General Classification
- See also User:Atcovi/Science/Biology Terms
- See also User:Atcovi/Science/Introduction to Science, Experimental Design, and Graphing
Introduction to Classification
[edit | edit source]- For 3.5 billion years, life on Earth has been constantly changing. Natural Selection and other processes have led to diversity of organisms.
- Why classify organisms? So that we have an organized system to help us study about the diversity of life.
- What is classification? Grouping of organisms based upon their similarities.
Taxonomy
[edit | edit source]
- Taxonomy is the branch of science that groups and names living organisms based on their relationships inferred by shared characters.
- Aristotle was the first scientist who attempted to classify organisms. He subdivided plants into three groups: shrubs, herbs and trees. He subdivided animals into their habitat: air, water and land.
- The problem with Aristotle's system was that it wasn't accurate enough... for example: It placed organisms that all fly in the same category: Bees, birds, and bats are related to each other!
Linneaus' System & Modern Evolutionary Classification
[edit | edit source]
- The foundation of today's modern classification actually goes back to Swedish botanist Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778).
- Linneaus classified organisms according to their physical and structural similarities.
- Linneaus used a two word naming system called Binomial Nomenclature to identify species. The first name is the genus and the second name is a descriptive word called the species.
- What is the correct way to write a scientific name? Give an example: Genus species
- (Write "Genus" (capitalize), then species--either italicized/underlined).
- What language is used for scientific names? Latin Why?
- Latin is a dead language, so the language can't be changed.
- Many organisms have share common names/nicknames, so its good for them to have different scientific names.
Classification
[edit | edit source]How Living Things are Classified
[edit | edit source]
Organisms are ranked or grouped in groups, from very broad to very specific. These groups are known as taxas.
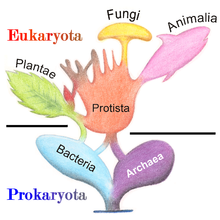
- Kingdoms
- Archaebacteria
- Eubacteria
- Protista
- Fungi
- Plantae
- Animalia
Each organism is subdivided into 7 categories called taxas. List each taxa below from most amount of organisms to least amount of organisms:
- Taxas
- Domain
- Kingdom
- Phylum
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
- What is the sentence to help you out with thee 7 taxas? Did King Phillip Come Over From German Soil?
- Most organisms? Domain
- Least organisms? Species
- Which grouping is a subdivision of the phylum? Class
- A group of similar orders is called a what? Class
- A Genus is a group of similar species.
- Kingdom Plantae may not use the term, phylum, for a group of similar classes, instead it might use the taxa term, divisions.
- Species: Group of organisms in a population that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
The Three-Domain System/Six-Kingdom System
[edit | edit source]Based upon recent evidence, the five-kingdom system of classification has now expanded to six kingdoms. The kingdoms, archaebacteria and eubacteria, used to be one kingdom called the Monera Kingdom.
- Molecular Analyses have given rise to a new taxonomic category that is now recognized by many scientists.
- List the three domains and which kingdoms belong to each domain below
-Domain Bacteria
--Kingdom Eubacteria
-Domain Archaea
--Kingdom Archaebacteria
-Domain Eukarya
--Kingdom Protista
--Kingdom Fungi
--Kingdom Plantae
--Kingdom Animalia
Diagrams and Keys used to Classify Organisms
[edit | edit source]Dichotomous Key- Series of paired statements that describe physical characteristic of different organisms.
Cladogram- Diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms.
