Fundamentals of Neuroscience/Neural Cells
Appearance
(Redirected from Fundamentals of Neuroscience/The Nervous System)
| Type classification: this is a lesson resource. |
| Subject Classification: this is a neuroscience resource. |
Goals
[edit | edit source]- To learn the functions and major subtypes of neurons and neuroglia.
- To learn the basic parts of a neuron and their functions.
- To understand how neural cells differ from most other cell types.
Structure of Neurons
[edit | edit source]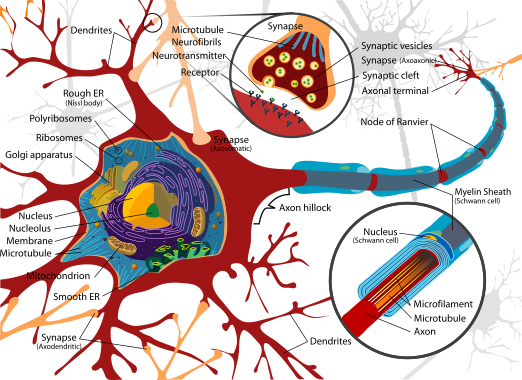
- Neurons are the basic functional unit of the nervous system, and are divided into three main parts:
- Neurons themselves can be divided into several main types, depending on their functions:
- Afferent neurons: sensory neurons that receive and transmit stimuli
- Efferent neurons: motor neurons that produce a response in targeted cells
Neurons and Neuroglia
[edit | edit source]- There are two types of neural cells, neurons and neuroglia.
- Neurons, approximately 86 billion of which are contained in a human brain, transmit electrical and chemical signals to one another.
- Neuroglia, also known as glia, support and protect neurons. Some of their functions include:
- Nourishing neurons
- Maintaining neural homeostasis
- Forming myelin, which speeds up signal transmission.
- Reacting to damage
- There are two major types of glia, microglia and macroglia.
- Microglia: macrophages capable of phagocytosis, which protect and repair the neurons of the central nervous system. They are capable of moving within the brain, and will multiply and expand when the brain is damaged.
- Macroglia: These are larger than microglia and include three major subtypes.
- Astrocytes: provide the appropriate ionic milieu for neurons to be able to generate action potentials
- Oligodendrocytes: form and maintain the myelin that surrounds neurons in the Central Nervous System
- Schwann Cells: form and maintain the myelin that surrounds neurons in the Peripheral Nervous System
- Ependymal cells: produce and regulate CSF
Exercises
[edit | edit source]- Identify the type(s) or subtype(s) of neural cell performing the following functions:
- Repairing damaged neurons
- Forming myelin in the spinal cord
- Transmitting chemical signals
ANSWERS
- Microglia
- Oligodendrocytes
- Neurons
