Materials Science and Engineering/Derivations/Models of Micro and Nanoscale Processing
Appearance
First-Order Planar Growth Kinetics - The Linear Parabolic Model
[edit | edit source]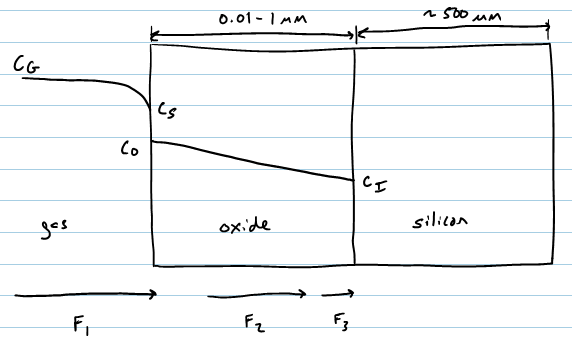
Oxide grows by indiffusion
Chemical Reaction
[edit | edit source]
Three Fluxes
[edit | edit source]Transport of the oxidant to the oxide surface
[edit | edit source]
- : flux in molecules
- : concentration difference between gas flow and surface
- : mass transfer coefficient
Equilibrium concentration of a gas species
[edit | edit source]The equilibrium concentration of a gas species dissolved in a solid is proportional to partial pressure of species at the surface.
- :oxidant concentration in oxide that would be in equilibrium with
- : bulk gas pressure
From the ideal gas law:
Diffusion of oxidant through oxide to interface
[edit | edit source]In steady state,
- and : concetration at two interfaces
- : oxide thickness
Oxygen and water seem to diffuse in different manners, though the effective diffusivities are of the same order.
Reaction at the Si/SiO2 interface
[edit | edit source]
- : interface reaction rate constant
Equating three fluxes
[edit | edit source]With
The approximations are based on the observation that is very large. Gas absorption occurs rapidly compared with chemistry at interface.
Limiting cases
[edit | edit source]Reaction rate controlled - thin oxides
[edit | edit source]
Oxidant supplied to interface fast compared to that required to sustain the interface reaction

Diffusion controlled - thick oxides
[edit | edit source]
- : number of oxidant molecules incorporated
Integrate from initial oxide thickness to final thickness :
Limiting forms of the linear parabolic growth law
[edit | edit source]











































