4), 40.
Whiting, A., & Williams, D. (2013). Why people use social media: A uses and gratifications approach. Qualitative Market Research, 16(4), 362-369. doi:10.1108/QMR-06-2013-0041
External links
[edit | edit source]- Resources needing improved grammar
- Resources needing rewritten
- Resources needing facts checked
- Resources needing clarification
- Resources needing clarification by how
- Resources needing clarification by who
- Resources needing clarification by what
- Motivation and emotion/Book/2014
- Motivation and emotion/Book/Social media
