Rational numbers/Advanced Study
Appearance
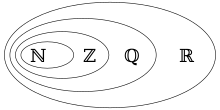
A rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers, a numerator p and a non-zero denominator q.[1]
Examples
[edit | edit source]- 5
- 0.2
Notice the number 5 in second example! It is because all numbers are divisible by 1 and at such it is actually but it is more convenient to write it as 5. Note Though all numbers are divisible by 1 some numbers are considered irrational ie they cannot be represented in the form also note that it impossible to have a number with 0 as the denominator (b must not be equal to 0 in ).
Operations Involving Rational Numbers
[edit | edit source]Addition
[edit | edit source]+ =
Subtraction
[edit | edit source]- =
Multiplication
[edit | edit source]• =
Division
[edit | edit source]÷ = • = .










