Quizbank/Electricity and Magnetism (calculus based)/QB153099154229
QB153099154229
QB:Ch 5:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1)
is an integral that calculates the magnitude of the electric field at a distance fromthe center of a thin circular disk as measured along a line normal to the plane of the disk. The disk's radius is and the surface charge density is . Evaluate at .
- a) 1.022E+00 V/m2
- b) 1.125E+00 V/m2
- c) 1.237E+00 V/m2
- d) 1.361E+00 V/m2
- e) 1.497E+00 V/m2

- a) 4.766E+01 degrees
- b) 5.243E+01 degrees
- c) 5.767E+01 degrees
- d) 6.343E+01 degrees
- e) 6.978E+01 degrees

- a) 4.171E-14 N
- b) 4.588E-14 N
- c) 5.047E-14 N
- d) 5.551E-14 N
- e) 6.107E-14 N
KEY:QB:Ch 5:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1)
is an integral that calculates the magnitude of the electric field at a distance fromthe center of a thin circular disk as measured along a line normal to the plane of the disk. The disk's radius is and the surface charge density is . Evaluate at .
- +a) 1.022E+00 V/m2
- -b) 1.125E+00 V/m2
- -c) 1.237E+00 V/m2
- -d) 1.361E+00 V/m2
- -e) 1.497E+00 V/m2

- -a) 4.766E+01 degrees
- -b) 5.243E+01 degrees
- -c) 5.767E+01 degrees
- +d) 6.343E+01 degrees
- -e) 6.978E+01 degrees

- -a) 4.171E-14 N
- -b) 4.588E-14 N
- +c) 5.047E-14 N
- -d) 5.551E-14 N
- -e) 6.107E-14 N
QB:Ch 5:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1)
is an integral that calculates the magnitude of the electric field at a distance fromthe center of a thin circular disk as measured along a line normal to the plane of the disk. The disk's radius is and the surface charge density is . Evaluate at .
- a) 8.933E+00 V/m2
- b) 9.826E+00 V/m2
- c) 1.081E+01 V/m2
- d) 1.189E+01 V/m2
- e) 1.308E+01 V/m2

- a) 3.426E-15 N
- b) 3.768E-15 N
- c) 4.145E-15 N
- d) 4.560E-15 N
- e) 5.015E-15 N

- a) 5.243E+01 degrees
- b) 5.767E+01 degrees
- c) 6.343E+01 degrees
- d) 6.978E+01 degrees
- e) 7.676E+01 degrees
KEY:QB:Ch 5:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1)
is an integral that calculates the magnitude of the electric field at a distance fromthe center of a thin circular disk as measured along a line normal to the plane of the disk. The disk's radius is and the surface charge density is . Evaluate at .
- -a) 8.933E+00 V/m2
- -b) 9.826E+00 V/m2
- +c) 1.081E+01 V/m2
- -d) 1.189E+01 V/m2
- -e) 1.308E+01 V/m2

- -a) 3.426E-15 N
- -b) 3.768E-15 N
- -c) 4.145E-15 N
- -d) 4.560E-15 N
- +e) 5.015E-15 N

- -a) 5.243E+01 degrees
- -b) 5.767E+01 degrees
- +c) 6.343E+01 degrees
- -d) 6.978E+01 degrees
- -e) 7.676E+01 degrees
QB:Ch 5:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1)
is an integral that calculates the magnitude of the electric field at a distance fromthe center of a thin circular disk as measured along a line normal to the plane of the disk. The disk's radius is and the surface charge density is . Evaluate at .
- a) 3.722E-01 V/m2
- b) 4.094E-01 V/m2
- c) 4.504E-01 V/m2
- d) 4.954E-01 V/m2
- e) 5.450E-01 V/m2

- a) 5.243E-14 N
- b) 5.768E-14 N
- c) 6.344E-14 N
- d) 6.979E-14 N
- e) 7.677E-14 N

- a) 5.272E+01 degrees
- b) 5.799E+01 degrees
- c) 6.379E+01 degrees
- d) 7.017E+01 degrees
- e) 7.719E+01 degrees
KEY:QB:Ch 5:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1)
is an integral that calculates the magnitude of the electric field at a distance fromthe center of a thin circular disk as measured along a line normal to the plane of the disk. The disk's radius is and the surface charge density is . Evaluate at .
- -a) 3.722E-01 V/m2
- -b) 4.094E-01 V/m2
- -c) 4.504E-01 V/m2
- +d) 4.954E-01 V/m2
- -e) 5.450E-01 V/m2

- -a) 5.243E-14 N
- +b) 5.768E-14 N
- -c) 6.344E-14 N
- -d) 6.979E-14 N
- -e) 7.677E-14 N

- -a) 5.272E+01 degrees
- +b) 5.799E+01 degrees
- -c) 6.379E+01 degrees
- -d) 7.017E+01 degrees
- -e) 7.719E+01 degrees
QB:Ch 6:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- a) 5.989E+01 N·m2/C
- b) 6.588E+01 N·m2/C
- c) 7.247E+01 N·m2/C
- d) 7.971E+01 N·m2/C
- e) 8.769E+01 N·m2/C

- a) 5.385E+01 N·m2/C
- b) 5.923E+01 N·m2/C
- c) 6.516E+01 N·m2/C
- d) 7.167E+01 N·m2/C
- e) 7.884E+01 N·m2/C
3) What is the magnetude (absolute value) of the electric flux through a rectangle that occupies the z=0 plane with corners at (x,y)= (x=0, y=0), (x=6, y=0), (x=0, y=6), and (x=6, y=6), where x and y are measured in meters. The electric field is,
- a) 4.820E+03 V·m
- b) 5.302E+03 V·m
- c) 5.832E+03 V·m
- d) 6.415E+03 V·m
- e) 7.057E+03 V·m
KEY:QB:Ch 6:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- -a) 5.989E+01 N·m2/C
- -b) 6.588E+01 N·m2/C
- -c) 7.247E+01 N·m2/C
- +d) 7.971E+01 N·m2/C
- -e) 8.769E+01 N·m2/C

- +a) 5.385E+01 N·m2/C
- -b) 5.923E+01 N·m2/C
- -c) 6.516E+01 N·m2/C
- -d) 7.167E+01 N·m2/C
- -e) 7.884E+01 N·m2/C
3) What is the magnetude (absolute value) of the electric flux through a rectangle that occupies the z=0 plane with corners at (x,y)= (x=0, y=0), (x=6, y=0), (x=0, y=6), and (x=6, y=6), where x and y are measured in meters. The electric field is,
- -a) 4.820E+03 V·m
- -b) 5.302E+03 V·m
- +c) 5.832E+03 V·m
- -d) 6.415E+03 V·m
- -e) 7.057E+03 V·m
QB:Ch 6:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- a) 2.756E+01 N·m2/C
- b) 3.032E+01 N·m2/C
- c) 3.335E+01 N·m2/C
- d) 3.668E+01 N·m2/C
- e) 4.035E+01 N·m2/C
2) What is the magnetude (absolute value) of the electric flux through a rectangle that occupies the z=0 plane with corners at (x,y)= (x=0, y=0), (x=5, y=0), (x=0, y=7), and (x=5, y=7), where x and y are measured in meters. The electric field is,
- a) 4.286E+03 V·m
- b) 4.714E+03 V·m
- c) 5.186E+03 V·m
- d) 5.704E+03 V·m
- e) 6.275E+03 V·m

- a) 3.695E+01 N·m2/C
- b) 4.065E+01 N·m2/C
- c) 4.472E+01 N·m2/C
- d) 4.919E+01 N·m2/C
- e) 5.411E+01 N·m2/C
KEY:QB:Ch 6:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- -a) 2.756E+01 N·m2/C
- -b) 3.032E+01 N·m2/C
- -c) 3.335E+01 N·m2/C
- -d) 3.668E+01 N·m2/C
- +e) 4.035E+01 N·m2/C
2) What is the magnetude (absolute value) of the electric flux through a rectangle that occupies the z=0 plane with corners at (x,y)= (x=0, y=0), (x=5, y=0), (x=0, y=7), and (x=5, y=7), where x and y are measured in meters. The electric field is,
- -a) 4.286E+03 V·m
- -b) 4.714E+03 V·m
- +c) 5.186E+03 V·m
- -d) 5.704E+03 V·m
- -e) 6.275E+03 V·m

- -a) 3.695E+01 N·m2/C
- -b) 4.065E+01 N·m2/C
- -c) 4.472E+01 N·m2/C
- -d) 4.919E+01 N·m2/C
- +e) 5.411E+01 N·m2/C
QB:Ch 6:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- a) 9.823E+00 N·m2/C
- b) 1.080E+01 N·m2/C
- c) 1.189E+01 N·m2/C
- d) 1.307E+01 N·m2/C
- e) 1.438E+01 N·m2/C

- a) 1.698E+01 N·m2/C
- b) 1.868E+01 N·m2/C
- c) 2.055E+01 N·m2/C
- d) 2.260E+01 N·m2/C
- e) 2.486E+01 N·m2/C
3) What is the magnetude (absolute value) of the electric flux through a rectangle that occupies the z=0 plane with corners at (x,y)= (x=0, y=0), (x=7, y=0), (x=0, y=6), and (x=7, y=6), where x and y are measured in meters. The electric field is,
- a) 3.337E+03 V·m
- b) 3.670E+03 V·m
- c) 4.037E+03 V·m
- d) 4.441E+03 V·m
- e) 4.885E+03 V·m
KEY:QB:Ch 6:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- -a) 9.823E+00 N·m2/C
- +b) 1.080E+01 N·m2/C
- -c) 1.189E+01 N·m2/C
- -d) 1.307E+01 N·m2/C
- -e) 1.438E+01 N·m2/C

- -a) 1.698E+01 N·m2/C
- -b) 1.868E+01 N·m2/C
- -c) 2.055E+01 N·m2/C
- -d) 2.260E+01 N·m2/C
- +e) 2.486E+01 N·m2/C
3) What is the magnetude (absolute value) of the electric flux through a rectangle that occupies the z=0 plane with corners at (x,y)= (x=0, y=0), (x=7, y=0), (x=0, y=6), and (x=7, y=6), where x and y are measured in meters. The electric field is,
- +a) 3.337E+03 V·m
- -b) 3.670E+03 V·m
- -c) 4.037E+03 V·m
- -d) 4.441E+03 V·m
- -e) 4.885E+03 V·m
QB:Ch 7:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A 7 C charge is separated from a 15 C charge by distance of 14 cm. What is the work done by increasing this separation to 20 cm?
- a) 1.519E-06 J
- b) 1.671E-06 J
- c) 1.838E-06 J
- d) 2.022E-06 J
- e) 2.224E-06 J
2) Calculate the final speed of a free electron accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 45 V.
- a) 3.617E+06 m/s
- b) 3.979E+06 m/s
- c) 4.376E+06 m/s
- d) 4.814E+06 m/s
- e) 5.296E+06 m/s
3) If a 16 nC charge is situated at the origin, the equipotential surface for V(x,y,z)=19 V is x2 + y2 + z2 = R2, where R=
- a) 5.169E+00 m
- b) 5.686E+00 m
- c) 6.255E+00 m
- d) 6.880E+00 m
- e) 7.568E+00 m
KEY:QB:Ch 7:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A 7 C charge is separated from a 15 C charge by distance of 14 cm. What is the work done by increasing this separation to 20 cm?
- -a) 1.519E-06 J
- -b) 1.671E-06 J
- -c) 1.838E-06 J
- +d) 2.022E-06 J
- -e) 2.224E-06 J
2) Calculate the final speed of a free electron accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 45 V.
- -a) 3.617E+06 m/s
- +b) 3.979E+06 m/s
- -c) 4.376E+06 m/s
- -d) 4.814E+06 m/s
- -e) 5.296E+06 m/s
3) If a 16 nC charge is situated at the origin, the equipotential surface for V(x,y,z)=19 V is x2 + y2 + z2 = R2, where R=
- -a) 5.169E+00 m
- -b) 5.686E+00 m
- -c) 6.255E+00 m
- -d) 6.880E+00 m
- +e) 7.568E+00 m
QB:Ch 7:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) If a 24 nC charge is situated at the origin, the equipotential surface for V(x,y,z)=97 V is x2 + y2 + z2 = R2, where R=
- a) 1.838E+00 m
- b) 2.022E+00 m
- c) 2.224E+00 m
- d) 2.446E+00 m
- e) 2.691E+00 m
2) Calculate the final speed of a free electron accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 30 V.
- a) 2.441E+06 m/s
- b) 2.685E+06 m/s
- c) 2.953E+06 m/s
- d) 3.249E+06 m/s
- e) 3.573E+06 m/s
3) A 6 C charge is separated from a 13 C charge by distance of 8 cm. What is the work done by increasing this separation to 16 cm?
- a) 3.292E-06 J
- b) 3.621E-06 J
- c) 3.983E-06 J
- d) 4.381E-06 J
- e) 4.820E-06 J
KEY:QB:Ch 7:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) If a 24 nC charge is situated at the origin, the equipotential surface for V(x,y,z)=97 V is x2 + y2 + z2 = R2, where R=
- -a) 1.838E+00 m
- -b) 2.022E+00 m
- +c) 2.224E+00 m
- -d) 2.446E+00 m
- -e) 2.691E+00 m
2) Calculate the final speed of a free electron accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 30 V.
- -a) 2.441E+06 m/s
- -b) 2.685E+06 m/s
- -c) 2.953E+06 m/s
- +d) 3.249E+06 m/s
- -e) 3.573E+06 m/s
3) A 6 C charge is separated from a 13 C charge by distance of 8 cm. What is the work done by increasing this separation to 16 cm?
- -a) 3.292E-06 J
- -b) 3.621E-06 J
- -c) 3.983E-06 J
- +d) 4.381E-06 J
- -e) 4.820E-06 J
QB:Ch 7:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) Calculate the final speed of a free electron accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 45 V.
- a) 3.617E+06 m/s
- b) 3.979E+06 m/s
- c) 4.376E+06 m/s
- d) 4.814E+06 m/s
- e) 5.296E+06 m/s
2) A 6 C charge is separated from a 13 C charge by distance of 8 cm. What is the work done by increasing this separation to 16 cm?
- a) 3.292E-06 J
- b) 3.621E-06 J
- c) 3.983E-06 J
- d) 4.381E-06 J
- e) 4.820E-06 J
3) If a 16 nC charge is situated at the origin, the equipotential surface for V(x,y,z)=19 V is x2 + y2 + z2 = R2, where R=
- a) 5.169E+00 m
- b) 5.686E+00 m
- c) 6.255E+00 m
- d) 6.880E+00 m
- e) 7.568E+00 m
KEY:QB:Ch 7:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) Calculate the final speed of a free electron accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 45 V.
- -a) 3.617E+06 m/s
- +b) 3.979E+06 m/s
- -c) 4.376E+06 m/s
- -d) 4.814E+06 m/s
- -e) 5.296E+06 m/s
2) A 6 C charge is separated from a 13 C charge by distance of 8 cm. What is the work done by increasing this separation to 16 cm?
- -a) 3.292E-06 J
- -b) 3.621E-06 J
- -c) 3.983E-06 J
- +d) 4.381E-06 J
- -e) 4.820E-06 J
3) If a 16 nC charge is situated at the origin, the equipotential surface for V(x,y,z)=19 V is x2 + y2 + z2 = R2, where R=
- -a) 5.169E+00 m
- -b) 5.686E+00 m
- -c) 6.255E+00 m
- -d) 6.880E+00 m
- +e) 7.568E+00 m
QB:Ch 8:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) An empty parallel-plate capacitor with metal plates has an area of 2.45 m2, separated by 1.18 mm. How much charge does it store if the voltage is 4.060E+03 V?
- a) 5.608E+01 μC
- b) 6.168E+01 μC
- c) 6.785E+01 μC
- d) 7.464E+01 μC
- e) 8.210E+01 μC

- a) 6.750E+00 μJ
- b) 7.425E+00 μJ
- c) 8.168E+00 μJ
- d) 8.984E+00 μJ
- e) 9.883E+00 μJ

- a) 6.298E+01 μC
- b) 6.928E+01 μC
- c) 7.621E+01 μC
- d) 8.383E+01 μC
- e) 9.221E+01 μC
KEY:QB:Ch 8:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) An empty parallel-plate capacitor with metal plates has an area of 2.45 m2, separated by 1.18 mm. How much charge does it store if the voltage is 4.060E+03 V?
- -a) 5.608E+01 μC
- -b) 6.168E+01 μC
- -c) 6.785E+01 μC
- +d) 7.464E+01 μC
- -e) 8.210E+01 μC

- -a) 6.750E+00 μJ
- -b) 7.425E+00 μJ
- +c) 8.168E+00 μJ
- -d) 8.984E+00 μJ
- -e) 9.883E+00 μJ

- +a) 6.298E+01 μC
- -b) 6.928E+01 μC
- -c) 7.621E+01 μC
- -d) 8.383E+01 μC
- -e) 9.221E+01 μC
QB:Ch 8:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- a) 2.515E+01 μC
- b) 2.766E+01 μC
- c) 3.043E+01 μC
- d) 3.347E+01 μC
- e) 3.682E+01 μC
2) An empty parallel-plate capacitor with metal plates has an area of 2.42 m2, separated by 1.33 mm. How much charge does it store if the voltage is 1.130E+03 V?
- a) 1.368E+01 μC
- b) 1.505E+01 μC
- c) 1.655E+01 μC
- d) 1.820E+01 μC
- e) 2.003E+01 μC

- a) 6.750E+00 μJ
- b) 7.425E+00 μJ
- c) 8.168E+00 μJ
- d) 8.984E+00 μJ
- e) 9.883E+00 μJ
KEY:QB:Ch 8:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- -a) 2.515E+01 μC
- -b) 2.766E+01 μC
- -c) 3.043E+01 μC
- +d) 3.347E+01 μC
- -e) 3.682E+01 μC
2) An empty parallel-plate capacitor with metal plates has an area of 2.42 m2, separated by 1.33 mm. How much charge does it store if the voltage is 1.130E+03 V?
- -a) 1.368E+01 μC
- -b) 1.505E+01 μC
- -c) 1.655E+01 μC
- +d) 1.820E+01 μC
- -e) 2.003E+01 μC

- -a) 6.750E+00 μJ
- -b) 7.425E+00 μJ
- +c) 8.168E+00 μJ
- -d) 8.984E+00 μJ
- -e) 9.883E+00 μJ
QB:Ch 8:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- a) 5.474E+01 μC
- b) 6.022E+01 μC
- c) 6.624E+01 μC
- d) 7.287E+01 μC
- e) 8.015E+01 μC

- a) 6.890E+00 μJ
- b) 7.579E+00 μJ
- c) 8.337E+00 μJ
- d) 9.171E+00 μJ
- e) 1.009E+01 μJ
3) An empty parallel-plate capacitor with metal plates has an area of 1.94 m2, separated by 1.27 mm. How much charge does it store if the voltage is 8.780E+03 V?
- a) 1.080E+02 μC
- b) 1.188E+02 μC
- c) 1.306E+02 μC
- d) 1.437E+02 μC
- e) 1.581E+02 μC
KEY:QB:Ch 8:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- -a) 5.474E+01 μC
- -b) 6.022E+01 μC
- -c) 6.624E+01 μC
- +d) 7.287E+01 μC
- -e) 8.015E+01 μC

- -a) 6.890E+00 μJ
- -b) 7.579E+00 μJ
- -c) 8.337E+00 μJ
- -d) 9.171E+00 μJ
- +e) 1.009E+01 μJ
3) An empty parallel-plate capacitor with metal plates has an area of 1.94 m2, separated by 1.27 mm. How much charge does it store if the voltage is 8.780E+03 V?
- -a) 1.080E+02 μC
- +b) 1.188E+02 μC
- -c) 1.306E+02 μC
- -d) 1.437E+02 μC
- -e) 1.581E+02 μC
QB:Ch 9:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) Calculate the drift speed of electrons in a copper wire with a diameter of 4.38 mm carrying a 5.79 A current, given that there is one free electron per copper atom. The density of copper is 8.80 x 103kg/m3 and the atomic mass of copper is 63.54 g/mol. Avagadro's number is 6.02 x 1023atoms/mol.
- a) 2.615E-05 m/s
- b) 2.876E-05 m/s
- c) 3.164E-05 m/s
- d) 3.480E-05 m/s
- e) 3.828E-05 m/s
2) What is the average current involved when a truck battery sets in motion 631 C of charge in 3.8 s while starting an engine?
- a) 1.661E+02 A
- b) 1.827E+02 A
- c) 2.009E+02 A
- d) 2.210E+02 A
- e) 2.431E+02 A
3) Imagine a substance could be made into a very hot filament. Suppose the resitance is 6.06 Ω at a temperature of 80°C and that the temperature coefficient of expansion is 4.290E-03 (°C)−1). What is the resistance at a temperature of 330 °C?
- a) 1.196E+01 Ω
- b) 1.256E+01 Ω
- c) 1.319E+01 Ω
- d) 1.385E+01 Ω
- e) 1.454E+01 Ω
KEY:QB:Ch 9:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) Calculate the drift speed of electrons in a copper wire with a diameter of 4.38 mm carrying a 5.79 A current, given that there is one free electron per copper atom. The density of copper is 8.80 x 103kg/m3 and the atomic mass of copper is 63.54 g/mol. Avagadro's number is 6.02 x 1023atoms/mol.
- -a) 2.615E-05 m/s
- +b) 2.876E-05 m/s
- -c) 3.164E-05 m/s
- -d) 3.480E-05 m/s
- -e) 3.828E-05 m/s
2) What is the average current involved when a truck battery sets in motion 631 C of charge in 3.8 s while starting an engine?
- +a) 1.661E+02 A
- -b) 1.827E+02 A
- -c) 2.009E+02 A
- -d) 2.210E+02 A
- -e) 2.431E+02 A
3) Imagine a substance could be made into a very hot filament. Suppose the resitance is 6.06 Ω at a temperature of 80°C and that the temperature coefficient of expansion is 4.290E-03 (°C)−1). What is the resistance at a temperature of 330 °C?
- -a) 1.196E+01 Ω
- +b) 1.256E+01 Ω
- -c) 1.319E+01 Ω
- -d) 1.385E+01 Ω
- -e) 1.454E+01 Ω
QB:Ch 9:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) What is the average current involved when a truck battery sets in motion 760 C of charge in 5.35 s while starting an engine?
- a) 1.291E+02 A
- b) 1.421E+02 A
- c) 1.563E+02 A
- d) 1.719E+02 A
- e) 1.891E+02 A
2) Imagine a substance could be made into a very hot filament. Suppose the resitance is 2.61 Ω at a temperature of 92°C and that the temperature coefficient of expansion is 4.260E-03 (°C)−1). What is the resistance at a temperature of 422 °C?
- a) 6.279E+00 Ω
- b) 6.593E+00 Ω
- c) 6.923E+00 Ω
- d) 7.269E+00 Ω
- e) 7.632E+00 Ω
3) Calculate the drift speed of electrons in a copper wire with a diameter of 5.33 mm carrying a 5.1 A current, given that there is one free electron per copper atom. The density of copper is 8.80 x 103kg/m3 and the atomic mass of copper is 63.54 g/mol. Avagadro's number is 6.02 x 1023atoms/mol.
- a) 1.711E-05 m/s
- b) 1.882E-05 m/s
- c) 2.070E-05 m/s
- d) 2.277E-05 m/s
- e) 2.505E-05 m/s
KEY:QB:Ch 9:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) What is the average current involved when a truck battery sets in motion 760 C of charge in 5.35 s while starting an engine?
- -a) 1.291E+02 A
- +b) 1.421E+02 A
- -c) 1.563E+02 A
- -d) 1.719E+02 A
- -e) 1.891E+02 A
2) Imagine a substance could be made into a very hot filament. Suppose the resitance is 2.61 Ω at a temperature of 92°C and that the temperature coefficient of expansion is 4.260E-03 (°C)−1). What is the resistance at a temperature of 422 °C?
- +a) 6.279E+00 Ω
- -b) 6.593E+00 Ω
- -c) 6.923E+00 Ω
- -d) 7.269E+00 Ω
- -e) 7.632E+00 Ω
3) Calculate the drift speed of electrons in a copper wire with a diameter of 5.33 mm carrying a 5.1 A current, given that there is one free electron per copper atom. The density of copper is 8.80 x 103kg/m3 and the atomic mass of copper is 63.54 g/mol. Avagadro's number is 6.02 x 1023atoms/mol.
- +a) 1.711E-05 m/s
- -b) 1.882E-05 m/s
- -c) 2.070E-05 m/s
- -d) 2.277E-05 m/s
- -e) 2.505E-05 m/s
QB:Ch 9:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) What is the average current involved when a truck battery sets in motion 669 C of charge in 4.3 s while starting an engine?
- a) 1.063E+02 A
- b) 1.169E+02 A
- c) 1.286E+02 A
- d) 1.414E+02 A
- e) 1.556E+02 A
2) Imagine a substance could be made into a very hot filament. Suppose the resitance is 3.64 Ω at a temperature of 82°C and that the temperature coefficient of expansion is 4.530E-03 (°C)−1). What is the resistance at a temperature of 390 °C?
- a) 7.532E+00 Ω
- b) 7.908E+00 Ω
- c) 8.303E+00 Ω
- d) 8.719E+00 Ω
- e) 9.155E+00 Ω
3) Calculate the drift speed of electrons in a copper wire with a diameter of 5.33 mm carrying a 5.1 A current, given that there is one free electron per copper atom. The density of copper is 8.80 x 103kg/m3 and the atomic mass of copper is 63.54 g/mol. Avagadro's number is 6.02 x 1023atoms/mol.
- a) 1.711E-05 m/s
- b) 1.882E-05 m/s
- c) 2.070E-05 m/s
- d) 2.277E-05 m/s
- e) 2.505E-05 m/s
KEY:QB:Ch 9:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) What is the average current involved when a truck battery sets in motion 669 C of charge in 4.3 s while starting an engine?
- -a) 1.063E+02 A
- -b) 1.169E+02 A
- -c) 1.286E+02 A
- -d) 1.414E+02 A
- +e) 1.556E+02 A
2) Imagine a substance could be made into a very hot filament. Suppose the resitance is 3.64 Ω at a temperature of 82°C and that the temperature coefficient of expansion is 4.530E-03 (°C)−1). What is the resistance at a temperature of 390 °C?
- -a) 7.532E+00 Ω
- -b) 7.908E+00 Ω
- -c) 8.303E+00 Ω
- +d) 8.719E+00 Ω
- -e) 9.155E+00 Ω
3) Calculate the drift speed of electrons in a copper wire with a diameter of 5.33 mm carrying a 5.1 A current, given that there is one free electron per copper atom. The density of copper is 8.80 x 103kg/m3 and the atomic mass of copper is 63.54 g/mol. Avagadro's number is 6.02 x 1023atoms/mol.
- +a) 1.711E-05 m/s
- -b) 1.882E-05 m/s
- -c) 2.070E-05 m/s
- -d) 2.277E-05 m/s
- -e) 2.505E-05 m/s
QB:Ch 10:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- a) 1.701E-01 A
- b) 1.871E-01 A
- c) 2.058E-01 A
- d) 2.264E-01 A
- e) 2.490E-01 A

- a) 1.096E+01 W
- b) 1.206E+01 W
- c) 1.326E+01 W
- d) 1.459E+01 W
- e) 1.605E+01 W

- a) 9.718E+00 s
- b) 1.069E+01 s
- c) 1.176E+01 s
- d) 1.293E+01 s
- e) 1.423E+01 s
KEY:QB:Ch 10:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- -a) 1.701E-01 A
- +b) 1.871E-01 A
- -c) 2.058E-01 A
- -d) 2.264E-01 A
- -e) 2.490E-01 A

- -a) 1.096E+01 W
- -b) 1.206E+01 W
- -c) 1.326E+01 W
- -d) 1.459E+01 W
- +e) 1.605E+01 W

- -a) 9.718E+00 s
- -b) 1.069E+01 s
- +c) 1.176E+01 s
- -d) 1.293E+01 s
- -e) 1.423E+01 s
QB:Ch 10:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- a) 9.024E+00 s
- b) 9.927E+00 s
- c) 1.092E+01 s
- d) 1.201E+01 s
- e) 1.321E+01 s

- a) 1.721E-01 A
- b) 1.893E-01 A
- c) 2.082E-01 A
- d) 2.291E-01 A
- e) 2.520E-01 A

- a) 7.827E+00 W
- b) 8.610E+00 W
- c) 9.470E+00 W
- d) 1.042E+01 W
- e) 1.146E+01 W
KEY:QB:Ch 10:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- -a) 9.024E+00 s
- -b) 9.927E+00 s
- -c) 1.092E+01 s
- +d) 1.201E+01 s
- -e) 1.321E+01 s

- +a) 1.721E-01 A
- -b) 1.893E-01 A
- -c) 2.082E-01 A
- -d) 2.291E-01 A
- -e) 2.520E-01 A

- -a) 7.827E+00 W
- +b) 8.610E+00 W
- -c) 9.470E+00 W
- -d) 1.042E+01 W
- -e) 1.146E+01 W
QB:Ch 10:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- a) 7.688E+00 s
- b) 8.457E+00 s
- c) 9.303E+00 s
- d) 1.023E+01 s
- e) 1.126E+01 s

- a) 7.123E+00 W
- b) 7.835E+00 W
- c) 8.618E+00 W
- d) 9.480E+00 W
- e) 1.043E+01 W

- a) 1.114E-01 A
- b) 1.225E-01 A
- c) 1.348E-01 A
- d) 1.483E-01 A
- e) 1.631E-01 A
KEY:QB:Ch 10:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- -a) 7.688E+00 s
- -b) 8.457E+00 s
- -c) 9.303E+00 s
- +d) 1.023E+01 s
- -e) 1.126E+01 s

- -a) 7.123E+00 W
- -b) 7.835E+00 W
- -c) 8.618E+00 W
- -d) 9.480E+00 W
- +e) 1.043E+01 W

- -a) 1.114E-01 A
- +b) 1.225E-01 A
- -c) 1.348E-01 A
- -d) 1.483E-01 A
- -e) 1.631E-01 A
QB:Ch 11:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- a) 8.660E-06 V
- b) 9.526E-06 V
- c) 1.048E-05 V
- d) 1.153E-05 V
- e) 1.268E-05 V
2) A circular current loop of radius 1.56 cm carries a current of 2.57 mA. What is the magnitude of the torque if the dipole is oriented at 38 ° to a uniform magnetic fied of 0.79 T?
- a) 7.898E-07 N m
- b) 8.688E-07 N m
- c) 9.557E-07 N m
- d) 1.051E-06 N m
- e) 1.156E-06 N m
3) A cyclotron used to accelerate alpha particlesm=6.64 x 10−27kg, q=3.2 x 10−19C) has a radius of 0.413 m and a magneticfield of 0.988 T. What is their maximum kinetic energy?
- a) 6.029E+00 MeV
- b) 6.631E+00 MeV
- c) 7.295E+00 MeV
- d) 8.024E+00 MeV
- e) 8.827E+00 MeV
KEY:QB:Ch 11:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- +a) 8.660E-06 V
- -b) 9.526E-06 V
- -c) 1.048E-05 V
- -d) 1.153E-05 V
- -e) 1.268E-05 V
2) A circular current loop of radius 1.56 cm carries a current of 2.57 mA. What is the magnitude of the torque if the dipole is oriented at 38 ° to a uniform magnetic fied of 0.79 T?
- -a) 7.898E-07 N m
- -b) 8.688E-07 N m
- +c) 9.557E-07 N m
- -d) 1.051E-06 N m
- -e) 1.156E-06 N m
3) A cyclotron used to accelerate alpha particlesm=6.64 x 10−27kg, q=3.2 x 10−19C) has a radius of 0.413 m and a magneticfield of 0.988 T. What is their maximum kinetic energy?
- -a) 6.029E+00 MeV
- -b) 6.631E+00 MeV
- -c) 7.295E+00 MeV
- +d) 8.024E+00 MeV
- -e) 8.827E+00 MeV
QB:Ch 11:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A cyclotron used to accelerate alpha particlesm=6.64 x 10−27kg, q=3.2 x 10−19C) has a radius of 0.388 m and a magneticfield of 1.19 T. What is their maximum kinetic energy?
- a) 8.491E+00 MeV
- b) 9.340E+00 MeV
- c) 1.027E+01 MeV
- d) 1.130E+01 MeV
- e) 1.243E+01 MeV
2) A circular current loop of radius 2.99 cm carries a current of 4.54 mA. What is the magnitude of the torque if the dipole is oriented at 34 ° to a uniform magnetic fied of 0.107 T?
- a) 7.629E-07 N m
- b) 8.392E-07 N m
- c) 9.232E-07 N m
- d) 1.015E-06 N m
- e) 1.117E-06 N m

- a) 7.153E-07 V
- b) 7.869E-07 V
- c) 8.655E-07 V
- d) 9.521E-07 V
- e) 1.047E-06 V
KEY:QB:Ch 11:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A cyclotron used to accelerate alpha particlesm=6.64 x 10−27kg, q=3.2 x 10−19C) has a radius of 0.388 m and a magneticfield of 1.19 T. What is their maximum kinetic energy?
- -a) 8.491E+00 MeV
- -b) 9.340E+00 MeV
- +c) 1.027E+01 MeV
- -d) 1.130E+01 MeV
- -e) 1.243E+01 MeV
2) A circular current loop of radius 2.99 cm carries a current of 4.54 mA. What is the magnitude of the torque if the dipole is oriented at 34 ° to a uniform magnetic fied of 0.107 T?
- +a) 7.629E-07 N m
- -b) 8.392E-07 N m
- -c) 9.232E-07 N m
- -d) 1.015E-06 N m
- -e) 1.117E-06 N m

- -a) 7.153E-07 V
- -b) 7.869E-07 V
- -c) 8.655E-07 V
- +d) 9.521E-07 V
- -e) 1.047E-06 V
QB:Ch 11:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A cyclotron used to accelerate alpha particlesm=6.64 x 10−27kg, q=3.2 x 10−19C) has a radius of 0.145 m and a magneticfield of 1.03 T. What is their maximum kinetic energy?
- a) 7.342E-01 MeV
- b) 8.076E-01 MeV
- c) 8.884E-01 MeV
- d) 9.772E-01 MeV
- e) 1.075E+00 MeV

- a) 1.322E-06 V
- b) 1.454E-06 V
- c) 1.600E-06 V
- d) 1.759E-06 V
- e) 1.935E-06 V
3) A circular current loop of radius 2.84 cm carries a current of 3.01 mA. What is the magnitude of the torque if the dipole is oriented at 63 ° to a uniform magnetic fied of 0.174 T?
- a) 1.075E-06 N m
- b) 1.182E-06 N m
- c) 1.301E-06 N m
- d) 1.431E-06 N m
- e) 1.574E-06 N m
KEY:QB:Ch 11:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A cyclotron used to accelerate alpha particlesm=6.64 x 10−27kg, q=3.2 x 10−19C) has a radius of 0.145 m and a magneticfield of 1.03 T. What is their maximum kinetic energy?
- -a) 7.342E-01 MeV
- -b) 8.076E-01 MeV
- -c) 8.884E-01 MeV
- -d) 9.772E-01 MeV
- +e) 1.075E+00 MeV

- -a) 1.322E-06 V
- +b) 1.454E-06 V
- -c) 1.600E-06 V
- -d) 1.759E-06 V
- -e) 1.935E-06 V
3) A circular current loop of radius 2.84 cm carries a current of 3.01 mA. What is the magnitude of the torque if the dipole is oriented at 63 ° to a uniform magnetic fied of 0.174 T?
- -a) 1.075E-06 N m
- +b) 1.182E-06 N m
- -c) 1.301E-06 N m
- -d) 1.431E-06 N m
- -e) 1.574E-06 N m
QB:Ch 12:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
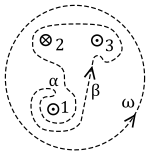
:
- a) 6.535E-03 T-m
- b) 7.188E-03 T-m
- c) 7.907E-03 T-m
- d) 8.697E-03 T-m
- e) 9.567E-03 T-m
2) Two parallel wires each carry a 2.12 mA current and are oriented in the z direction. The first wire is located in the x-y plane at (3.67 cm, 1.25 cm), while the other is located at (4.69 cm, 4.27 cm). What is the force per unit length between the wires?
- a) 2.119E-11 N/m
- b) 2.331E-11 N/m
- c) 2.564E-11 N/m
- d) 2.820E-11 N/m
- e) 3.102E-11 N/m

- a) By= 6.118E-05 T
- b) By= 6.730E-05 T
- c) By= 7.403E-05 T
- d) By= 8.144E-05 T
- e) By= 8.958E-05 T
KEY:QB:Ch 12:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

:
- +a) 6.535E-03 T-m
- -b) 7.188E-03 T-m
- -c) 7.907E-03 T-m
- -d) 8.697E-03 T-m
- -e) 9.567E-03 T-m
2) Two parallel wires each carry a 2.12 mA current and are oriented in the z direction. The first wire is located in the x-y plane at (3.67 cm, 1.25 cm), while the other is located at (4.69 cm, 4.27 cm). What is the force per unit length between the wires?
- -a) 2.119E-11 N/m
- -b) 2.331E-11 N/m
- -c) 2.564E-11 N/m
- +d) 2.820E-11 N/m
- -e) 3.102E-11 N/m

- -a) By= 6.118E-05 T
- -b) By= 6.730E-05 T
- -c) By= 7.403E-05 T
- -d) By= 8.144E-05 T
- +e) By= 8.958E-05 T
QB:Ch 12:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- a) By= 7.518E-05 T
- b) By= 8.270E-05 T
- c) By= 9.097E-05 T
- d) By= 1.001E-04 T
- e) By= 1.101E-04 T

:
- a) 3.770E-03 T-m
- b) 4.147E-03 T-m
- c) 4.562E-03 T-m
- d) 5.018E-03 T-m
- e) 5.520E-03 T-m
3) Two parallel wires each carry a 4.15 mA current and are oriented in the z direction. The first wire is located in the x-y plane at (3.19 cm, 1.78 cm), while the other is located at (3.73 cm, 4.12 cm). What is the force per unit length between the wires?
- a) 1.434E-10 N/m
- b) 1.578E-10 N/m
- c) 1.736E-10 N/m
- d) 1.909E-10 N/m
- e) 2.100E-10 N/m
KEY:QB:Ch 12:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- +a) By= 7.518E-05 T
- -b) By= 8.270E-05 T
- -c) By= 9.097E-05 T
- -d) By= 1.001E-04 T
- -e) By= 1.101E-04 T

:
- -a) 3.770E-03 T-m
- +b) 4.147E-03 T-m
- -c) 4.562E-03 T-m
- -d) 5.018E-03 T-m
- -e) 5.520E-03 T-m
3) Two parallel wires each carry a 4.15 mA current and are oriented in the z direction. The first wire is located in the x-y plane at (3.19 cm, 1.78 cm), while the other is located at (3.73 cm, 4.12 cm). What is the force per unit length between the wires?
- +a) 1.434E-10 N/m
- -b) 1.578E-10 N/m
- -c) 1.736E-10 N/m
- -d) 1.909E-10 N/m
- -e) 2.100E-10 N/m
QB:Ch 12:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

:
- a) 4.354E-03 T-m
- b) 4.789E-03 T-m
- c) 5.268E-03 T-m
- d) 5.795E-03 T-m
- e) 6.374E-03 T-m
2) Two parallel wires each carry a 9.59 mA current and are oriented in the z direction. The first wire is located in the x-y plane at (3.97 cm, 1.4 cm), while the other is located at (4.02 cm, 5.19 cm). What is the force per unit length between the wires?
- a) 4.412E-10 N/m
- b) 4.853E-10 N/m
- c) 5.338E-10 N/m
- d) 5.872E-10 N/m
- e) 6.459E-10 N/m

- a) By= 6.118E-05 T
- b) By= 6.730E-05 T
- c) By= 7.403E-05 T
- d) By= 8.144E-05 T
- e) By= 8.958E-05 T
KEY:QB:Ch 12:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

:
- -a) 4.354E-03 T-m
- +b) 4.789E-03 T-m
- -c) 5.268E-03 T-m
- -d) 5.795E-03 T-m
- -e) 6.374E-03 T-m
2) Two parallel wires each carry a 9.59 mA current and are oriented in the z direction. The first wire is located in the x-y plane at (3.97 cm, 1.4 cm), while the other is located at (4.02 cm, 5.19 cm). What is the force per unit length between the wires?
- -a) 4.412E-10 N/m
- +b) 4.853E-10 N/m
- -c) 5.338E-10 N/m
- -d) 5.872E-10 N/m
- -e) 6.459E-10 N/m

- -a) By= 6.118E-05 T
- -b) By= 6.730E-05 T
- -c) By= 7.403E-05 T
- -d) By= 8.144E-05 T
- +e) By= 8.958E-05 T
QB:Ch 13:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) The current through the windings of a solenoid with n= 1.830E+03 turns per meter is changing at a rate dI/dt=14 A/s. The solenoid is 87 cm long and has a cross-sectional diameter of 2.5 cm. A small coil consisting of N=30turns wraped in a circle of diameter 1.34 cm is placed in the middle of the solenoid such that the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the central axis of the solenoid. Assume that the infinite-solenoid approximation is valid inside the small coil. What is the emf induced in the coil?
- a) 1.126E-04 V
- b) 1.238E-04 V
- c) 1.362E-04 V
- d) 1.498E-04 V
- e) 1.648E-04 V
2) A time dependent magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of a circular coil with a radius of 0.594 m. The magnetic field is spatially uniform but decays in time according to , where 9.6 s. What is the current in the coil if the impedance of the coil is 6.65 Ω?
- a) 2.088E+00 A
- b) 2.297E+00 A
- c) 2.527E+00 A
- d) 2.779E+00 A
- e) 3.057E+00 A
3) A square coil has sides that are L= 0.568 m long and is tightly wound with N=482 turns of wire. The resistance of the coil is R=8.78 Ω. The coil is placed in a spacially uniform magnetic field that is directed perpendicular to the face of the coil and whose magnitude is increasing at a rate dB/dt=0.0544 T/s. If R represents the only impedance of the coil, what is the magnitude of the current circulting through it?
- a) 6.581E-01 A
- b) 7.239E-01 A
- c) 7.963E-01 A
- d) 8.759E-01 A
- e) 9.635E-01 A
KEY:QB:Ch 13:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) The current through the windings of a solenoid with n= 1.830E+03 turns per meter is changing at a rate dI/dt=14 A/s. The solenoid is 87 cm long and has a cross-sectional diameter of 2.5 cm. A small coil consisting of N=30turns wraped in a circle of diameter 1.34 cm is placed in the middle of the solenoid such that the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the central axis of the solenoid. Assume that the infinite-solenoid approximation is valid inside the small coil. What is the emf induced in the coil?
- -a) 1.126E-04 V
- -b) 1.238E-04 V
- +c) 1.362E-04 V
- -d) 1.498E-04 V
- -e) 1.648E-04 V
2) A time dependent magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of a circular coil with a radius of 0.594 m. The magnetic field is spatially uniform but decays in time according to , where 9.6 s. What is the current in the coil if the impedance of the coil is 6.65 Ω?
- -a) 2.088E+00 A
- +b) 2.297E+00 A
- -c) 2.527E+00 A
- -d) 2.779E+00 A
- -e) 3.057E+00 A
3) A square coil has sides that are L= 0.568 m long and is tightly wound with N=482 turns of wire. The resistance of the coil is R=8.78 Ω. The coil is placed in a spacially uniform magnetic field that is directed perpendicular to the face of the coil and whose magnitude is increasing at a rate dB/dt=0.0544 T/s. If R represents the only impedance of the coil, what is the magnitude of the current circulting through it?
- -a) 6.581E-01 A
- -b) 7.239E-01 A
- -c) 7.963E-01 A
- -d) 8.759E-01 A
- +e) 9.635E-01 A
QB:Ch 13:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A square coil has sides that are L= 0.861 m long and is tightly wound with N=538 turns of wire. The resistance of the coil is R=9.04 Ω. The coil is placed in a spacially uniform magnetic field that is directed perpendicular to the face of the coil and whose magnitude is increasing at a rate dB/dt=0.0433 T/s. If R represents the only impedance of the coil, what is the magnitude of the current circulting through it?
- a) 1.737E+00 A
- b) 1.910E+00 A
- c) 2.101E+00 A
- d) 2.311E+00 A
- e) 2.543E+00 A
2) The current through the windings of a solenoid with n= 2.040E+03 turns per meter is changing at a rate dI/dt=19 A/s. The solenoid is 76 cm long and has a cross-sectional diameter of 3.23 cm. A small coil consisting of N=25turns wraped in a circle of diameter 1.67 cm is placed in the middle of the solenoid such that the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the central axis of the solenoid. Assume that the infinite-solenoid approximation is valid inside the small coil. What is the emf induced in the coil?
- a) 2.204E-04 V
- b) 2.425E-04 V
- c) 2.667E-04 V
- d) 2.934E-04 V
- e) 3.227E-04 V
3) A time dependent magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of a circular coil with a radius of 0.8 m. The magnetic field is spatially uniform but decays in time according to , where 8.91 s. What is the current in the coil if the impedance of the coil is 61.7 Ω?
- a) 5.369E-01 A
- b) 5.906E-01 A
- c) 6.496E-01 A
- d) 7.146E-01 A
- e) 7.860E-01 A
KEY:QB:Ch 13:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A square coil has sides that are L= 0.861 m long and is tightly wound with N=538 turns of wire. The resistance of the coil is R=9.04 Ω. The coil is placed in a spacially uniform magnetic field that is directed perpendicular to the face of the coil and whose magnitude is increasing at a rate dB/dt=0.0433 T/s. If R represents the only impedance of the coil, what is the magnitude of the current circulting through it?
- -a) 1.737E+00 A
- +b) 1.910E+00 A
- -c) 2.101E+00 A
- -d) 2.311E+00 A
- -e) 2.543E+00 A
2) The current through the windings of a solenoid with n= 2.040E+03 turns per meter is changing at a rate dI/dt=19 A/s. The solenoid is 76 cm long and has a cross-sectional diameter of 3.23 cm. A small coil consisting of N=25turns wraped in a circle of diameter 1.67 cm is placed in the middle of the solenoid such that the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the central axis of the solenoid. Assume that the infinite-solenoid approximation is valid inside the small coil. What is the emf induced in the coil?
- -a) 2.204E-04 V
- -b) 2.425E-04 V
- +c) 2.667E-04 V
- -d) 2.934E-04 V
- -e) 3.227E-04 V
3) A time dependent magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of a circular coil with a radius of 0.8 m. The magnetic field is spatially uniform but decays in time according to , where 8.91 s. What is the current in the coil if the impedance of the coil is 61.7 Ω?
- -a) 5.369E-01 A
- -b) 5.906E-01 A
- -c) 6.496E-01 A
- -d) 7.146E-01 A
- +e) 7.860E-01 A
QB:Ch 13:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A time dependent magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of a circular coil with a radius of 0.655 m. The magnetic field is spatially uniform but decays in time according to , where 9.62 s. What is the current in the coil if the impedance of the coil is 48.9 Ω?
- a) 7.890E-01 A
- b) 8.679E-01 A
- c) 9.547E-01 A
- d) 1.050E+00 A
- e) 1.155E+00 A
2) The current through the windings of a solenoid with n= 2.960E+03 turns per meter is changing at a rate dI/dt=10 A/s. The solenoid is 85 cm long and has a cross-sectional diameter of 3.12 cm. A small coil consisting of N=32turns wraped in a circle of diameter 1.44 cm is placed in the middle of the solenoid such that the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the central axis of the solenoid. Assume that the infinite-solenoid approximation is valid inside the small coil. What is the emf induced in the coil?
- a) 1.602E-04 V
- b) 1.762E-04 V
- c) 1.939E-04 V
- d) 2.132E-04 V
- e) 2.346E-04 V
3) A square coil has sides that are L= 0.547 m long and is tightly wound with N=198 turns of wire. The resistance of the coil is R=4.62 Ω. The coil is placed in a spacially uniform magnetic field that is directed perpendicular to the face of the coil and whose magnitude is increasing at a rate dB/dt=0.0768 T/s. If R represents the only impedance of the coil, what is the magnitude of the current circulting through it?
- a) 8.953E-01 A
- b) 9.848E-01 A
- c) 1.083E+00 A
- d) 1.192E+00 A
- e) 1.311E+00 A
KEY:QB:Ch 13:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A time dependent magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of a circular coil with a radius of 0.655 m. The magnetic field is spatially uniform but decays in time according to , where 9.62 s. What is the current in the coil if the impedance of the coil is 48.9 Ω?
- +a) 7.890E-01 A
- -b) 8.679E-01 A
- -c) 9.547E-01 A
- -d) 1.050E+00 A
- -e) 1.155E+00 A
2) The current through the windings of a solenoid with n= 2.960E+03 turns per meter is changing at a rate dI/dt=10 A/s. The solenoid is 85 cm long and has a cross-sectional diameter of 3.12 cm. A small coil consisting of N=32turns wraped in a circle of diameter 1.44 cm is placed in the middle of the solenoid such that the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the central axis of the solenoid. Assume that the infinite-solenoid approximation is valid inside the small coil. What is the emf induced in the coil?
- -a) 1.602E-04 V
- -b) 1.762E-04 V
- +c) 1.939E-04 V
- -d) 2.132E-04 V
- -e) 2.346E-04 V
3) A square coil has sides that are L= 0.547 m long and is tightly wound with N=198 turns of wire. The resistance of the coil is R=4.62 Ω. The coil is placed in a spacially uniform magnetic field that is directed perpendicular to the face of the coil and whose magnitude is increasing at a rate dB/dt=0.0768 T/s. If R represents the only impedance of the coil, what is the magnitude of the current circulting through it?
- -a) 8.953E-01 A
- +b) 9.848E-01 A
- -c) 1.083E+00 A
- -d) 1.192E+00 A
- -e) 1.311E+00 A
QB:Ch 14:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) An induced emf of 4.02V is measured across a coil of 85 closely wound turns while the current throuth it increases uniformly from 0.0 to 3.53A in 0.438s. What is the self-inductance of the coil?
- a) 4.535E-01 H
- b) 4.988E-01 H
- c) 5.487E-01 H
- d) 6.035E-01 H
- e) 6.639E-01 H
2) A washer has an inner diameter of 2.74 cm and an outer diamter of 4.71 cm. The thickness is where is measured in cm, , and . What is the volume of the washer?
- a) 8.141E-01 cm3
- b) 8.955E-01 cm3
- c) 9.850E-01 cm3
- d) 1.084E+00 cm3
- e) 1.192E+00 cm3

- a) -1.700E+00 s
- b) -1.870E+00 s
- c) -2.057E+00 s
- d) -2.262E+00 s
- e) -2.489E+00 s
KEY:QB:Ch 14:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) An induced emf of 4.02V is measured across a coil of 85 closely wound turns while the current throuth it increases uniformly from 0.0 to 3.53A in 0.438s. What is the self-inductance of the coil?
- -a) 4.535E-01 H
- +b) 4.988E-01 H
- -c) 5.487E-01 H
- -d) 6.035E-01 H
- -e) 6.639E-01 H
2) A washer has an inner diameter of 2.74 cm and an outer diamter of 4.71 cm. The thickness is where is measured in cm, , and . What is the volume of the washer?
- +a) 8.141E-01 cm3
- -b) 8.955E-01 cm3
- -c) 9.850E-01 cm3
- -d) 1.084E+00 cm3
- -e) 1.192E+00 cm3

- -a) -1.700E+00 s
- -b) -1.870E+00 s
- -c) -2.057E+00 s
- +d) -2.262E+00 s
- -e) -2.489E+00 s
QB:Ch 14:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- a) -2.476E+00 s
- b) -2.724E+00 s
- c) -2.996E+00 s
- d) -3.296E+00 s
- e) -3.625E+00 s
2) An induced emf of 6.75V is measured across a coil of 79 closely wound turns while the current throuth it increases uniformly from 0.0 to 7.76A in 0.115s. What is the self-inductance of the coil?
- a) 9.094E-02 H
- b) 1.000E-01 H
- c) 1.100E-01 H
- d) 1.210E-01 H
- e) 1.331E-01 H
3) A washer has an inner diameter of 2.12 cm and an outer diamter of 4.47 cm. The thickness is where is measured in cm, , and . What is the volume of the washer?
- a) 1.228E+00 cm3
- b) 1.351E+00 cm3
- c) 1.486E+00 cm3
- d) 1.634E+00 cm3
- e) 1.798E+00 cm3
KEY:QB:Ch 14:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- -a) -2.476E+00 s
- -b) -2.724E+00 s
- -c) -2.996E+00 s
- -d) -3.296E+00 s
- +e) -3.625E+00 s
2) An induced emf of 6.75V is measured across a coil of 79 closely wound turns while the current throuth it increases uniformly from 0.0 to 7.76A in 0.115s. What is the self-inductance of the coil?
- -a) 9.094E-02 H
- +b) 1.000E-01 H
- -c) 1.100E-01 H
- -d) 1.210E-01 H
- -e) 1.331E-01 H
3) A washer has an inner diameter of 2.12 cm and an outer diamter of 4.47 cm. The thickness is where is measured in cm, , and . What is the volume of the washer?
- -a) 1.228E+00 cm3
- -b) 1.351E+00 cm3
- -c) 1.486E+00 cm3
- +d) 1.634E+00 cm3
- -e) 1.798E+00 cm3
QB:Ch 14:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A washer has an inner diameter of 2.3 cm and an outer diamter of 4.44 cm. The thickness is where is measured in cm, , and . What is the volume of the washer?
- a) 1.089E+00 cm3
- b) 1.198E+00 cm3
- c) 1.318E+00 cm3
- d) 1.449E+00 cm3
- e) 1.594E+00 cm3
2) An induced emf of 5.33V is measured across a coil of 77 closely wound turns while the current throuth it increases uniformly from 0.0 to 6.57A in 0.648s. What is the self-inductance of the coil?
- a) 4.779E-01 H
- b) 5.257E-01 H
- c) 5.783E-01 H
- d) 6.361E-01 H
- e) 6.997E-01 H

- a) -3.114E-01 s
- b) -3.425E-01 s
- c) -3.767E-01 s
- d) -4.144E-01 s
- e) -4.559E-01 s
KEY:QB:Ch 14:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A washer has an inner diameter of 2.3 cm and an outer diamter of 4.44 cm. The thickness is where is measured in cm, , and . What is the volume of the washer?
- -a) 1.089E+00 cm3
- -b) 1.198E+00 cm3
- +c) 1.318E+00 cm3
- -d) 1.449E+00 cm3
- -e) 1.594E+00 cm3
2) An induced emf of 5.33V is measured across a coil of 77 closely wound turns while the current throuth it increases uniformly from 0.0 to 6.57A in 0.648s. What is the self-inductance of the coil?
- -a) 4.779E-01 H
- +b) 5.257E-01 H
- -c) 5.783E-01 H
- -d) 6.361E-01 H
- -e) 6.997E-01 H

- -a) -3.114E-01 s
- -b) -3.425E-01 s
- +c) -3.767E-01 s
- -d) -4.144E-01 s
- -e) -4.559E-01 s
QB:Ch 15:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A step-down transformer steps 16 kV down to 210 V. The high-voltage input is provided by a 200 Ω power line that carries 7 A of currentWhat is the output current (at the 210 V side ?)
- a) 4.007E+02 A
- b) 4.408E+02 A
- c) 4.848E+02 A
- d) 5.333E+02 A
- e) 5.867E+02 A
2) An RLC series combination is driven with an applied voltage of of V=V0sin(ωt), where V0=0.44 V. The resistance, inductance, and capacitance are R =7 Ω, L= 5.40E-03H , and C=5.70E-04 F, respectively. What is the amplitude of the current?
- a) 4.723E-02 A
- b) 5.195E-02 A
- c) 5.714E-02 A
- d) 6.286E-02 A
- e) 6.914E-02 A
3) The output of an ac generator connected to an RLC series combination has a frequency of 710 Hz and an amplitude of 0.88 V;. If R =2 Ω, L= 2.60E-03H , and C=8.00E-04 F, what is the impedance?
- a) 1.045E+01 Ω
- b) 1.149E+01 Ω
- c) 1.264E+01 Ω
- d) 1.391E+01 Ω
- e) 1.530E+01 Ω
KEY:QB:Ch 15:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A step-down transformer steps 16 kV down to 210 V. The high-voltage input is provided by a 200 Ω power line that carries 7 A of currentWhat is the output current (at the 210 V side ?)
- -a) 4.007E+02 A
- -b) 4.408E+02 A
- -c) 4.848E+02 A
- +d) 5.333E+02 A
- -e) 5.867E+02 A
2) An RLC series combination is driven with an applied voltage of of V=V0sin(ωt), where V0=0.44 V. The resistance, inductance, and capacitance are R =7 Ω, L= 5.40E-03H , and C=5.70E-04 F, respectively. What is the amplitude of the current?
- -a) 4.723E-02 A
- -b) 5.195E-02 A
- -c) 5.714E-02 A
- +d) 6.286E-02 A
- -e) 6.914E-02 A
3) The output of an ac generator connected to an RLC series combination has a frequency of 710 Hz and an amplitude of 0.88 V;. If R =2 Ω, L= 2.60E-03H , and C=8.00E-04 F, what is the impedance?
- -a) 1.045E+01 Ω
- +b) 1.149E+01 Ω
- -c) 1.264E+01 Ω
- -d) 1.391E+01 Ω
- -e) 1.530E+01 Ω
QB:Ch 15:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A step-down transformer steps 14 kV down to 210 V. The high-voltage input is provided by a 240 Ω power line that carries 3 A of currentWhat is the output current (at the 210 V side ?)
- a) 2.000E+02 A
- b) 2.200E+02 A
- c) 2.420E+02 A
- d) 2.662E+02 A
- e) 2.928E+02 A
2) The output of an ac generator connected to an RLC series combination has a frequency of 470 Hz and an amplitude of 0.67 V;. If R =4 Ω, L= 2.40E-03H , and C=5.10E-04 F, what is the impedance?
- a) 6.254E+00 Ω
- b) 6.879E+00 Ω
- c) 7.567E+00 Ω
- d) 8.324E+00 Ω
- e) 9.156E+00 Ω
3) An RLC series combination is driven with an applied voltage of of V=V0sin(ωt), where V0=0.3 V. The resistance, inductance, and capacitance are R =2 Ω, L= 8.10E-03H , and C=9.40E-04 F, respectively. What is the amplitude of the current?
- a) 1.364E-01 A
- b) 1.500E-01 A
- c) 1.650E-01 A
- d) 1.815E-01 A
- e) 1.997E-01 A
KEY:QB:Ch 15:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) A step-down transformer steps 14 kV down to 210 V. The high-voltage input is provided by a 240 Ω power line that carries 3 A of currentWhat is the output current (at the 210 V side ?)
- +a) 2.000E+02 A
- -b) 2.200E+02 A
- -c) 2.420E+02 A
- -d) 2.662E+02 A
- -e) 2.928E+02 A
2) The output of an ac generator connected to an RLC series combination has a frequency of 470 Hz and an amplitude of 0.67 V;. If R =4 Ω, L= 2.40E-03H , and C=5.10E-04 F, what is the impedance?
- -a) 6.254E+00 Ω
- -b) 6.879E+00 Ω
- +c) 7.567E+00 Ω
- -d) 8.324E+00 Ω
- -e) 9.156E+00 Ω
3) An RLC series combination is driven with an applied voltage of of V=V0sin(ωt), where V0=0.3 V. The resistance, inductance, and capacitance are R =2 Ω, L= 8.10E-03H , and C=9.40E-04 F, respectively. What is the amplitude of the current?
- -a) 1.364E-01 A
- +b) 1.500E-01 A
- -c) 1.650E-01 A
- -d) 1.815E-01 A
- -e) 1.997E-01 A
QB:Ch 15:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) An RLC series combination is driven with an applied voltage of of V=V0sin(ωt), where V0=0.25 V. The resistance, inductance, and capacitance are R =7 Ω, L= 5.00E-03H , and C=7.70E-04 F, respectively. What is the amplitude of the current?
- a) 2.439E-02 A
- b) 2.683E-02 A
- c) 2.952E-02 A
- d) 3.247E-02 A
- e) 3.571E-02 A
2) The output of an ac generator connected to an RLC series combination has a frequency of 910 Hz and an amplitude of 0.88 V;. If R =7 Ω, L= 6.80E-03H , and C=9.60E-04 F, what is the impedance?
- a) 3.575E+01 Ω
- b) 3.933E+01 Ω
- c) 4.326E+01 Ω
- d) 4.758E+01 Ω
- e) 5.234E+01 Ω
3) A step-down transformer steps 12 kV down to 170 V. The high-voltage input is provided by a 140 Ω power line that carries 9 A of currentWhat is the output current (at the 170 V side ?)
- a) 4.773E+02 A
- b) 5.250E+02 A
- c) 5.775E+02 A
- d) 6.353E+02 A
- e) 6.988E+02 A
KEY:QB:Ch 15:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) An RLC series combination is driven with an applied voltage of of V=V0sin(ωt), where V0=0.25 V. The resistance, inductance, and capacitance are R =7 Ω, L= 5.00E-03H , and C=7.70E-04 F, respectively. What is the amplitude of the current?
- -a) 2.439E-02 A
- -b) 2.683E-02 A
- -c) 2.952E-02 A
- -d) 3.247E-02 A
- +e) 3.571E-02 A
2) The output of an ac generator connected to an RLC series combination has a frequency of 910 Hz and an amplitude of 0.88 V;. If R =7 Ω, L= 6.80E-03H , and C=9.60E-04 F, what is the impedance?
- -a) 3.575E+01 Ω
- +b) 3.933E+01 Ω
- -c) 4.326E+01 Ω
- -d) 4.758E+01 Ω
- -e) 5.234E+01 Ω
3) A step-down transformer steps 12 kV down to 170 V. The high-voltage input is provided by a 140 Ω power line that carries 9 A of currentWhat is the output current (at the 170 V side ?)
- -a) 4.773E+02 A
- -b) 5.250E+02 A
- -c) 5.775E+02 A
- +d) 6.353E+02 A
- -e) 6.988E+02 A
QB:Ch 16:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) What is the radiation pressure on an object that is 1.20E+11 m away from the sun and has cross-sectional area of 0.082 m2? The average power output of the Sun is 3.80E+26 W.
- a) 9.568E-06 N/m2
- b) 1.053E-05 N/m2
- c) 1.158E-05 N/m2
- d) 1.274E-05 N/m2
- e) 1.401E-05 N/m2

- a) 3.972E+03 V/m
- b) 4.369E+03 V/m
- c) 4.806E+03 V/m
- d) 5.287E+03 V/m
- e) 5.816E+03 V/m
3) What is the radiation force on an object that is 3.80E+11 m away from the sun and has cross-sectional area of 0.094 m2? The average power output of the Sun is 3.80E+26 W.
- a) 8.969E-08 N
- b) 9.866E-08 N
- c) 1.085E-07 N
- d) 1.194E-07 N
- e) 1.313E-07 N
KEY:QB:Ch 16:V0[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) What is the radiation pressure on an object that is 1.20E+11 m away from the sun and has cross-sectional area of 0.082 m2? The average power output of the Sun is 3.80E+26 W.
- -a) 9.568E-06 N/m2
- -b) 1.053E-05 N/m2
- -c) 1.158E-05 N/m2
- -d) 1.274E-05 N/m2
- +e) 1.401E-05 N/m2

- -a) 3.972E+03 V/m
- -b) 4.369E+03 V/m
- +c) 4.806E+03 V/m
- -d) 5.287E+03 V/m
- -e) 5.816E+03 V/m
3) What is the radiation force on an object that is 3.80E+11 m away from the sun and has cross-sectional area of 0.094 m2? The average power output of the Sun is 3.80E+26 W.
- -a) 8.969E-08 N
- -b) 9.866E-08 N
- -c) 1.085E-07 N
- -d) 1.194E-07 N
- +e) 1.313E-07 N
QB:Ch 16:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- a) 1.049E+04 V/m
- b) 1.154E+04 V/m
- c) 1.269E+04 V/m
- d) 1.396E+04 V/m
- e) 1.535E+04 V/m
2) What is the radiation pressure on an object that is 2.20E+11 m away from the sun and has cross-sectional area of 0.082 m2? The average power output of the Sun is 3.80E+26 W.
- a) 3.131E-06 N/m2
- b) 3.445E-06 N/m2
- c) 3.789E-06 N/m2
- d) 4.168E-06 N/m2
- e) 4.585E-06 N/m2
3) What is the radiation force on an object that is 1.70E+11 m away from the sun and has cross-sectional area of 0.033 m2? The average power output of the Sun is 3.80E+26 W.
- a) 1.904E-07 N
- b) 2.094E-07 N
- c) 2.303E-07 N
- d) 2.534E-07 N
- e) 2.787E-07 N
KEY:QB:Ch 16:V1[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229

- -a) 1.049E+04 V/m
- -b) 1.154E+04 V/m
- -c) 1.269E+04 V/m
- -d) 1.396E+04 V/m
- +e) 1.535E+04 V/m
2) What is the radiation pressure on an object that is 2.20E+11 m away from the sun and has cross-sectional area of 0.082 m2? The average power output of the Sun is 3.80E+26 W.
- -a) 3.131E-06 N/m2
- -b) 3.445E-06 N/m2
- -c) 3.789E-06 N/m2
- +d) 4.168E-06 N/m2
- -e) 4.585E-06 N/m2
3) What is the radiation force on an object that is 1.70E+11 m away from the sun and has cross-sectional area of 0.033 m2? The average power output of the Sun is 3.80E+26 W.
- -a) 1.904E-07 N
- -b) 2.094E-07 N
- +c) 2.303E-07 N
- -d) 2.534E-07 N
- -e) 2.787E-07 N
QB:Ch 16:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) What is the radiation pressure on an object that is 8.90E+11 m away from the sun and has cross-sectional area of 0.013 m2? The average power output of the Sun is 3.80E+26 W.
- a) 2.315E-07 N/m2
- b) 2.547E-07 N/m2
- c) 2.801E-07 N/m2
- d) 3.082E-07 N/m2
- e) 3.390E-07 N/m2
2) What is the radiation force on an object that is 2.00E+11 m away from the sun and has cross-sectional area of 0.053 m2? The average power output of the Sun is 3.80E+26 W.
- a) 2.673E-07 N
- b) 2.940E-07 N
- c) 3.234E-07 N
- d) 3.558E-07 N
- e) 3.913E-07 N

- a) 6.651E+03 V/m
- b) 7.316E+03 V/m
- c) 8.048E+03 V/m
- d) 8.853E+03 V/m
- e) 9.738E+03 V/m
KEY:QB:Ch 16:V2[edit | edit source]
QB153099154229
1) What is the radiation pressure on an object that is 8.90E+11 m away from the sun and has cross-sectional area of 0.013 m2? The average power output of the Sun is 3.80E+26 W.
- -a) 2.315E-07 N/m2
- +b) 2.547E-07 N/m2
- -c) 2.801E-07 N/m2
- -d) 3.082E-07 N/m2
- -e) 3.390E-07 N/m2
2) What is the radiation force on an object that is 2.00E+11 m away from the sun and has cross-sectional area of 0.053 m2? The average power output of the Sun is 3.80E+26 W.
- +a) 2.673E-07 N
- -b) 2.940E-07 N
- -c) 3.234E-07 N
- -d) 3.558E-07 N
- -e) 3.913E-07 N

- -a) 6.651E+03 V/m
- -b) 7.316E+03 V/m
- +c) 8.048E+03 V/m
- -d) 8.853E+03 V/m
- -e) 9.738E+03 V/m











































