Programming Fundamentals/Conditions/Compound Conditions
Appearance
Compound conditions perform different computations or actions depending on whether multiple combined programmer-specified Boolean conditions evaluate to true or false.[1] This activity introduces compound conditions. This activity will help you understand how to use compound conditions in a program.
Objectives
[edit | edit source]- Understand compound condition concepts.
- Understand how compound conditions are specified in a program.
- Create truth tables for "and" and "or" logical operators.
- Single-step through a program to observe nested condition execution.
Prerequisites
[edit | edit source]Learners should already be familiar with nested conditions.
Introduction
[edit | edit source]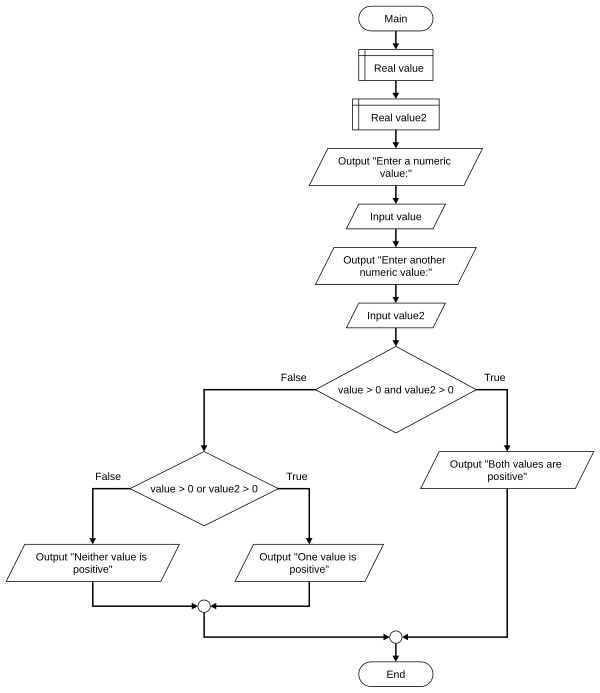
Review the flowchart example on the right.
Questions
[edit | edit source]- What flowcharting symbol is used to indicate a condition?
- How are compound conditions structured?
- What is the difference between "and" and "or"?
- What are truth tables?
- What do "and" and "or" truth tables include?
Activity
[edit | edit source]With a partner, perform the following:
- Using a visual programming language, create a program matching the flowchart on the right.
- Save the program.
- Test the program to verify that it works correctly.
- Trade places, so that both partners have an opportunity to "drive" the visual programming environment.
- Change the environment to use a slow run speed and/or step through the program one shape at a time.
- Working together, identify the compound conditions that would be used to either convert Fahrenheit temperature to Celsius or convert Celsius temperature to Fahrenheit, depending on user choice.
Applications
[edit | edit source]- Identify specific steps which must be followed when creating a program using compound conditions.
- Discuss your activity experience with your classmates. What surprised you? What have you learned that you can apply to your own school or work environment?
