Recovery psychology/Biological Theory
- Biochemistry Textbook
- Introduction to Psychology Textbook
- Biological Psychology Textbook
- Cognitive Psychology and Cognitive Neuroscience Textbook
- Human Physiology Textbook
- Consciousness Studies Textbook
- Neuroscience Textbook
- Neurology and Neurosurgery Textbook
- Human Physiology Textbook
- Psychology/Neuroscience Textbook
- Pharmacology Textbook
Biological Perspective
[edit | edit source]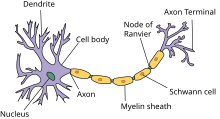
Philosophical perspectives are important to understand in discussing the mind and the brain. Monism is the belief that mind and brain are only words and that there is no clear distinction between the two. Mentalism is the belief that everything is substance of the mind. Dualism is the belief that mind is an abstract or nontangible object that has some relationship to the brain, a biological organ. Paralellism is the belief that mind and brain work together somehow or share the same information. Emergent Property theory holds that the mind is a quality that emerges when matter is composed in way that produces the brain. Cognitive psychology deals with the mind, although it may be somewhat reductionist. Cognitive behavioral psychology addresses to some degree the interaction of mind and brain; at least in the context of emotions. Biological psychology and Behavioristic psychology tend to lean towards reductionism in their premises. Emergent Property theory however seems to gain more acceptance in humanistic psychology. Humanism holds that man is the measure of all things. The sentiment of humanism and the emergent identity could be summed as: "If these components of matter are composed in a certain way, and this constitutes living cells and these cells consitute a person, than I must be this person."

"We would never doubt that the brain acts as a physico-chemical mechanism if treated as such; but for an understanding of psychic phenomenon we would start from the fact that the human mind enters as object and subject into the scientific process of psychology"-Werner Heisenber (1958)Physics and Philosophy:The revolution of modern science
- Astonishing Functions of Human Brain and Miracles of Mind by Shriram Sharma Acharya
- Neuroimaging on Wikipedia
- The Human Body
- Mind-brain Dualism and the philosophy of mind
- Can thoughts in the mind be related to chemistry in our brains?
- Wikistudy guide on Biology (Neurology)
- Neurons
- Neurology
- Brain Structure
- Neuropsychiatry
- Neuroscience
- The Analysis of Mind by Bertrand Russell
- Introduction to Psychology WikiBook Read in Particular Chapter 3
- Theory of Chemical Imbalance and the Biopsychiatry controversy
- Biological Psychology Wikibook
- Biological Psychological Disorders
- Brodmann’s Area 25 is an area of the brain researched by Helen Mayberg and others in the future we will be hearing more about this part of the brain, as we research "recovery" instead of "remission"
Treatment
[edit | edit source]Any clinical psychology textbook would discuss in great detail the many different types of interventions that are possible. However in the real mental health system these idealistic interventions are never used, often as a result of politicians cutting the mental health budget. This often reduces the mental health system down to a skeleton system of assessment and psychopharmacology; and if the client is lucky their personal needs can be addressed to an outside cognitive behavioral therapist or some rehabilitation program.
- Assessment
- Psychopharmacology
Dr. David Henley gives an explanation of the biological concepts of mental disorders, he explains psychiatry and psychology. He explains somewhat that science is not a matter of belief, while explaining the overall contention of nueroscience, psychologist and psychiatrists.
Biploar Disorder
[edit | edit source]- It's a Brain Thing: Bipolar Disorder Part 1 of 6 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Bipolar Disorder Part 2 of 6 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Bipolar Disorder Part 3 of 6 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Bipolar Disorder Part 4 of 6 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Bipolar Disorder Part 5 of 6 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Bipolar Disorder Part 6 of 6 by henleydb on YouTube
Panic Disorder
[edit | edit source]- It's a Brain Thing: Panic Disorder part 1 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Panic Disorder part 2 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Panic Disorder part 3 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Panic Disorder part 4 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Panic Disorder part 5 by henleydb on YouTube
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
[edit | edit source]- It's a Brain Thing: Generalized Anxiety Disorder part 1 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Generalized Anxiety Disorder part 2 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Generalized Anxiety Disorder part 3 by henleydb on YouTube
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
[edit | edit source]- It's a Brain Thing: OCD: part 1 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: OCD: part 2 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Obsessive/Compulsive Disorder: part 3 by henleydb on YouTube
Social Phobias
[edit | edit source]- It's a Brain Thing Social Phobia: Part 1 by henlydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing Social Phobia: Part 2 by henlydb on YouTube
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
[edit | edit source]- It's a Brain Thing Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Part 1 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: part 2 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: part 3 by henleydb on YouTube
Personality Disorder
[edit | edit source]- It's a Brain Thing: Personality and its Disorders: part 1 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Personality and its Disorders: part 2 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Personality and its Disorders: part 3 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Personality and its Disorders: part 4 by henleydb on YouTube
Depressive Subtypes
[edit | edit source]Psychotic Disorders
[edit | edit source]- It's a Brain Thing: Psychosis/ Psychotic disorders: part 1 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Psychosis/ Psychotic disorders: part 2 by henleydb on YouTube
Addictions
[edit | edit source]- It's a Brain Thing: Addictions and the Brain Part 1 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Addictions and the Brain Part 2 by henleydb on YouTube
Eating Disorders
[edit | edit source]- It's A Brain Thing: Eating Disorders Part I by henleydb on YouTube
- It's A Brain Thing: Eating Disorders Part II by henleydb on YouTube
Alzheimer's and other dementias
[edit | edit source]- It's a Brain Thing: Alzheimer's and other dementias part 1 by henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Alzheimer's and other dementias part 2 henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Alzheimer's and other dementias part 3 henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Alzheimer's and other dementias part 4 henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Alzheimer's and other dementias part 5 henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Alzheimer's and other dementias part 5 henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Alzheimer's and other dementias part 7 henleydb on YouTube
- It's a Brain Thing: Alzheimer's and other dementias part 8 henleydb on YouTube
Medication Issues
[edit | edit source]- Video from YouTube Psychiatric Drug Withdrawal Jodie Fisher talks about her experiences getting off psychiatric drugs.
- What You Should Know About Medicines Wikibook
- Serotonin syndrome on Wikipedia
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) on Wikipedia
- Extrapyramidal syndrome on Wikipedia
- Tardive dyskinesia on wikipedia
- Adverse drug reaction A.k.a. "Side Effects" on Wikipedia
- Paradoxical reaction on wikipedia
Medications: A possible tool of recovery or possible threat to recovery
[edit | edit source]- Psycholeptic
- Psychiatric medication
- Stimulants
- Mood stabilizers
- Anticonvulsants
- Anticholinergic
- Anxiolytic
- Hypnotic
- Sedative
- Antipsychotic
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (SSRIs)
- Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor(SNRIs)
- Noradrenergic and Specific Serotonergic Antidepressant(NASSAs)
- Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) reuptake inhibitors (NRIs)
- Norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitor(MAO Inhibitor)
- Augmenter drugs
See
- Psychoanaleptic
- Psychostimulant
- Nootropic
- List of psychiatric medications by condition treated
- List of psychiatric medications
Lack of research
[edit | edit source]- If a psychological disorder looks like this or that in a |fMRI, MRI, PET, CAT or other brain imaging equipment, then should not recovery look like something?
- What does a PET scan of recovery from depression look like? What is the biochemistry of recovery from psychological disorders look like at the nueral synapses? What does the blood flow of cerebreal regions look like in the fMRI of a person who has a new found sense of hope and new role identification as a result of their recovery from mental illness? Has anyone ever got a CAT scan after they recieved help for psychosis? What does recovery look like through a microscope?
ESSAY QUESTIONS
[edit | edit source]- Explain the difference between mind and brain
- Explain the relationship between thoughts and behaviors
