3-bit Walsh permutation/matrix columns
There are 25 transforms that look similar to the neutral position.
This is the case when the view from one or two axes remains the same or almost the same.
Almost the same means, that the original square is sheared into a (simple) parallelogram.
These are the 25 permutations in the middle cluster of the positive component of the neighbor graph.
(There are only 18 transforms that do not look like a square or simple parallelogram from any side, namely those who's matrices have seven 1s.)
The big table below shows all 168 transforms in 28 rows and 6 columns.
The shown transforms are those with binary matrices. For the transforms with matrices that have some negative entries see here.
For the 25 rows with sums < 7 the position in the table corresponds with that in the neighbor graph: Left, middle or right cluster in the positive or negative component.
| conjugacy class | neut. | 2+2 | 2+4 | 7a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cycle shape | Paris | Rome | Florence | Buenos Aires 5 | Buenos Aires 6 | Santiago + | |
| sum | 3 | 4 | 5a | 5b | 6 | 7 | |
| quantity | 1 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 3 |
| 12 | 12 | ||||||
Permutations in the same row have the same complement pattern,
and each complement pattern corresponds to four rows.
| complement patterns to table rows | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Each of the 28 table rows is identified by the vector (and corresponding matrix) in its main column.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The big table can be sorted by some properties of the permutations in the main column:
- cc conjugacy class
- cs cycle shape: abbreviated (city) name of the cycle shape; below the sum (3...7), which corresponds to the position in the cluster (which is why 5a and 5b are distinguished)
- cp complement pattern: above the weight (1...3), below the value (1...7)
- t triple of numbers used in the vectors in the row (number in ascending order)
Let be a permutation from the symmetric subgroup in the top row, and a permutation in the main column.
Then the permutation in the row of and the column of is . E.g. 314 (second row, negative left column) is 134 ⋅ 214.
| cc | cs | cp | t | main | positive | negative | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| neut. | neut. 3 | 37 | 124
|
 |
 241 |
 124 |
 412 |
 214 |
 421 |
 142 |
| 2+2 | P 4 | 26 | 134
|
 |
 341 |
 134 |
 413 |
 314 |
 431 |
 143 |
| 2+2 | P 4 | 26 | 125
|
 |
 251 |
 125 |
 512 |
 215 |
 521 |
 152 |
| 2+2 | P 4 | 25 | 234
|
 |
 243 |
 324 |
 432 |
 234 |
 423 |
 342 |
| 2+2 | P 4 | 25 | 126
|
 |
 261 |
 126 |
 612 |
 216 |
 621 |
 162 |
| 2+2 | P 4 | 23 | 245
|
 |
 245 |
 524 |
 452 |
 254 |
 425 |
 542 |
| 2+2 | P 4 | 23 | 146
|
 |
 641 |
 164 |
 416 |
 614 |
 461 |
 146 |
| 2+2 | R 5a | 11 | 247
|
 |
 247 |
 724 |
 472 |
 274 |
 427 |
 742 |
| 2+2 | R 5a | 12 | 147
|
 |
 741 |
 174 |
 417 |
 714 |
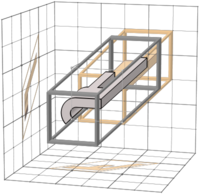 471 |
 147 |
| 2+2 | R 5a | 14 | 127
|
 |
 271 |
 127 |
 712 |
 217 |
 721 |
 172 |
| 2+2 | F 5a | 37 | 135
|
 |
 351 |
 135 |
 513 |
 315 |
 531 |
 153 |
| 2+2 | F 5a | 37 | 236
|
 |
 263 |
 326 |
 632 |
 236 |
 623 |
 362 |
| 2+2 | F 5a | 37 | 456
|
 |
 645 |
 564 |
 456 |
 654 |
 465 |
 546 |
| 2+4 | BA 5 5b | 12 | 156
|
 |
 651 |
 165 |
 516 |
 615 |
 561 |
 156 |
| 2+4 | BA 5 5b | 14 | 136
|
 |
 361 |
 136 |
 613 |
 316 |
 631 |
 163 |
| 2+4 | BA 5 5b | 14 | 235
|
 |
 253 |
 325 |
 532 |
 235 |
 523 |
 352 |
| 2+4 | BA 5 5b | 11 | 256
|
 |
 265 |
 526 |
 652 |
 256 |
 625 |
 562 |
| 2+4 | BA 5 5b | 12 | 345
|
 |
 345 |
 534 |
 453 |
 354 |
 435 |
 543 |
| 2+4 | BA 5 5b | 11 | 346
|
 |
 643 |
 364 |
 436 |
 634 |
 463 |
 346 |
| 2+4 | BA 6 6 | 23 | 157
|
 |
 751 |
 175 |
 517 |
 715 |
 571 |
 157 |
| 2+4 | BA 6 6 | 25 | 137
|
 |
 371 |
 137 |
 713 |
 317 |
 731 |
 173 |
| 2+4 | BA 6 6 | 23 | 267
|
 |
 267 |
 726 |
 672 |
 276 |
 627 |
 762 |
| 2+4 | BA 6 6 | 26 | 237
|
 |
 273 |
 327 |
 732 |
 237 |
 723 |
 372 |
| 2+4 | BA 6 6 | 25 | 467
|
 |
 647 |
 764 |
 476 |
 674 |
 467 |
 746 |
| 2+4 | BA 6 6 | 26 | 457
|
 |
 745 |
 574 |
 457 |
 754 |
 475 |
 547 |
| 7a | S +7 | 11 | 357
|
 |
 537 |
 753 |
 375 |
 573 |
 357 |
 735 |
| 7a | S +7 | 12 | 367
|
 |
 736 |
 673 |
 367 |
 763 |
 376 |
 637 |
| 7a | S +7 | 14 | 567
|
 |
 576 |
 657 |
 765 |
 567 |
 756 |
 675 |











