Quizbank/Electricity and Magnetism (calculus based)/QB153089888034
QB153089888034
QB:Ch 5:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1)
is an integral that calculates the magnitude of the electric field at a distance fromthe center of a thin circular disk as measured along a line normal to the plane of the disk. The disk's radius is and the surface charge density is . Evaluate at .
- a) 8.253E-01 V/m2
- b) 9.079E-01 V/m2
- c) 9.987E-01 V/m2
- d) 1.099E+00 V/m2
- e) 1.208E+00 V/m2

- a) 5.377E+01 degrees
- b) 5.914E+01 degrees
- c) 6.506E+01 degrees
- d) 7.157E+01 degrees
- e) 7.872E+01 degrees

is an integral that calculates the z-component of the electric field at point P situated above the x-axis where a charged rod of length (a+b) is located. The distance between point P and the x-axis is z=1.7 m. Evaluate at x=0.52 m if a=0.88 m, b=1.3 m. The total charge on the rod is 6 nC.
- a) 6.804E+00 V/m2
- b) 7.485E+00 V/m2
- c) 8.233E+00 V/m2
- d) 9.056E+00 V/m2
- e) 9.962E+00 V/m2
KEY:QB:Ch 5:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1)
is an integral that calculates the magnitude of the electric field at a distance fromthe center of a thin circular disk as measured along a line normal to the plane of the disk. The disk's radius is and the surface charge density is . Evaluate at .
- -a) 8.253E-01 V/m2
- -b) 9.079E-01 V/m2
- +c) 9.987E-01 V/m2
- -d) 1.099E+00 V/m2
- -e) 1.208E+00 V/m2

- -a) 5.377E+01 degrees
- -b) 5.914E+01 degrees
- -c) 6.506E+01 degrees
- +d) 7.157E+01 degrees
- -e) 7.872E+01 degrees

is an integral that calculates the z-component of the electric field at point P situated above the x-axis where a charged rod of length (a+b) is located. The distance between point P and the x-axis is z=1.7 m. Evaluate at x=0.52 m if a=0.88 m, b=1.3 m. The total charge on the rod is 6 nC.
- -a) 6.804E+00 V/m2
- +b) 7.485E+00 V/m2
- -c) 8.233E+00 V/m2
- -d) 9.056E+00 V/m2
- -e) 9.962E+00 V/m2
QB:Ch 5:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

is an integral that calculates the z-component of the electric field at point P situated above the x-axis where a charged rod of length (a+b) is located. The distance between point P and the x-axis is z=1.7 m. Evaluate at x=0.76 m if a=1.1 m, b=1.6 m. The total charge on the rod is 8 nC.
- a) 5.267E+00 V/m2
- b) 5.794E+00 V/m2
- c) 6.374E+00 V/m2
- d) 7.011E+00 V/m2
- e) 7.712E+00 V/m2

- a) 6.343E+01 degrees
- b) 6.978E+01 degrees
- c) 7.676E+01 degrees
- d) 8.443E+01 degrees
- e) 9.288E+01 degrees
3)
is an integral that calculates the magnitude of the electric field at a distance fromthe center of a thin circular disk as measured along a line normal to the plane of the disk. The disk's radius is and the surface charge density is . Evaluate at .
- a) 3.228E+00 V/m2
- b) 3.551E+00 V/m2
- c) 3.906E+00 V/m2
- d) 4.297E+00 V/m2
- e) 4.727E+00 V/m2
KEY:QB:Ch 5:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

is an integral that calculates the z-component of the electric field at point P situated above the x-axis where a charged rod of length (a+b) is located. The distance between point P and the x-axis is z=1.7 m. Evaluate at x=0.76 m if a=1.1 m, b=1.6 m. The total charge on the rod is 8 nC.
- -a) 5.267E+00 V/m2
- -b) 5.794E+00 V/m2
- -c) 6.374E+00 V/m2
- +d) 7.011E+00 V/m2
- -e) 7.712E+00 V/m2

- +a) 6.343E+01 degrees
- -b) 6.978E+01 degrees
- -c) 7.676E+01 degrees
- -d) 8.443E+01 degrees
- -e) 9.288E+01 degrees
3)
is an integral that calculates the magnitude of the electric field at a distance fromthe center of a thin circular disk as measured along a line normal to the plane of the disk. The disk's radius is and the surface charge density is . Evaluate at .
- -a) 3.228E+00 V/m2
- -b) 3.551E+00 V/m2
- -c) 3.906E+00 V/m2
- -d) 4.297E+00 V/m2
- +e) 4.727E+00 V/m2
QB:Ch 5:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1)
is an integral that calculates the magnitude of the electric field at a distance fromthe center of a thin circular disk as measured along a line normal to the plane of the disk. The disk's radius is and the surface charge density is . Evaluate at .
- a) 7.517E+00 V/m2
- b) 8.269E+00 V/m2
- c) 9.096E+00 V/m2
- d) 1.001E+01 V/m2
- e) 1.101E+01 V/m2

- a) 5.914E+01 degrees
- b) 6.506E+01 degrees
- c) 7.157E+01 degrees
- d) 7.872E+01 degrees
- e) 8.659E+01 degrees

is an integral that calculates the z-component of the electric field at point P situated above the x-axis where a charged rod of length (a+b) is located. The distance between point P and the x-axis is z=1.3 m. Evaluate at x=0.96 m if a=0.63 m, b=1.4 m. The total charge on the rod is 3 nC.
- a) 3.719E+00 V/m2
- b) 4.091E+00 V/m2
- c) 4.500E+00 V/m2
- d) 4.950E+00 V/m2
- e) 5.445E+00 V/m2
KEY:QB:Ch 5:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1)
is an integral that calculates the magnitude of the electric field at a distance fromthe center of a thin circular disk as measured along a line normal to the plane of the disk. The disk's radius is and the surface charge density is . Evaluate at .
- -a) 7.517E+00 V/m2
- -b) 8.269E+00 V/m2
- -c) 9.096E+00 V/m2
- -d) 1.001E+01 V/m2
- +e) 1.101E+01 V/m2

- -a) 5.914E+01 degrees
- -b) 6.506E+01 degrees
- +c) 7.157E+01 degrees
- -d) 7.872E+01 degrees
- -e) 8.659E+01 degrees

is an integral that calculates the z-component of the electric field at point P situated above the x-axis where a charged rod of length (a+b) is located. The distance between point P and the x-axis is z=1.3 m. Evaluate at x=0.96 m if a=0.63 m, b=1.4 m. The total charge on the rod is 3 nC.
- -a) 3.719E+00 V/m2
- +b) 4.091E+00 V/m2
- -c) 4.500E+00 V/m2
- -d) 4.950E+00 V/m2
- -e) 5.445E+00 V/m2
QB:Ch 6:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- a) 6.614E+01 N·m2/C
- b) 7.275E+01 N·m2/C
- c) 8.003E+01 N·m2/C
- d) 8.803E+01 N·m2/C
- e) 9.683E+01 N·m2/C
2) What is the magnetude (absolute value) of the electric flux through a rectangle that occupies the z=0 plane with corners at (x,y)= (x=0, y=0), (x=6, y=0), (x=0, y=6), and (x=6, y=6), where x and y are measured in meters. The electric field is,
- a) 9.952E+03 V·m
- b) 1.095E+04 V·m
- c) 1.204E+04 V·m
- d) 1.325E+04 V·m
- e) 1.457E+04 V·m

- a) 3.959E+01 N·m2/C
- b) 4.354E+01 N·m2/C
- c) 4.790E+01 N·m2/C
- d) 5.269E+01 N·m2/C
- e) 5.796E+01 N·m2/C
KEY:QB:Ch 6:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- -a) 6.614E+01 N·m2/C
- +b) 7.275E+01 N·m2/C
- -c) 8.003E+01 N·m2/C
- -d) 8.803E+01 N·m2/C
- -e) 9.683E+01 N·m2/C
2) What is the magnetude (absolute value) of the electric flux through a rectangle that occupies the z=0 plane with corners at (x,y)= (x=0, y=0), (x=6, y=0), (x=0, y=6), and (x=6, y=6), where x and y are measured in meters. The electric field is,
- -a) 9.952E+03 V·m
- -b) 1.095E+04 V·m
- -c) 1.204E+04 V·m
- +d) 1.325E+04 V·m
- -e) 1.457E+04 V·m

- -a) 3.959E+01 N·m2/C
- -b) 4.354E+01 N·m2/C
- -c) 4.790E+01 N·m2/C
- +d) 5.269E+01 N·m2/C
- -e) 5.796E+01 N·m2/C
QB:Ch 6:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- a) 4.730E+01 N·m2/C
- b) 5.203E+01 N·m2/C
- c) 5.723E+01 N·m2/C
- d) 6.295E+01 N·m2/C
- e) 6.925E+01 N·m2/C

- a) 3.959E+01 N·m2/C
- b) 4.354E+01 N·m2/C
- c) 4.790E+01 N·m2/C
- d) 5.269E+01 N·m2/C
- e) 5.796E+01 N·m2/C
3) What is the magnetude (absolute value) of the electric flux through a rectangle that occupies the z=0 plane with corners at (x,y)= (x=0, y=0), (x=5, y=0), (x=0, y=7), and (x=5, y=7), where x and y are measured in meters. The electric field is,
- a) 1.997E+03 V·m
- b) 2.197E+03 V·m
- c) 2.417E+03 V·m
- d) 2.659E+03 V·m
- e) 2.924E+03 V·m
KEY:QB:Ch 6:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- -a) 4.730E+01 N·m2/C
- +b) 5.203E+01 N·m2/C
- -c) 5.723E+01 N·m2/C
- -d) 6.295E+01 N·m2/C
- -e) 6.925E+01 N·m2/C

- -a) 3.959E+01 N·m2/C
- -b) 4.354E+01 N·m2/C
- -c) 4.790E+01 N·m2/C
- +d) 5.269E+01 N·m2/C
- -e) 5.796E+01 N·m2/C
3) What is the magnetude (absolute value) of the electric flux through a rectangle that occupies the z=0 plane with corners at (x,y)= (x=0, y=0), (x=5, y=0), (x=0, y=7), and (x=5, y=7), where x and y are measured in meters. The electric field is,
- -a) 1.997E+03 V·m
- +b) 2.197E+03 V·m
- -c) 2.417E+03 V·m
- -d) 2.659E+03 V·m
- -e) 2.924E+03 V·m
QB:Ch 6:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) What is the magnetude (absolute value) of the electric flux through a rectangle that occupies the z=0 plane with corners at (x,y)= (x=0, y=0), (x=7, y=0), (x=0, y=6), and (x=7, y=6), where x and y are measured in meters. The electric field is,
- a) 3.337E+03 V·m
- b) 3.670E+03 V·m
- c) 4.037E+03 V·m
- d) 4.441E+03 V·m
- e) 4.885E+03 V·m

- a) 2.079E+01 N·m2/C
- b) 2.287E+01 N·m2/C
- c) 2.516E+01 N·m2/C
- d) 2.768E+01 N·m2/C
- e) 3.044E+01 N·m2/C

- a) 3.750E+01 N·m2/C
- b) 4.125E+01 N·m2/C
- c) 4.537E+01 N·m2/C
- d) 4.991E+01 N·m2/C
- e) 5.490E+01 N·m2/C
KEY:QB:Ch 6:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) What is the magnetude (absolute value) of the electric flux through a rectangle that occupies the z=0 plane with corners at (x,y)= (x=0, y=0), (x=7, y=0), (x=0, y=6), and (x=7, y=6), where x and y are measured in meters. The electric field is,
- +a) 3.337E+03 V·m
- -b) 3.670E+03 V·m
- -c) 4.037E+03 V·m
- -d) 4.441E+03 V·m
- -e) 4.885E+03 V·m

- -a) 2.079E+01 N·m2/C
- -b) 2.287E+01 N·m2/C
- -c) 2.516E+01 N·m2/C
- +d) 2.768E+01 N·m2/C
- -e) 3.044E+01 N·m2/C

- -a) 3.750E+01 N·m2/C
- -b) 4.125E+01 N·m2/C
- -c) 4.537E+01 N·m2/C
- +d) 4.991E+01 N·m2/C
- -e) 5.490E+01 N·m2/C
QB:Ch 7:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) Assume that a 24 nC charge is situated at the origin. Calculate the the magnitude (absolute value) of the potential difference between points P1 and P2 where the polar coordinates (r,φ) of P1 are (9 cm, 0°) and P2 is at (13 cm, 27°).
- a) 5.540E+02 V
- b) 6.095E+02 V
- c) 6.704E+02 V
- d) 7.374E+02 V
- e) 8.112E+02 V

- a) 5.434E-01 N
- b) 5.977E-01 N
- c) 6.575E-01 N
- d) 7.233E-01 N
- e) 7.956E-01 N

- a) 3.910E+01 J
- b) 4.301E+01 J
- c) 4.731E+01 J
- d) 5.204E+01 J
- e) 5.725E+01 J
KEY:QB:Ch 7:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) Assume that a 24 nC charge is situated at the origin. Calculate the the magnitude (absolute value) of the potential difference between points P1 and P2 where the polar coordinates (r,φ) of P1 are (9 cm, 0°) and P2 is at (13 cm, 27°).
- -a) 5.540E+02 V
- -b) 6.095E+02 V
- -c) 6.704E+02 V
- +d) 7.374E+02 V
- -e) 8.112E+02 V

- +a) 5.434E-01 N
- -b) 5.977E-01 N
- -c) 6.575E-01 N
- -d) 7.233E-01 N
- -e) 7.956E-01 N

- -a) 3.910E+01 J
- -b) 4.301E+01 J
- -c) 4.731E+01 J
- -d) 5.204E+01 J
- +e) 5.725E+01 J
QB:Ch 7:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- a) 5.178E+01 J
- b) 5.696E+01 J
- c) 6.266E+01 J
- d) 6.892E+01 J
- e) 7.582E+01 J
2) Assume that a 26 nC charge is situated at the origin. Calculate the the magnitude (absolute value) of the potential difference between points P1 and P2 where the polar coordinates (r,φ) of P1 are (9 cm, 0°) and P2 is at (13 cm, 42°).
- a) 7.263E+02 V
- b) 7.989E+02 V
- c) 8.788E+02 V
- d) 9.667E+02 V
- e) 1.063E+03 V

- a) 5.367E-01 N
- b) 5.904E-01 N
- c) 6.494E-01 N
- d) 7.144E-01 N
- e) 7.858E-01 N
KEY:QB:Ch 7:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- -a) 5.178E+01 J
- +b) 5.696E+01 J
- -c) 6.266E+01 J
- -d) 6.892E+01 J
- -e) 7.582E+01 J
2) Assume that a 26 nC charge is situated at the origin. Calculate the the magnitude (absolute value) of the potential difference between points P1 and P2 where the polar coordinates (r,φ) of P1 are (9 cm, 0°) and P2 is at (13 cm, 42°).
- -a) 7.263E+02 V
- +b) 7.989E+02 V
- -c) 8.788E+02 V
- -d) 9.667E+02 V
- -e) 1.063E+03 V

- +a) 5.367E-01 N
- -b) 5.904E-01 N
- -c) 6.494E-01 N
- -d) 7.144E-01 N
- -e) 7.858E-01 N
QB:Ch 7:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- a) 8.206E-01 N
- b) 9.027E-01 N
- c) 9.930E-01 N
- d) 1.092E+00 N
- e) 1.201E+00 N

- a) 4.235E+01 J
- b) 4.659E+01 J
- c) 5.125E+01 J
- d) 5.637E+01 J
- e) 6.201E+01 J
3) Assume that a 15 nC charge is situated at the origin. Calculate the the magnitude (absolute value) of the potential difference between points P1 and P2 where the polar coordinates (r,φ) of P1 are (5 cm, 0°) and P2 is at (14 cm, 77°).
- a) 1.184E+03 V
- b) 1.302E+03 V
- c) 1.432E+03 V
- d) 1.576E+03 V
- e) 1.733E+03 V
KEY:QB:Ch 7:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- -a) 8.206E-01 N
- +b) 9.027E-01 N
- -c) 9.930E-01 N
- -d) 1.092E+00 N
- -e) 1.201E+00 N

- -a) 4.235E+01 J
- +b) 4.659E+01 J
- -c) 5.125E+01 J
- -d) 5.637E+01 J
- -e) 6.201E+01 J
3) Assume that a 15 nC charge is situated at the origin. Calculate the the magnitude (absolute value) of the potential difference between points P1 and P2 where the polar coordinates (r,φ) of P1 are (5 cm, 0°) and P2 is at (14 cm, 77°).
- -a) 1.184E+03 V
- -b) 1.302E+03 V
- -c) 1.432E+03 V
- -d) 1.576E+03 V
- +e) 1.733E+03 V
QB:Ch 8:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- a) 2.698E+00 μF
- b) 2.968E+00 μF
- c) 3.265E+00 μF
- d) 3.591E+00 μF
- e) 3.950E+00 μF

- a) 2.188E+01 μJ
- b) 2.407E+01 μJ
- c) 2.647E+01 μJ
- d) 2.912E+01 μJ
- e) 3.203E+01 μJ

- a) 5.969E+01 μC
- b) 6.566E+01 μC
- c) 7.222E+01 μC
- d) 7.944E+01 μC
- e) 8.739E+01 μC
KEY:QB:Ch 8:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- -a) 2.698E+00 μF
- -b) 2.968E+00 μF
- -c) 3.265E+00 μF
- -d) 3.591E+00 μF
- +e) 3.950E+00 μF

- -a) 2.188E+01 μJ
- -b) 2.407E+01 μJ
- -c) 2.647E+01 μJ
- +d) 2.912E+01 μJ
- -e) 3.203E+01 μJ

- -a) 5.969E+01 μC
- -b) 6.566E+01 μC
- +c) 7.222E+01 μC
- -d) 7.944E+01 μC
- -e) 8.739E+01 μC
QB:Ch 8:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- a) 1.508E+01 μJ
- b) 1.659E+01 μJ
- c) 1.825E+01 μJ
- d) 2.007E+01 μJ
- e) 2.208E+01 μJ

- a) 4.275E+00 μF
- b) 4.703E+00 μF
- c) 5.173E+00 μF
- d) 5.691E+00 μF
- e) 6.260E+00 μF

- a) 2.444E+01 μC
- b) 2.689E+01 μC
- c) 2.958E+01 μC
- d) 3.253E+01 μC
- e) 3.579E+01 μC
KEY:QB:Ch 8:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- -a) 1.508E+01 μJ
- +b) 1.659E+01 μJ
- -c) 1.825E+01 μJ
- -d) 2.007E+01 μJ
- -e) 2.208E+01 μJ

- -a) 4.275E+00 μF
- -b) 4.703E+00 μF
- +c) 5.173E+00 μF
- -d) 5.691E+00 μF
- -e) 6.260E+00 μF

- -a) 2.444E+01 μC
- -b) 2.689E+01 μC
- -c) 2.958E+01 μC
- +d) 3.253E+01 μC
- -e) 3.579E+01 μC
QB:Ch 8:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- a) 4.809E+01 μC
- b) 5.290E+01 μC
- c) 5.819E+01 μC
- d) 6.401E+01 μC
- e) 7.041E+01 μC

- a) 4.489E+00 μF
- b) 4.938E+00 μF
- c) 5.432E+00 μF
- d) 5.975E+00 μF
- e) 6.573E+00 μF

- a) 1.764E+01 μJ
- b) 1.940E+01 μJ
- c) 2.134E+01 μJ
- d) 2.348E+01 μJ
- e) 2.583E+01 μJ
KEY:QB:Ch 8:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- -a) 4.809E+01 μC
- +b) 5.290E+01 μC
- -c) 5.819E+01 μC
- -d) 6.401E+01 μC
- -e) 7.041E+01 μC

- -a) 4.489E+00 μF
- -b) 4.938E+00 μF
- +c) 5.432E+00 μF
- -d) 5.975E+00 μF
- -e) 6.573E+00 μF

- -a) 1.764E+01 μJ
- +b) 1.940E+01 μJ
- -c) 2.134E+01 μJ
- -d) 2.348E+01 μJ
- -e) 2.583E+01 μJ
QB:Ch 9:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) Calculate the drift speed of electrons in a copper wire with a diameter of 4.9 mm carrying a 6.43 A current, given that there is one free electron per copper atom. The density of copper is 8.80 x 103kg/m3 and the atomic mass of copper is 63.54 g/mol. Avagadro's number is 6.02 x 1023atoms/mol.
- a) 2.109E-05 m/s
- b) 2.320E-05 m/s
- c) 2.552E-05 m/s
- d) 2.807E-05 m/s
- e) 3.088E-05 m/s
2) What is the average current involved when a truck battery sets in motion 618 C of charge in 2.28 s while starting an engine?
- a) 2.240E+02 A
- b) 2.464E+02 A
- c) 2.711E+02 A
- d) 2.982E+02 A
- e) 3.280E+02 A
3) A make-believe metal has a density of 7.000E+03 kg/m3 and an atomic mass of 89.4 g/mol. Taking Avogadro's number to be 6.020E+23 atoms/mol and assuming one free electron per atom, calculate the number of free electrons per cubic meter.
- a) 3.219E+28 e−/m3
- b) 3.541E+28 e−/m3
- c) 3.896E+28 e−/m3
- d) 4.285E+28 e−/m3
- e) 4.714E+28 e−/m3
KEY:QB:Ch 9:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) Calculate the drift speed of electrons in a copper wire with a diameter of 4.9 mm carrying a 6.43 A current, given that there is one free electron per copper atom. The density of copper is 8.80 x 103kg/m3 and the atomic mass of copper is 63.54 g/mol. Avagadro's number is 6.02 x 1023atoms/mol.
- -a) 2.109E-05 m/s
- -b) 2.320E-05 m/s
- +c) 2.552E-05 m/s
- -d) 2.807E-05 m/s
- -e) 3.088E-05 m/s
2) What is the average current involved when a truck battery sets in motion 618 C of charge in 2.28 s while starting an engine?
- -a) 2.240E+02 A
- -b) 2.464E+02 A
- +c) 2.711E+02 A
- -d) 2.982E+02 A
- -e) 3.280E+02 A
3) A make-believe metal has a density of 7.000E+03 kg/m3 and an atomic mass of 89.4 g/mol. Taking Avogadro's number to be 6.020E+23 atoms/mol and assuming one free electron per atom, calculate the number of free electrons per cubic meter.
- -a) 3.219E+28 e−/m3
- -b) 3.541E+28 e−/m3
- -c) 3.896E+28 e−/m3
- -d) 4.285E+28 e−/m3
- +e) 4.714E+28 e−/m3
QB:Ch 9:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A make-believe metal has a density of 8.690E+03 kg/m3 and an atomic mass of 48.4 g/mol. Taking Avogadro's number to be 6.020E+23 atoms/mol and assuming one free electron per atom, calculate the number of free electrons per cubic meter.
- a) 1.081E+29 e−/m3
- b) 1.189E+29 e−/m3
- c) 1.308E+29 e−/m3
- d) 1.439E+29 e−/m3
- e) 1.582E+29 e−/m3
2) What is the average current involved when a truck battery sets in motion 537 C of charge in 5.08 s while starting an engine?
- a) 8.736E+01 A
- b) 9.610E+01 A
- c) 1.057E+02 A
- d) 1.163E+02 A
- e) 1.279E+02 A
3) Calculate the drift speed of electrons in a copper wire with a diameter of 3.53 mm carrying a 2.8 A current, given that there is one free electron per copper atom. The density of copper is 8.80 x 103kg/m3 and the atomic mass of copper is 63.54 g/mol. Avagadro's number is 6.02 x 1023atoms/mol.
- a) 1.947E-05 m/s
- b) 2.141E-05 m/s
- c) 2.355E-05 m/s
- d) 2.591E-05 m/s
- e) 2.850E-05 m/s
KEY:QB:Ch 9:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A make-believe metal has a density of 8.690E+03 kg/m3 and an atomic mass of 48.4 g/mol. Taking Avogadro's number to be 6.020E+23 atoms/mol and assuming one free electron per atom, calculate the number of free electrons per cubic meter.
- +a) 1.081E+29 e−/m3
- -b) 1.189E+29 e−/m3
- -c) 1.308E+29 e−/m3
- -d) 1.439E+29 e−/m3
- -e) 1.582E+29 e−/m3
2) What is the average current involved when a truck battery sets in motion 537 C of charge in 5.08 s while starting an engine?
- -a) 8.736E+01 A
- -b) 9.610E+01 A
- +c) 1.057E+02 A
- -d) 1.163E+02 A
- -e) 1.279E+02 A
3) Calculate the drift speed of electrons in a copper wire with a diameter of 3.53 mm carrying a 2.8 A current, given that there is one free electron per copper atom. The density of copper is 8.80 x 103kg/m3 and the atomic mass of copper is 63.54 g/mol. Avagadro's number is 6.02 x 1023atoms/mol.
- -a) 1.947E-05 m/s
- +b) 2.141E-05 m/s
- -c) 2.355E-05 m/s
- -d) 2.591E-05 m/s
- -e) 2.850E-05 m/s
QB:Ch 9:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A make-believe metal has a density of 8.690E+03 kg/m3 and an atomic mass of 48.4 g/mol. Taking Avogadro's number to be 6.020E+23 atoms/mol and assuming one free electron per atom, calculate the number of free electrons per cubic meter.
- a) 1.081E+29 e−/m3
- b) 1.189E+29 e−/m3
- c) 1.308E+29 e−/m3
- d) 1.439E+29 e−/m3
- e) 1.582E+29 e−/m3
2) Calculate the drift speed of electrons in a copper wire with a diameter of 3.53 mm carrying a 2.8 A current, given that there is one free electron per copper atom. The density of copper is 8.80 x 103kg/m3 and the atomic mass of copper is 63.54 g/mol. Avagadro's number is 6.02 x 1023atoms/mol.
- a) 1.947E-05 m/s
- b) 2.141E-05 m/s
- c) 2.355E-05 m/s
- d) 2.591E-05 m/s
- e) 2.850E-05 m/s
3) What is the average current involved when a truck battery sets in motion 537 C of charge in 5.08 s while starting an engine?
- a) 8.736E+01 A
- b) 9.610E+01 A
- c) 1.057E+02 A
- d) 1.163E+02 A
- e) 1.279E+02 A
KEY:QB:Ch 9:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A make-believe metal has a density of 8.690E+03 kg/m3 and an atomic mass of 48.4 g/mol. Taking Avogadro's number to be 6.020E+23 atoms/mol and assuming one free electron per atom, calculate the number of free electrons per cubic meter.
- +a) 1.081E+29 e−/m3
- -b) 1.189E+29 e−/m3
- -c) 1.308E+29 e−/m3
- -d) 1.439E+29 e−/m3
- -e) 1.582E+29 e−/m3
2) Calculate the drift speed of electrons in a copper wire with a diameter of 3.53 mm carrying a 2.8 A current, given that there is one free electron per copper atom. The density of copper is 8.80 x 103kg/m3 and the atomic mass of copper is 63.54 g/mol. Avagadro's number is 6.02 x 1023atoms/mol.
- -a) 1.947E-05 m/s
- +b) 2.141E-05 m/s
- -c) 2.355E-05 m/s
- -d) 2.591E-05 m/s
- -e) 2.850E-05 m/s
3) What is the average current involved when a truck battery sets in motion 537 C of charge in 5.08 s while starting an engine?
- -a) 8.736E+01 A
- -b) 9.610E+01 A
- +c) 1.057E+02 A
- -d) 1.163E+02 A
- -e) 1.279E+02 A
QB:Ch 10:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- a) 1.085E+00 mA
- b) 1.194E+00 mA
- c) 1.313E+00 mA
- d) 1.444E+00 mA
- e) 1.589E+00 mA

- a) 9.571E+00 s
- b) 1.053E+01 s
- c) 1.158E+01 s
- d) 1.274E+01 s
- e) 1.401E+01 s

- a) 8.147E-02 A
- b) 8.962E-02 A
- c) 9.858E-02 A
- d) 1.084E-01 A
- e) 1.193E-01 A
KEY:QB:Ch 10:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- +a) 1.085E+00 mA
- -b) 1.194E+00 mA
- -c) 1.313E+00 mA
- -d) 1.444E+00 mA
- -e) 1.589E+00 mA

- -a) 9.571E+00 s
- -b) 1.053E+01 s
- +c) 1.158E+01 s
- -d) 1.274E+01 s
- -e) 1.401E+01 s

- -a) 8.147E-02 A
- -b) 8.962E-02 A
- -c) 9.858E-02 A
- +d) 1.084E-01 A
- -e) 1.193E-01 A
QB:Ch 10:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- a) 1.203E-01 A
- b) 1.324E-01 A
- c) 1.456E-01 A
- d) 1.602E-01 A
- e) 1.762E-01 A

- a) 1.296E+01 s
- b) 1.425E+01 s
- c) 1.568E+01 s
- d) 1.725E+01 s
- e) 1.897E+01 s

- a) 6.970E+00 mA
- b) 7.667E+00 mA
- c) 8.434E+00 mA
- d) 9.277E+00 mA
- e) 1.020E+01 mA
KEY:QB:Ch 10:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- -a) 1.203E-01 A
- -b) 1.324E-01 A
- +c) 1.456E-01 A
- -d) 1.602E-01 A
- -e) 1.762E-01 A

- -a) 1.296E+01 s
- -b) 1.425E+01 s
- +c) 1.568E+01 s
- -d) 1.725E+01 s
- -e) 1.897E+01 s

- +a) 6.970E+00 mA
- -b) 7.667E+00 mA
- -c) 8.434E+00 mA
- -d) 9.277E+00 mA
- -e) 1.020E+01 mA
QB:Ch 10:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- a) 7.264E-01 mA
- b) 7.990E-01 mA
- c) 8.789E-01 mA
- d) 9.668E-01 mA
- e) 1.063E+00 mA

- a) 9.571E+00 s
- b) 1.053E+01 s
- c) 1.158E+01 s
- d) 1.274E+01 s
- e) 1.401E+01 s

- a) 9.287E-02 A
- b) 1.022E-01 A
- c) 1.124E-01 A
- d) 1.236E-01 A
- e) 1.360E-01 A
KEY:QB:Ch 10:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- -a) 7.264E-01 mA
- +b) 7.990E-01 mA
- -c) 8.789E-01 mA
- -d) 9.668E-01 mA
- -e) 1.063E+00 mA

- -a) 9.571E+00 s
- -b) 1.053E+01 s
- +c) 1.158E+01 s
- -d) 1.274E+01 s
- -e) 1.401E+01 s

- -a) 9.287E-02 A
- -b) 1.022E-01 A
- -c) 1.124E-01 A
- +d) 1.236E-01 A
- -e) 1.360E-01 A
QB:Ch 11:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) An electron beam (m=9.1 x 10−31kg, q=1.6 x 10−19C) enters a crossed-field velocity selector with magnetic and electric fields of 4.66 mT and 2.860E+03 N/C, respectively. What must the velocity of the electron beam be to transverse the crossed fields undeflected ?
- a) 5.072E+05 m/s
- b) 5.579E+05 m/s
- c) 6.137E+05 m/s
- d) 6.751E+05 m/s
- e) 7.426E+05 m/s
2) A cyclotron used to accelerate alpha particlesm=6.64 x 10−27kg, q=3.2 x 10−19C) has a radius of 0.157 m and a magneticfield of 1.03 T. What is their maximum kinetic energy?
- a) 8.608E-01 MeV
- b) 9.468E-01 MeV
- c) 1.042E+00 MeV
- d) 1.146E+00 MeV
- e) 1.260E+00 MeV
3) A circular current loop of radius 2.16 cm carries a current of 1.72 mA. What is the magnitude of the torque if the dipole is oriented at 52 ° to a uniform magnetic fied of 0.24 T?
- a) 3.582E-07 N m
- b) 3.940E-07 N m
- c) 4.334E-07 N m
- d) 4.768E-07 N m
- e) 5.245E-07 N m
KEY:QB:Ch 11:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) An electron beam (m=9.1 x 10−31kg, q=1.6 x 10−19C) enters a crossed-field velocity selector with magnetic and electric fields of 4.66 mT and 2.860E+03 N/C, respectively. What must the velocity of the electron beam be to transverse the crossed fields undeflected ?
- -a) 5.072E+05 m/s
- -b) 5.579E+05 m/s
- +c) 6.137E+05 m/s
- -d) 6.751E+05 m/s
- -e) 7.426E+05 m/s
2) A cyclotron used to accelerate alpha particlesm=6.64 x 10−27kg, q=3.2 x 10−19C) has a radius of 0.157 m and a magneticfield of 1.03 T. What is their maximum kinetic energy?
- -a) 8.608E-01 MeV
- -b) 9.468E-01 MeV
- -c) 1.042E+00 MeV
- -d) 1.146E+00 MeV
- +e) 1.260E+00 MeV
3) A circular current loop of radius 2.16 cm carries a current of 1.72 mA. What is the magnitude of the torque if the dipole is oriented at 52 ° to a uniform magnetic fied of 0.24 T?
- -a) 3.582E-07 N m
- -b) 3.940E-07 N m
- -c) 4.334E-07 N m
- +d) 4.768E-07 N m
- -e) 5.245E-07 N m
QB:Ch 11:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A cyclotron used to accelerate alpha particlesm=6.64 x 10−27kg, q=3.2 x 10−19C) has a radius of 0.409 m and a magneticfield of 1.27 T. What is their maximum kinetic energy?
- a) 8.881E+00 MeV
- b) 9.769E+00 MeV
- c) 1.075E+01 MeV
- d) 1.182E+01 MeV
- e) 1.300E+01 MeV
2) A circular current loop of radius 1.59 cm carries a current of 1.13 mA. What is the magnitude of the torque if the dipole is oriented at 41 ° to a uniform magnetic fied of 0.189 T?
- a) 1.113E-07 N m
- b) 1.224E-07 N m
- c) 1.347E-07 N m
- d) 1.481E-07 N m
- e) 1.629E-07 N m
3) An electron beam (m=9.1 x 10−31kg, q=1.6 x 10−19C) enters a crossed-field velocity selector with magnetic and electric fields of 9.23 mT and 6.120E+03 N/C, respectively. What must the velocity of the electron beam be to transverse the crossed fields undeflected ?
- a) 4.982E+05 m/s
- b) 5.480E+05 m/s
- c) 6.028E+05 m/s
- d) 6.631E+05 m/s
- e) 7.294E+05 m/s
KEY:QB:Ch 11:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A cyclotron used to accelerate alpha particlesm=6.64 x 10−27kg, q=3.2 x 10−19C) has a radius of 0.409 m and a magneticfield of 1.27 T. What is their maximum kinetic energy?
- -a) 8.881E+00 MeV
- -b) 9.769E+00 MeV
- -c) 1.075E+01 MeV
- -d) 1.182E+01 MeV
- +e) 1.300E+01 MeV
2) A circular current loop of radius 1.59 cm carries a current of 1.13 mA. What is the magnitude of the torque if the dipole is oriented at 41 ° to a uniform magnetic fied of 0.189 T?
- +a) 1.113E-07 N m
- -b) 1.224E-07 N m
- -c) 1.347E-07 N m
- -d) 1.481E-07 N m
- -e) 1.629E-07 N m
3) An electron beam (m=9.1 x 10−31kg, q=1.6 x 10−19C) enters a crossed-field velocity selector with magnetic and electric fields of 9.23 mT and 6.120E+03 N/C, respectively. What must the velocity of the electron beam be to transverse the crossed fields undeflected ?
- -a) 4.982E+05 m/s
- -b) 5.480E+05 m/s
- -c) 6.028E+05 m/s
- +d) 6.631E+05 m/s
- -e) 7.294E+05 m/s
QB:Ch 11:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) An electron beam (m=9.1 x 10−31kg, q=1.6 x 10−19C) enters a crossed-field velocity selector with magnetic and electric fields of 4.15 mT and 4.440E+03 N/C, respectively. What must the velocity of the electron beam be to transverse the crossed fields undeflected ?
- a) 1.070E+06 m/s
- b) 1.177E+06 m/s
- c) 1.295E+06 m/s
- d) 1.424E+06 m/s
- e) 1.566E+06 m/s
2) A cyclotron used to accelerate alpha particlesm=6.64 x 10−27kg, q=3.2 x 10−19C) has a radius of 0.448 m and a magneticfield of 0.812 T. What is their maximum kinetic energy?
- a) 5.798E+00 MeV
- b) 6.377E+00 MeV
- c) 7.015E+00 MeV
- d) 7.717E+00 MeV
- e) 8.488E+00 MeV
3) A circular current loop of radius 1.56 cm carries a current of 2.57 mA. What is the magnitude of the torque if the dipole is oriented at 38 ° to a uniform magnetic fied of 0.79 T?
- a) 7.898E-07 N m
- b) 8.688E-07 N m
- c) 9.557E-07 N m
- d) 1.051E-06 N m
- e) 1.156E-06 N m
KEY:QB:Ch 11:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) An electron beam (m=9.1 x 10−31kg, q=1.6 x 10−19C) enters a crossed-field velocity selector with magnetic and electric fields of 4.15 mT and 4.440E+03 N/C, respectively. What must the velocity of the electron beam be to transverse the crossed fields undeflected ?
- +a) 1.070E+06 m/s
- -b) 1.177E+06 m/s
- -c) 1.295E+06 m/s
- -d) 1.424E+06 m/s
- -e) 1.566E+06 m/s
2) A cyclotron used to accelerate alpha particlesm=6.64 x 10−27kg, q=3.2 x 10−19C) has a radius of 0.448 m and a magneticfield of 0.812 T. What is their maximum kinetic energy?
- -a) 5.798E+00 MeV
- +b) 6.377E+00 MeV
- -c) 7.015E+00 MeV
- -d) 7.717E+00 MeV
- -e) 8.488E+00 MeV
3) A circular current loop of radius 1.56 cm carries a current of 2.57 mA. What is the magnitude of the torque if the dipole is oriented at 38 ° to a uniform magnetic fied of 0.79 T?
- -a) 7.898E-07 N m
- -b) 8.688E-07 N m
- +c) 9.557E-07 N m
- -d) 1.051E-06 N m
- -e) 1.156E-06 N m
QB:Ch 12:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
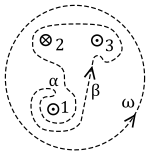
:
- a) 8.204E-04 T-m
- b) 9.025E-04 T-m
- c) 9.927E-04 T-m
- d) 1.092E-03 T-m
- e) 1.201E-03 T-m
2) Under most conditions the current is distributed uniformly over the cross section of the wire. What is the magnetic field 1.86 mm from the center of a wire of radius 5 mm if the current is 1A?
- a) 1.488E-05 T
- b) 1.637E-05 T
- c) 1.800E-05 T
- d) 1.981E-05 T
- e) 2.179E-05 T
3) A solenoid has 7.610E+04 turns wound around a cylinder of diameter 1.21 cm and length 9 m. The current through the coils is 0.696 A. Define the origin to be the center of the solenoid and neglect end effects as you calculate the line integral alongthe axis from z=−1.52 cm to z=+2.04 cm
- a) 2.176E-04 T-m
- b) 2.393E-04 T-m
- c) 2.633E-04 T-m
- d) 2.896E-04 T-m
- e) 3.186E-04 T-m
KEY:QB:Ch 12:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

:
- -a) 8.204E-04 T-m
- -b) 9.025E-04 T-m
- +c) 9.927E-04 T-m
- -d) 1.092E-03 T-m
- -e) 1.201E-03 T-m
2) Under most conditions the current is distributed uniformly over the cross section of the wire. What is the magnetic field 1.86 mm from the center of a wire of radius 5 mm if the current is 1A?
- +a) 1.488E-05 T
- -b) 1.637E-05 T
- -c) 1.800E-05 T
- -d) 1.981E-05 T
- -e) 2.179E-05 T
3) A solenoid has 7.610E+04 turns wound around a cylinder of diameter 1.21 cm and length 9 m. The current through the coils is 0.696 A. Define the origin to be the center of the solenoid and neglect end effects as you calculate the line integral alongthe axis from z=−1.52 cm to z=+2.04 cm
- -a) 2.176E-04 T-m
- -b) 2.393E-04 T-m
- +c) 2.633E-04 T-m
- -d) 2.896E-04 T-m
- -e) 3.186E-04 T-m
QB:Ch 12:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A solenoid has 5.980E+04 turns wound around a cylinder of diameter 1.8 cm and length 17 m. The current through the coils is 0.933 A. Define the origin to be the center of the solenoid and neglect end effects as you calculate the line integral alongthe axis from z=−3.68 cm to z=+1.29 cm
- a) 1.863E-04 T-m
- b) 2.050E-04 T-m
- c) 2.255E-04 T-m
- d) 2.480E-04 T-m
- e) 2.728E-04 T-m

:
- a) 8.204E-04 T-m
- b) 9.025E-04 T-m
- c) 9.927E-04 T-m
- d) 1.092E-03 T-m
- e) 1.201E-03 T-m
3) Under most conditions the current is distributed uniformly over the cross section of the wire. What is the magnetic field 2.04 mm from the center of a wire of radius 5 mm if the current is 1A?
- a) 1.115E-05 T
- b) 1.226E-05 T
- c) 1.349E-05 T
- d) 1.484E-05 T
- e) 1.632E-05 T
KEY:QB:Ch 12:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A solenoid has 5.980E+04 turns wound around a cylinder of diameter 1.8 cm and length 17 m. The current through the coils is 0.933 A. Define the origin to be the center of the solenoid and neglect end effects as you calculate the line integral alongthe axis from z=−3.68 cm to z=+1.29 cm
- -a) 1.863E-04 T-m
- +b) 2.050E-04 T-m
- -c) 2.255E-04 T-m
- -d) 2.480E-04 T-m
- -e) 2.728E-04 T-m

:
- -a) 8.204E-04 T-m
- -b) 9.025E-04 T-m
- +c) 9.927E-04 T-m
- -d) 1.092E-03 T-m
- -e) 1.201E-03 T-m
3) Under most conditions the current is distributed uniformly over the cross section of the wire. What is the magnetic field 2.04 mm from the center of a wire of radius 5 mm if the current is 1A?
- -a) 1.115E-05 T
- -b) 1.226E-05 T
- -c) 1.349E-05 T
- -d) 1.484E-05 T
- +e) 1.632E-05 T
QB:Ch 12:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A solenoid has 7.170E+04 turns wound around a cylinder of diameter 1.56 cm and length 9 m. The current through the coils is 0.391 A. Define the origin to be the center of the solenoid and neglect end effects as you calculate the line integral alongthe axis from z=−2.73 cm to z=+2.56 cm
- a) 1.414E-04 T-m
- b) 1.556E-04 T-m
- c) 1.711E-04 T-m
- d) 1.882E-04 T-m
- e) 2.071E-04 T-m
2) Under most conditions the current is distributed uniformly over the cross section of the wire. What is the magnetic field 1.18 mm from the center of a wire of radius 3 mm if the current is 1A?
- a) 1.791E-05 T
- b) 1.970E-05 T
- c) 2.167E-05 T
- d) 2.384E-05 T
- e) 2.622E-05 T

:
- a) 1.724E-03 T-m
- b) 1.896E-03 T-m
- c) 2.086E-03 T-m
- d) 2.295E-03 T-m
- e) 2.524E-03 T-m
KEY:QB:Ch 12:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A solenoid has 7.170E+04 turns wound around a cylinder of diameter 1.56 cm and length 9 m. The current through the coils is 0.391 A. Define the origin to be the center of the solenoid and neglect end effects as you calculate the line integral alongthe axis from z=−2.73 cm to z=+2.56 cm
- -a) 1.414E-04 T-m
- -b) 1.556E-04 T-m
- -c) 1.711E-04 T-m
- -d) 1.882E-04 T-m
- +e) 2.071E-04 T-m
2) Under most conditions the current is distributed uniformly over the cross section of the wire. What is the magnetic field 1.18 mm from the center of a wire of radius 3 mm if the current is 1A?
- -a) 1.791E-05 T
- -b) 1.970E-05 T
- -c) 2.167E-05 T
- -d) 2.384E-05 T
- +e) 2.622E-05 T

:
- -a) 1.724E-03 T-m
- -b) 1.896E-03 T-m
- +c) 2.086E-03 T-m
- -d) 2.295E-03 T-m
- -e) 2.524E-03 T-m
QB:Ch 13:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) The current through the windings of a solenoid with n= 2.980E+03 turns per meter is changing at a rate dI/dt=9 A/s. The solenoid is 88 cm long and has a cross-sectional diameter of 2.69 cm. A small coil consisting of N=28turns wraped in a circle of diameter 1.64 cm is placed in the middle of the solenoid such that the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the central axis of the solenoid. Assume that the infinite-solenoid approximation is valid inside the small coil. What is the emf induced in the coil?
- a) 1.498E-04 V
- b) 1.647E-04 V
- c) 1.812E-04 V
- d) 1.993E-04 V
- e) 2.193E-04 V
2) A time dependent magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of a circular coil with a radius of 0.655 m. The magnetic field is spatially uniform but decays in time according to , where 9.62 s. What is the current in the coil if the impedance of the coil is 48.9 Ω?
- a) 7.890E-01 A
- b) 8.679E-01 A
- c) 9.547E-01 A
- d) 1.050E+00 A
- e) 1.155E+00 A
3) A square coil has sides that are L= 0.308 m long and is tightly wound with N=969 turns of wire. The resistance of the coil is R=8.64 Ω. The coil is placed in a spacially uniform magnetic field that is directed perpendicular to the face of the coil and whose magnitude is increasing at a rate dB/dt=0.0498 T/s. If R represents the only impedance of the coil, what is the magnitude of the current circulting through it?
- a) 4.817E-01 A
- b) 5.298E-01 A
- c) 5.828E-01 A
- d) 6.411E-01 A
- e) 7.052E-01 A
KEY:QB:Ch 13:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) The current through the windings of a solenoid with n= 2.980E+03 turns per meter is changing at a rate dI/dt=9 A/s. The solenoid is 88 cm long and has a cross-sectional diameter of 2.69 cm. A small coil consisting of N=28turns wraped in a circle of diameter 1.64 cm is placed in the middle of the solenoid such that the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the central axis of the solenoid. Assume that the infinite-solenoid approximation is valid inside the small coil. What is the emf induced in the coil?
- -a) 1.498E-04 V
- -b) 1.647E-04 V
- -c) 1.812E-04 V
- +d) 1.993E-04 V
- -e) 2.193E-04 V
2) A time dependent magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of a circular coil with a radius of 0.655 m. The magnetic field is spatially uniform but decays in time according to , where 9.62 s. What is the current in the coil if the impedance of the coil is 48.9 Ω?
- +a) 7.890E-01 A
- -b) 8.679E-01 A
- -c) 9.547E-01 A
- -d) 1.050E+00 A
- -e) 1.155E+00 A
3) A square coil has sides that are L= 0.308 m long and is tightly wound with N=969 turns of wire. The resistance of the coil is R=8.64 Ω. The coil is placed in a spacially uniform magnetic field that is directed perpendicular to the face of the coil and whose magnitude is increasing at a rate dB/dt=0.0498 T/s. If R represents the only impedance of the coil, what is the magnitude of the current circulting through it?
- -a) 4.817E-01 A
- +b) 5.298E-01 A
- -c) 5.828E-01 A
- -d) 6.411E-01 A
- -e) 7.052E-01 A
QB:Ch 13:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A time dependent magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of a circular coil with a radius of 0.549 m. The magnetic field is spatially uniform but decays in time according to , where 7.0 s. What is the current in the coil if the impedance of the coil is 46.7 Ω?
- a) 2.032E-01 A
- b) 2.235E-01 A
- c) 2.458E-01 A
- d) 2.704E-01 A
- e) 2.975E-01 A
2) The current through the windings of a solenoid with n= 2.260E+03 turns per meter is changing at a rate dI/dt=12 A/s. The solenoid is 62 cm long and has a cross-sectional diameter of 3.37 cm. A small coil consisting of N=23turns wraped in a circle of diameter 1.7 cm is placed in the middle of the solenoid such that the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the central axis of the solenoid. Assume that the infinite-solenoid approximation is valid inside the small coil. What is the emf induced in the coil?
- a) 1.215E-04 V
- b) 1.337E-04 V
- c) 1.470E-04 V
- d) 1.617E-04 V
- e) 1.779E-04 V
3) A square coil has sides that are L= 0.561 m long and is tightly wound with N=930 turns of wire. The resistance of the coil is R=5.08 Ω. The coil is placed in a spacially uniform magnetic field that is directed perpendicular to the face of the coil and whose magnitude is increasing at a rate dB/dt=0.0548 T/s. If R represents the only impedance of the coil, what is the magnitude of the current circulting through it?
- a) 2.609E+00 A
- b) 2.870E+00 A
- c) 3.157E+00 A
- d) 3.473E+00 A
- e) 3.820E+00 A
KEY:QB:Ch 13:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A time dependent magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of a circular coil with a radius of 0.549 m. The magnetic field is spatially uniform but decays in time according to , where 7.0 s. What is the current in the coil if the impedance of the coil is 46.7 Ω?
- -a) 2.032E-01 A
- -b) 2.235E-01 A
- -c) 2.458E-01 A
- -d) 2.704E-01 A
- +e) 2.975E-01 A
2) The current through the windings of a solenoid with n= 2.260E+03 turns per meter is changing at a rate dI/dt=12 A/s. The solenoid is 62 cm long and has a cross-sectional diameter of 3.37 cm. A small coil consisting of N=23turns wraped in a circle of diameter 1.7 cm is placed in the middle of the solenoid such that the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the central axis of the solenoid. Assume that the infinite-solenoid approximation is valid inside the small coil. What is the emf induced in the coil?
- -a) 1.215E-04 V
- -b) 1.337E-04 V
- -c) 1.470E-04 V
- -d) 1.617E-04 V
- +e) 1.779E-04 V
3) A square coil has sides that are L= 0.561 m long and is tightly wound with N=930 turns of wire. The resistance of the coil is R=5.08 Ω. The coil is placed in a spacially uniform magnetic field that is directed perpendicular to the face of the coil and whose magnitude is increasing at a rate dB/dt=0.0548 T/s. If R represents the only impedance of the coil, what is the magnitude of the current circulting through it?
- -a) 2.609E+00 A
- -b) 2.870E+00 A
- +c) 3.157E+00 A
- -d) 3.473E+00 A
- -e) 3.820E+00 A
QB:Ch 13:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A time dependent magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of a circular coil with a radius of 0.8 m. The magnetic field is spatially uniform but decays in time according to , where 8.91 s. What is the current in the coil if the impedance of the coil is 61.7 Ω?
- a) 5.369E-01 A
- b) 5.906E-01 A
- c) 6.496E-01 A
- d) 7.146E-01 A
- e) 7.860E-01 A
2) A square coil has sides that are L= 0.219 m long and is tightly wound with N=508 turns of wire. The resistance of the coil is R=8.42 Ω. The coil is placed in a spacially uniform magnetic field that is directed perpendicular to the face of the coil and whose magnitude is increasing at a rate dB/dt=0.0619 T/s. If R represents the only impedance of the coil, what is the magnitude of the current circulting through it?
- a) 1.791E-01 A
- b) 1.970E-01 A
- c) 2.167E-01 A
- d) 2.384E-01 A
- e) 2.622E-01 A
3) The current through the windings of a solenoid with n= 2.970E+03 turns per meter is changing at a rate dI/dt=15 A/s. The solenoid is 89 cm long and has a cross-sectional diameter of 3.48 cm. A small coil consisting of N=28turns wraped in a circle of diameter 1.5 cm is placed in the middle of the solenoid such that the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the central axis of the solenoid. Assume that the infinite-solenoid approximation is valid inside the small coil. What is the emf induced in the coil?
- a) 2.081E-04 V
- b) 2.289E-04 V
- c) 2.518E-04 V
- d) 2.770E-04 V
- e) 3.047E-04 V
KEY:QB:Ch 13:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A time dependent magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of a circular coil with a radius of 0.8 m. The magnetic field is spatially uniform but decays in time according to , where 8.91 s. What is the current in the coil if the impedance of the coil is 61.7 Ω?
- -a) 5.369E-01 A
- -b) 5.906E-01 A
- -c) 6.496E-01 A
- -d) 7.146E-01 A
- +e) 7.860E-01 A
2) A square coil has sides that are L= 0.219 m long and is tightly wound with N=508 turns of wire. The resistance of the coil is R=8.42 Ω. The coil is placed in a spacially uniform magnetic field that is directed perpendicular to the face of the coil and whose magnitude is increasing at a rate dB/dt=0.0619 T/s. If R represents the only impedance of the coil, what is the magnitude of the current circulting through it?
- +a) 1.791E-01 A
- -b) 1.970E-01 A
- -c) 2.167E-01 A
- -d) 2.384E-01 A
- -e) 2.622E-01 A
3) The current through the windings of a solenoid with n= 2.970E+03 turns per meter is changing at a rate dI/dt=15 A/s. The solenoid is 89 cm long and has a cross-sectional diameter of 3.48 cm. A small coil consisting of N=28turns wraped in a circle of diameter 1.5 cm is placed in the middle of the solenoid such that the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the central axis of the solenoid. Assume that the infinite-solenoid approximation is valid inside the small coil. What is the emf induced in the coil?
- -a) 2.081E-04 V
- -b) 2.289E-04 V
- -c) 2.518E-04 V
- +d) 2.770E-04 V
- -e) 3.047E-04 V
QB:Ch 14:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) In an LC circuit, the self-inductance is 0.0262 H and the capacitance is 4.540E-06 F. At t=0 all the energy is stored in the capacitor, which has a charge of 4.700E-05 C. How long does it take for the capacitor to become completely discharged?
- a) 4.070E-04 s
- b) 4.477E-04 s
- c) 4.925E-04 s
- d) 5.417E-04 s
- e) 5.959E-04 s
2) A washer has an inner diameter of 2.38 cm and an outer diamter of 4.83 cm. The thickness is where is measured in cm, , and . What is the volume of the washer?
- a) 1.118E+00 cm3
- b) 1.229E+00 cm3
- c) 1.352E+00 cm3
- d) 1.487E+00 cm3
- e) 1.636E+00 cm3
- a) 5.791E-02 V
- b) 6.370E-02 V
- c) 7.007E-02 V
- d) 7.708E-02 V
- e) 8.478E-02 V
KEY:QB:Ch 14:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) In an LC circuit, the self-inductance is 0.0262 H and the capacitance is 4.540E-06 F. At t=0 all the energy is stored in the capacitor, which has a charge of 4.700E-05 C. How long does it take for the capacitor to become completely discharged?
- -a) 4.070E-04 s
- -b) 4.477E-04 s
- -c) 4.925E-04 s
- +d) 5.417E-04 s
- -e) 5.959E-04 s
2) A washer has an inner diameter of 2.38 cm and an outer diamter of 4.83 cm. The thickness is where is measured in cm, , and . What is the volume of the washer?
- -a) 1.118E+00 cm3
- +b) 1.229E+00 cm3
- -c) 1.352E+00 cm3
- -d) 1.487E+00 cm3
- -e) 1.636E+00 cm3

- -a) 5.791E-02 V
- +b) 6.370E-02 V
- -c) 7.007E-02 V
- -d) 7.708E-02 V
- -e) 8.478E-02 V
QB:Ch 14:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- a) 2.328E-02 V
- b) 2.560E-02 V
- c) 2.817E-02 V
- d) 3.098E-02 V
- e) 3.408E-02 V
2) A washer has an inner diameter of 2.31 cm and an outer diamter of 4.19 cm. The thickness is where is measured in cm, , and . What is the volume of the washer?
- a) 1.071E+00 cm3
- b) 1.178E+00 cm3
- c) 1.296E+00 cm3
- d) 1.425E+00 cm3
- e) 1.568E+00 cm3
3) In an LC circuit, the self-inductance is 0.0464 H and the capacitance is 7.350E-06 F. At t=0 all the energy is stored in the capacitor, which has a charge of 3.280E-05 C. How long does it take for the capacitor to become completely discharged?
- a) 8.339E-04 s
- b) 9.173E-04 s
- c) 1.009E-03 s
- d) 1.110E-03 s
- e) 1.221E-03 s
KEY:QB:Ch 14:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- -a) 2.328E-02 V
- +b) 2.560E-02 V
- -c) 2.817E-02 V
- -d) 3.098E-02 V
- -e) 3.408E-02 V
2) A washer has an inner diameter of 2.31 cm and an outer diamter of 4.19 cm. The thickness is where is measured in cm, , and . What is the volume of the washer?
- +a) 1.071E+00 cm3
- -b) 1.178E+00 cm3
- -c) 1.296E+00 cm3
- -d) 1.425E+00 cm3
- -e) 1.568E+00 cm3
3) In an LC circuit, the self-inductance is 0.0464 H and the capacitance is 7.350E-06 F. At t=0 all the energy is stored in the capacitor, which has a charge of 3.280E-05 C. How long does it take for the capacitor to become completely discharged?
- -a) 8.339E-04 s
- +b) 9.173E-04 s
- -c) 1.009E-03 s
- -d) 1.110E-03 s
- -e) 1.221E-03 s
QB:Ch 14:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A washer has an inner diameter of 2.21 cm and an outer diamter of 4.5 cm. The thickness is where is measured in cm, , and . What is the volume of the washer?
- a) 1.325E+00 cm3
- b) 1.457E+00 cm3
- c) 1.603E+00 cm3
- d) 1.763E+00 cm3
- e) 1.939E+00 cm3

- a) 6.604E-02 V
- b) 7.264E-02 V
- c) 7.990E-02 V
- d) 8.789E-02 V
- e) 9.668E-02 V
3) In an LC circuit, the self-inductance is 0.0399 H and the capacitance is 8.450E-06 F. At t=0 all the energy is stored in the capacitor, which has a charge of 6.480E-05 C. How long does it take for the capacitor to become completely discharged?
- a) 6.230E-04 s
- b) 6.853E-04 s
- c) 7.538E-04 s
- d) 8.292E-04 s
- e) 9.121E-04 s
KEY:QB:Ch 14:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A washer has an inner diameter of 2.21 cm and an outer diamter of 4.5 cm. The thickness is where is measured in cm, , and . What is the volume of the washer?
- -a) 1.325E+00 cm3
- +b) 1.457E+00 cm3
- -c) 1.603E+00 cm3
- -d) 1.763E+00 cm3
- -e) 1.939E+00 cm3

- +a) 6.604E-02 V
- -b) 7.264E-02 V
- -c) 7.990E-02 V
- -d) 8.789E-02 V
- -e) 9.668E-02 V
3) In an LC circuit, the self-inductance is 0.0399 H and the capacitance is 8.450E-06 F. At t=0 all the energy is stored in the capacitor, which has a charge of 6.480E-05 C. How long does it take for the capacitor to become completely discharged?
- -a) 6.230E-04 s
- -b) 6.853E-04 s
- -c) 7.538E-04 s
- -d) 8.292E-04 s
- +e) 9.121E-04 s
QB:Ch 15:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A step-down transformer steps 18 kV down to 260 V. The high-voltage input is provided by a 290 Ω power line that carries 3 A of currentWhat is the output current (at the 260 V side ?)
- a) 1.888E+02 A
- b) 2.077E+02 A
- c) 2.285E+02 A
- d) 2.513E+02 A
- e) 2.764E+02 A
2) The quality factor Q is a dimensionless paramater involving the relative values of the magnitudes of the at three impedances (R, XL, XC). Since Q is calculatedat resonance, XL, XC and only twoimpedances are involved, Q=≡ω0L/R is definedso that Q is large if the resistance is low. Calculate the Q of an LRC series driven at resonance by an applied voltage of of V=V0sin(ωt), where V0=5 V. The resistance, inductance, and capacitance are R =0.27 Ω, L= 4.30E-03H , and C=2.20E-06 F, respectively.
- a) Q = 1.238E+02
- b) Q = 1.424E+02
- c) Q = 1.637E+02
- d) Q = 1.883E+02
- e) Q = 2.165E+02
3) An ac generator produces an emf of amplitude 60 V at a frequency of 130 Hz. What is the maximum amplitude of the current if the generator is connected to a 85 mF inductor?
- a) 7.856E-01 A
- b) 8.642E-01 A
- c) 9.506E-01 A
- d) 1.046E+00 A
- e) 1.150E+00 A
KEY:QB:Ch 15:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) A step-down transformer steps 18 kV down to 260 V. The high-voltage input is provided by a 290 Ω power line that carries 3 A of currentWhat is the output current (at the 260 V side ?)
- -a) 1.888E+02 A
- +b) 2.077E+02 A
- -c) 2.285E+02 A
- -d) 2.513E+02 A
- -e) 2.764E+02 A
2) The quality factor Q is a dimensionless paramater involving the relative values of the magnitudes of the at three impedances (R, XL, XC). Since Q is calculatedat resonance, XL, XC and only twoimpedances are involved, Q=≡ω0L/R is definedso that Q is large if the resistance is low. Calculate the Q of an LRC series driven at resonance by an applied voltage of of V=V0sin(ωt), where V0=5 V. The resistance, inductance, and capacitance are R =0.27 Ω, L= 4.30E-03H , and C=2.20E-06 F, respectively.
- -a) Q = 1.238E+02
- -b) Q = 1.424E+02
- +c) Q = 1.637E+02
- -d) Q = 1.883E+02
- -e) Q = 2.165E+02
3) An ac generator produces an emf of amplitude 60 V at a frequency of 130 Hz. What is the maximum amplitude of the current if the generator is connected to a 85 mF inductor?
- -a) 7.856E-01 A
- +b) 8.642E-01 A
- -c) 9.506E-01 A
- -d) 1.046E+00 A
- -e) 1.150E+00 A
QB:Ch 15:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) An ac generator produces an emf of amplitude 69 V at a frequency of 180 Hz. What is the maximum amplitude of the current if the generator is connected to a 57 mF inductor?
- a) 1.070E+00 A
- b) 1.177E+00 A
- c) 1.295E+00 A
- d) 1.425E+00 A
- e) 1.567E+00 A
2) The quality factor Q is a dimensionless paramater involving the relative values of the magnitudes of the at three impedances (R, XL, XC). Since Q is calculatedat resonance, XL, XC and only twoimpedances are involved, Q=≡ω0L/R is definedso that Q is large if the resistance is low. Calculate the Q of an LRC series driven at resonance by an applied voltage of of V=V0sin(ωt), where V0=3 V. The resistance, inductance, and capacitance are R =0.14 Ω, L= 5.20E-03H , and C=2.90E-06 F, respectively.
- a) Q = 2.287E+02
- b) Q = 2.630E+02
- c) Q = 3.025E+02
- d) Q = 3.478E+02
- e) Q = 4.000E+02
3) A step-down transformer steps 7 kV down to 190 V. The high-voltage input is provided by a 240 Ω power line that carries 5 A of currentWhat is the output current (at the 190 V side ?)
- a) 1.675E+02 A
- b) 1.842E+02 A
- c) 2.026E+02 A
- d) 2.229E+02 A
- e) 2.452E+02 A
KEY:QB:Ch 15:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) An ac generator produces an emf of amplitude 69 V at a frequency of 180 Hz. What is the maximum amplitude of the current if the generator is connected to a 57 mF inductor?
- +a) 1.070E+00 A
- -b) 1.177E+00 A
- -c) 1.295E+00 A
- -d) 1.425E+00 A
- -e) 1.567E+00 A
2) The quality factor Q is a dimensionless paramater involving the relative values of the magnitudes of the at three impedances (R, XL, XC). Since Q is calculatedat resonance, XL, XC and only twoimpedances are involved, Q=≡ω0L/R is definedso that Q is large if the resistance is low. Calculate the Q of an LRC series driven at resonance by an applied voltage of of V=V0sin(ωt), where V0=3 V. The resistance, inductance, and capacitance are R =0.14 Ω, L= 5.20E-03H , and C=2.90E-06 F, respectively.
- -a) Q = 2.287E+02
- -b) Q = 2.630E+02
- +c) Q = 3.025E+02
- -d) Q = 3.478E+02
- -e) Q = 4.000E+02
3) A step-down transformer steps 7 kV down to 190 V. The high-voltage input is provided by a 240 Ω power line that carries 5 A of currentWhat is the output current (at the 190 V side ?)
- -a) 1.675E+02 A
- +b) 1.842E+02 A
- -c) 2.026E+02 A
- -d) 2.229E+02 A
- -e) 2.452E+02 A
QB:Ch 15:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) The quality factor Q is a dimensionless paramater involving the relative values of the magnitudes of the at three impedances (R, XL, XC). Since Q is calculatedat resonance, XL, XC and only twoimpedances are involved, Q=≡ω0L/R is definedso that Q is large if the resistance is low. Calculate the Q of an LRC series driven at resonance by an applied voltage of of V=V0sin(ωt), where V0=3 V. The resistance, inductance, and capacitance are R =0.21 Ω, L= 4.70E-03H , and C=3.70E-06 F, respectively.
- a) Q = 1.476E+02
- b) Q = 1.697E+02
- c) Q = 1.952E+02
- d) Q = 2.245E+02
- e) Q = 2.581E+02
2) An ac generator produces an emf of amplitude 5 V at a frequency of 52 Hz. What is the maximum amplitude of the current if the generator is connected to a 49 mF inductor?
- a) 2.839E-01 A
- b) 3.123E-01 A
- c) 3.435E-01 A
- d) 3.779E-01 A
- e) 4.157E-01 A
3) A step-down transformer steps 12 kV down to 230 V. The high-voltage input is provided by a 140 Ω power line that carries 5 A of currentWhat is the output current (at the 230 V side ?)
- a) 2.156E+02 A
- b) 2.372E+02 A
- c) 2.609E+02 A
- d) 2.870E+02 A
- e) 3.157E+02 A
KEY:QB:Ch 15:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034
1) The quality factor Q is a dimensionless paramater involving the relative values of the magnitudes of the at three impedances (R, XL, XC). Since Q is calculatedat resonance, XL, XC and only twoimpedances are involved, Q=≡ω0L/R is definedso that Q is large if the resistance is low. Calculate the Q of an LRC series driven at resonance by an applied voltage of of V=V0sin(ωt), where V0=3 V. The resistance, inductance, and capacitance are R =0.21 Ω, L= 4.70E-03H , and C=3.70E-06 F, respectively.
- -a) Q = 1.476E+02
- +b) Q = 1.697E+02
- -c) Q = 1.952E+02
- -d) Q = 2.245E+02
- -e) Q = 2.581E+02
2) An ac generator produces an emf of amplitude 5 V at a frequency of 52 Hz. What is the maximum amplitude of the current if the generator is connected to a 49 mF inductor?
- -a) 2.839E-01 A
- +b) 3.123E-01 A
- -c) 3.435E-01 A
- -d) 3.779E-01 A
- -e) 4.157E-01 A
3) A step-down transformer steps 12 kV down to 230 V. The high-voltage input is provided by a 140 Ω power line that carries 5 A of currentWhat is the output current (at the 230 V side ?)
- -a) 2.156E+02 A
- -b) 2.372E+02 A
- +c) 2.609E+02 A
- -d) 2.870E+02 A
- -e) 3.157E+02 A
QB:Ch 16:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- a) 8.809E-02 A
- b) 9.690E-02 A
- c) 1.066E-01 A
- d) 1.173E-01 A
- e) 1.290E-01 A
2) A 59 kW radio transmitter on Earth sends it signal to a satellite 120 km away. At what distance in the same direction would the signal have the same maximum field strength if the transmitter's output power were increased to 84 kW?
- a) 9.780E+01 km
- b) 1.076E+02 km
- c) 1.183E+02 km
- d) 1.302E+02 km
- e) 1.432E+02 km

- a) 3.223E+03 V/m
- b) 3.546E+03 V/m
- c) 3.900E+03 V/m
- d) 4.290E+03 V/m
- e) 4.719E+03 V/m
KEY:QB:Ch 16:V0
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- -a) 8.809E-02 A
- +b) 9.690E-02 A
- -c) 1.066E-01 A
- -d) 1.173E-01 A
- -e) 1.290E-01 A
2) A 59 kW radio transmitter on Earth sends it signal to a satellite 120 km away. At what distance in the same direction would the signal have the same maximum field strength if the transmitter's output power were increased to 84 kW?
- -a) 9.780E+01 km
- -b) 1.076E+02 km
- -c) 1.183E+02 km
- -d) 1.302E+02 km
- +e) 1.432E+02 km

- -a) 3.223E+03 V/m
- -b) 3.546E+03 V/m
- -c) 3.900E+03 V/m
- -d) 4.290E+03 V/m
- +e) 4.719E+03 V/m
QB:Ch 16:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- a) 9.524E-01 A
- b) 1.048E+00 A
- c) 1.152E+00 A
- d) 1.268E+00 A
- e) 1.394E+00 A

- a) 5.050E+03 V/m
- b) 5.555E+03 V/m
- c) 6.111E+03 V/m
- d) 6.722E+03 V/m
- e) 7.394E+03 V/m
3) A 46 kW radio transmitter on Earth sends it signal to a satellite 120 km away. At what distance in the same direction would the signal have the same maximum field strength if the transmitter's output power were increased to 78 kW?
- a) 1.563E+02 km
- b) 1.719E+02 km
- c) 1.891E+02 km
- d) 2.080E+02 km
- e) 2.288E+02 km
KEY:QB:Ch 16:V1
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- -a) 9.524E-01 A
- +b) 1.048E+00 A
- -c) 1.152E+00 A
- -d) 1.268E+00 A
- -e) 1.394E+00 A

- -a) 5.050E+03 V/m
- -b) 5.555E+03 V/m
- -c) 6.111E+03 V/m
- -d) 6.722E+03 V/m
- +e) 7.394E+03 V/m
3) A 46 kW radio transmitter on Earth sends it signal to a satellite 120 km away. At what distance in the same direction would the signal have the same maximum field strength if the transmitter's output power were increased to 78 kW?
- +a) 1.563E+02 km
- -b) 1.719E+02 km
- -c) 1.891E+02 km
- -d) 2.080E+02 km
- -e) 2.288E+02 km
QB:Ch 16:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- a) 2.058E-03 A
- b) 2.263E-03 A
- c) 2.490E-03 A
- d) 2.739E-03 A
- e) 3.013E-03 A

- a) 1.579E+04 V/m
- b) 1.737E+04 V/m
- c) 1.911E+04 V/m
- d) 2.102E+04 V/m
- e) 2.312E+04 V/m
3) A 41 kW radio transmitter on Earth sends it signal to a satellite 100 km away. At what distance in the same direction would the signal have the same maximum field strength if the transmitter's output power were increased to 98 kW?
- a) 1.405E+02 km
- b) 1.546E+02 km
- c) 1.701E+02 km
- d) 1.871E+02 km
- e) 2.058E+02 km
KEY:QB:Ch 16:V2
[edit | edit source]QB153089888034

- -a) 2.058E-03 A
- -b) 2.263E-03 A
- +c) 2.490E-03 A
- -d) 2.739E-03 A
- -e) 3.013E-03 A

- -a) 1.579E+04 V/m
- -b) 1.737E+04 V/m
- -c) 1.911E+04 V/m
- +d) 2.102E+04 V/m
- -e) 2.312E+04 V/m
3) A 41 kW radio transmitter on Earth sends it signal to a satellite 100 km away. At what distance in the same direction would the signal have the same maximum field strength if the transmitter's output power were increased to 98 kW?
- -a) 1.405E+02 km
- +b) 1.546E+02 km
- -c) 1.701E+02 km
- -d) 1.871E+02 km
- -e) 2.058E+02 km








































