Italian phonology
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2012) |
| This article is part of the series on the |
| Italian language |
|---|
| History |
| Literature and other |
| Grammar |
| Alphabet |
| Phonology |
The phonology of Italian describes the sound system—the phonology and phonetics—of Standard Italian and its geographical variants.
Consonants
| Labial | Dental/ Alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | |||||
| Stop | p | b | t | d | k | ɡ | ||
| Affricate | t͡s | d͡z | t͡ʃ | d͡ʒ | ||||
| Fricative | f | v | s | z | ʃ | |||
| Approximant | j | w | ||||||
| Lateral | l | ʎ | ||||||
| Trill | r | |||||||
| Flap | ɾ | |||||||
Notes:
- Between two vowels, or between a vowel and an approximant or a liquid (/l, r, j, w/), consonants can be both singleton or geminated. Geminated consonants shorten the preceding vowel (or block phonetic lengthening) and the first geminated element is unreleased. For example, compare /fato/ [ˈfaː.to] ('fate') with /fatto/ [ˈfat.to] ('fact'). However, /ɲɲ/, /ʃʃ/, /ʎʎ/, are always geminated word-internally.[1] Similarly, nasals, liquids, and sibilants are pronounced slightly longer before medial consonant clusters.[2]
- /j/, /w/, and /z/ are the only consonants that cannot be geminated.
- /t, d/ are laminal denti-alveolar [t̪, d̪],[3][4][5] commonly called "dental" for simplicity.
- /k, ɡ/ are pre-velar before /i, e, ɛ, j/.[4]
- /t͡s, d͡z, s, z/ have two variants:
- Dentalized laminal alveolar [t̪͡s̪, d̪͡z̪, s̪, z̪][3][6] (commonly called "dental" for simplicity), pronounced with the blade of the tongue very close to the upper front teeth, with the tip of the tongue resting behind lower front teeth.[6]
- Non-retracted apical alveolar [t͡s̺, d͡z̺, s̺, z̺].[6] The stop components of the "apical" affricates is actually laminal denti-alveolar.[6]
- /n, l, r/ are apical alveolar [n̺, l̺, r̺] in most environments.[3][5][7] The first two are pronounced as laminal denti-alveolar [n̪, l̪] before /t, d, t͡s, d͡z, s, z/[5][8][9] and palatalized laminal postalveolar [n̠ʲ, l̠ʲ] before /t͡ʃ, d͡ʒ ʃ/.[10][11] /n/ has a velar allophone [ŋ] before /k, ɡ/.[12][13]
- /m/ and /n/ do not contrast before /p, b/ and /f, v/, where they are pronounced [m] and [ɱ], respectively.[12][14]
- In a large number of accents, /ʎ/ is a fricative [ʎ̝].[15]
- Some accents from central Italy[which?] do not have the /ʎ/ sound; instead, it is pronounced as [j], or, sometimes, [ʝ].
- /r/ is sometimes reduced to a single vibration when single, but it remains potentially a trill, not a flap [ɾ][citation needed].
- The distinction between [s] and [z] is neutralized before consonants and at the beginning of words: the former is used before voiceless consonants and before vowels at the beginning of words; the latter is used before voiced consonants (meaning [z] is an allophone of /s/ before voiced consonants). It can only contrast between two vowels within a word. According to Canepari,[16] though, the traditional standard has been replaced by a modern neutral pronunciation which always prefers /z/ when intervocalic, except when the intervocalic s is the initial sound of a word, if the compound is still felt as such: for example, presento /preˈsɛnto/[17] ('I foresee', with pre meaning 'before' and sento meaning 'I see') vs presento /preˈzɛnto/[18] ('I present'). There are many words in which dictionaries now indicate that both pronunciations with /z/ and with /s/ are acceptable. The two phonemes have merged in many regional varieties of Italian, either into /z/ (Northern-Central) or /s/ (Southern-Central). Geminate /ss/ can be pronounced as single [s].
Vowels

| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u | |
| Close-mid | e | o | |
| Open-mid | ɛ | ɔ | |
| Open | a |
In Italian there is no phonemic distinction between long and short vowels, but vowels in stressed open syllables, unless word-final, are long.[19] Adjacent identical vowels found at morpheme boundaries are not resyllabified, but pronounced separately ("quickly rearticulated"), and they might be reduced to a single short vowel in rapid speech.[20]
Although Italian contrasts close-mid (/e, o/) and open-mid (/ɛ, ɔ/) vowels in stressed syllables, this distinction is neutralised in unstressed position,[19] where only the close-mid vowels occur. The height of these vowels in unstressed position is context-sensitive; they are somewhat lowered ([e̞, o̞]) in the vicinity of more open vowels.[21] The distinction between close-mid and open-mid vowels is lost entirely in a few Southern varieties, especially in the Northern Sicilian dialect (Palermo), where they are realized as open-mid [ɛ, ɔ], as well as in some Northern varieties (in particular in Piedmont), where they are realized as mid [e̞, o̞].
Word-final stressed /ɔ/ is found in a small number of words: però, ciò, Giò (nickname), and the first person singular future of all verbs and the third person singular preterite of most verbs. Word-final unstressed /u/ is rare.[22] Major exceptions are onomatopoeic terms (babau);[23] loanwords (guru);[24] and place or family names of Sardinian origin (Gennargentu,[25] Porcu).[26]
When the last phoneme of a word is an unstressed vowel and the first phoneme of the following word is any vowel, the former vowel tends to become non-syllabic. This phenomenon is called synalepha and should be taken in account when counting syllables, e.g. in poetry.
In addition to monophthongs, Italian has diphthongs, but these are both phonemically and phonetically simply combinations of the other vowels, with some being very common (e.g. /ai, ia, io, au/), others being rarer (e.g. /ɛi, ɛa, ɛo, uo, ii/) and some never occurring within (native) Italian words (e.g. /ou, uu/). None of these diphthongs are however considered to have distinct phonemic status because their constituents do not behave differently than they would in isolation (and all occur in isolation), unlike the diphthongs in some languages like English and German. Grammatical tradition makes a distinction between as ‘falling’ and ‘rising’ diphthongs; however, since rising diphthongs are composed of one semiconsonantal sound [j] or [w] and one vowel sound, they are not actually technically diphthongs. The practice of referring to them as ‘diphthongs’ has been criticised by phoneticians like Luciano Canepari.[16]
Phonotactics
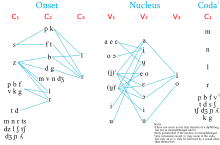
Onset
Italian allows up to three consonants in syllable-initial position, though there are limitations:[27]
CC
- /s/ + any voiceless stop or /f/. E.g. spavento ('fright')
- /z/ + any voiced stop, /v d͡ʒ m n l r/. E.g. srotolare ('unroll')
- /f v/, or any stop + /r/. E.g. frana ('landslide')
- /f v/, or any stop except /t d/ + /l/. E.g. platano ('planetree')
- /f v s z/, or any stop or nasal + /j w/. E.g. fiume ('river'), vuole ('he/she wants'), siamo ('we are'), suono ('sound')
- In words of foreign (mostly Greek) origin which are only partially assimilated, other combinations such as /pn/ (e.g. pneumatico), /mn/ (e.g. mnemonico), /tm/ (e.g. tmesi), and /ps/ (e.g. pseudo-) occur.
CCC
- /s/ + voiceless stop or /f/ + /r/. E.g. spregiare ('to despise')
- /s/ + /p k/ + /l/. E.g. sclerosi ('sclerosis')
- /z/ + voiced stop + /r/. E.g. sbracciato ('with bare arms'), sdraiare ('to lay down'), sgravare ('to relieve')
- /z/ + /b/ + /l/. E.g. sbloccato ('unblocked')
- /f v/ or any stop + /r/ + /j w/. E.g. priego (antiquated form of prego 'I pray'), proprio ('(one's) own' / proper / properly), pruovo (antiquated form of provo 'I try')
- /f v/ or any stop or nasal + /w/ + /j/. E.g. quieto ('quiet'), continuiamo ('we continue')
The last combination is however rare and one of the approximants is often vocalised, e.g. quieto /ˈkwjɛto, kwiˈɛto/, continuiamo /((kontiˈnwjamo)), kontinuˈjamo, kontinwiˈamo/
Nucleus
The syllable nucleus is the only mandatory part of a syllable (for instance, a is a word) and must be a vowel or a diphthong. In a diphthong the most common second elements are /i̯/ or /u̯/ but other combinations such as idea /iˈdɛa̯/, trae /ˈtrae̯/ may also be interpreted as diphthongs.[16] Combinations of /j w/ with vowels are often labelled diphthongs, allowing for combinations of /j w/ with real diphthongs to be called triphthongs. It is more practical to label /j w/ as normal consonants and /jV wV/ as normal consonant-vowel sequences. In that interpretation, Italian has only falling diphthongs (phonemically at least, cf. Synaeresis) and no triphthongs.[16]
Coda
A coda is only permissible in case of monophthong nuclei [citation needed], and can be one of:
- /r/. E.g. per ('for'), parte ('part')
- /l/. E.g. al ('to the'), alto ('high')
- /n/. E.g. con ('with'), conto ('count'), which undergoes assimilation if a consonantal onset follows, e.g. un poco [umˈpɔːko] ('a little')
- /m/. E.g. compro ('I buy'), ampio ('ample')
- an occlusive or fricative usually creating gemination with the following syllable onset. E.g. tutto ('everything'), avvertire ('to warn')
Syntactic gemination
Word-initial consonants are geminated after certain vowel-final words in the same prosodic unit. The words that trigger this include unstressed some proclitic particles, paroxytone prepositions, monosyllabic words, and oxytonic polysyllabic words.[28] For example, casa ('house') is pronounced [ˈkaːsa] but a casa ('homeward') is pronounced [ak̚ˈkaːsa]. This is not a purely phonological process, as the la in la casa ('the house') does not trigger this gemination: [la ˈkaːsa].
Regional variation
The above IPA symbols and description refer to standard Italian, based on a somewhat idealized version of the Tuscan-derived national language. As is common in many cultures, this single version of the language was pushed as neutral, proper, and eventually superior, leading to some stigmatization of varying accents. Television news anchors and other high-profile figures had to put aside their regional Italian when in the public sphere. However, in more recent years the enforcement of this standard has fallen out of favor in Italy, and news reporters, actors, and the like are now more free to deliver their words in their native regional variety of Italian, which appeals to the Italian population's range of linguistic diversity. The variety is still not represented in its wholeness and accents from the South are maybe to be considered less popular, except in shows set in the South and in comedy, a field in which Naples, Sicily and the South in general have always been present. Though it still represents the basics for the standard variety, the loosened restrictions have led to Tuscan being seen for what it is, just one dialect among many with its own regional peculiarities and qualities, many of which are shared with Umbria, Southern Marche and Northern Lazio.
- In Tuscany (though not in standard Italian, which is derived from, but not equivalent to Tuscan Italian), voiceless stops become fricatives between vowels.[29] That is, /p t k/ → [ɸ θ h/x]: e.g. i capitani ('the captains') [iˌhaɸiˈθaːni]. In a much more widespread area of Central Italy, postalveolar affricates are deaffricated when intervocalic so that in Cina ('in China') is pronounced [in t͡ʃiːna] but la Cina ('the China') is [laʃiːna].[30] Since /ʃ/ surfaces as long post-vocalically, this can produce minimal pairs distinguished only by length of the word-initial consonant:[citation needed] [laʃeːna] la cena vs. [laʃʃeːna] la scena.
- In nonstandard varieties of Central and Southern Italian, some stops at the end of a syllable completely assimilate to the following consonant.[citation needed] For example, a Venetian might say tecnica as [ˈtɛknika] or [ˈtɛɡnika] in violation of normal Italian consonant contact restrictions[clarification needed], while a Florentine would likely pronounce tecnica as [ˈtɛnniha], a Roman on a range from [ˈtɛnnika] to [ˈtɛnniɡa] (in Southern Italian, complex clusters usually are separated by a vowel: a Neapolitan would say [ˈtɛkkənikə], a Sicilian [ˈtɛkkɪnɪka]). Similarly, although the cluster /kt/ has developed historically as /tt/ through assimilation, a learned word such as ictus will be pronounced [ittus] by some, [iktus] by others.
- In popular (non-Tuscan) Central and Southern Italian speech, /b/ and /d͡ʒ/ tend to always be geminated ([bb] and [dd͡ʒ]) when between two vowels, or a vowel and a sonorant (/j/, /w/, /l/, or /r/). Sometimes this is also used in written language, e.g. writing robba instead of roba ('property'), to suggest a regional accent, though this spelling is considered incorrect. In Tuscany intervocalic (non geminated) /d͡ʒ/ is realized as [ʒ] (whereas intervocalic [non geminated] /t͡ʃ/ is realized as [ʃ] as in parts of Centro-Southern Italy).[citation needed]
- The two phonemes /s/ and /z/ have merged in many varieties of Italian: when between two vowels within the same word, it tends to always be pronounced [z] in Northern Italy, and [s] in Central and Southern Italy (except in the Arbëreshë community). A notable example is the word casa ('house'): in Northern Italy it is pronounced [ˈkaːza]; in Southern-Central Italy it's pronounced [ˈkaːsa].
- In several Southern varieties, voiceless stops tend to become voiced if following a sonorant, as an influence of the still largely spoken regional languages: campo /ˈkampo/ becomes /ˈkambo/, and Antonio /anˈtɔnjo/ becomes /anˈdɔnjo/.
Phonological development
Very little research has been done on the earliest stages of phonological development in Italian.[31] This article primarily describes phonological development after the first year of life. See the main article on phonological development for a description of first year stages. Many of the earliest stages are thought to be universal to all infants.
Phoneme inventory
Word-final consonants are rarely produced during the early stages of word production. Consonants are usually found in word-initial position, or in intervocalic position.[32]
17 months
Most consonants are word-initial: They are the stops /p/, /b/, /t/, and /k/ and the nasal /m/. A preference for a front place of articulation is present.[32]
21 months
More phones now appear in intervocalic contexts. The additions to the phonetic inventory are the voiced stop /d/, the nasal /n/, the voiceless affricate /t͡ʃ/, and the liquid /l/.[32]
24 months
The fricatives /f/, /v/, and /s/ are added, primarily at the intervocalic position.[32]
27 months
Approximately equal numbers of phones are now produced in word-initial and intervocalic position. Additions to the phonetic inventory are the voiced stop /ɡ/ and the consonant cluster /kw/. While the word-initial inventory now tends to have all the phones of the adult targets (adult production of the child's words), the intervocalic inventory tends to still be missing four consonants or consonant clusters of the adult targets: /f/, /d͡ʒ/, /r/, and /st/.[32]
Stops are the most common manner of articulation at all stages and are produced more often than they are present in the target words at around 18 months. Gradually this frequency decreases to almost target-like frequency by around 27 months. The opposite process happens with fricatives, affricates, laterals and trills. Initially, the production of these phonemes is significantly less than what is found in the target words and the production continues to increases to target-like frequency. Alveolars and bilabials are the two most common places of articulation, with alveolar production steadily increasing after the first stage and bilabial production gently decreasing. Labiodental and postalveolar production increases throughout development, while velar production decreases.[33]
Phonotactics
Syllable structures
6–10 months
Babbling becomes distinct from previous, less structured vocal play. Initially, syllable structure is limited to CVCV, called reduplicated babbling. At this stage, children’s vocalizations have a weak relation to adult Italian and the Italian lexicon.[34]
11–14 months
The most-used syllable type changes as children age, and the distribution of syllables takes on increasingly Italian characteristics. This ability significantly increases between the ages of 11 and 12 months, 12 and 13 months, and 13 and 14 months.[34] Consonant clusters are still absent. Children's first ten words appear around month 12, and take CVCV format (e.g. mama 'mother', papa 'father').[35]
18–24 months
Reduplicated babbling is replaced by variegated babbling, producing syllable structures such as C1VC2V (e.g. cane 'dog', topo 'mouse'). Production of trisyllabic words begins (e.g. pecora 'sheep', matita 'pencil').[35] Consonant clusters are now present (e.g. bimba 'female child', venti 'twenty'). Ambient language plays an increasingly significant role as children begin to solidify early syllable structure. Syllable combinations that are infrequent in the Italian lexicon, such as velar-labial sequences (e.g. capra 'goat' or gamba 'leg') are infrequently produced correctly by children, and are often subject to consonant harmony.[36]
Stress patterns
In Italian, stress is lexical, meaning it is word-specific and partly unpredictable. Penultimate stress (primary stress on the second-to-last syllable) is also generally preferred.[37][38] This goal, acting simultaneously with the child's initial inability to produce polysyllabic words, often results in weak-syllable deletion. The primary environment for weak-syllable deletion in polysyllabic words is word-initial, as deleting word-final or word-medial syllables would interfere with the penultimate stress pattern heard in ambient language.[39]
Phonological awareness
Children develop syllabic segmentation awareness earlier than phonemic segmentation awareness. In earlier stages, syllables are perceived as a separate phonetic unit, while phonemes are perceived as assimilated units by coarticulation in spoken language. By first grade, Italian children are nearing full development of segmentation awareness on both syllables and phonemes. Compared to those children whose mother tongue exhibits closed syllable structure (CVC,CCVC, CVCC, etc.), Italian-speaking children develop this segmentation awareness earlier, possibly due to its open syllable structure (CVCV, CVCVCV, etc.).[40] Rigidness in Italian (shallow orthography and open syllable structure) makes it easier for Italian-speaking children to be aware of those segments.[41]
Sample texts
From the Bible, Luke 2, 1-7 (for an English version click here)
You can listen to a rendition of this text as recorded by an Italian native speaker from Milan. As a northerner, his pronunciation lacks syntactic doubling ([ˈfu ˈfatto] instead of [ˈfu f.fatto]) and intervocalic [s] ([ˈkaːza] instead of [ˈkaːsa]).
2:1 In quei giorni, un decreto di Cesare Augusto ordinava che si facesse un censimento di tutta la terra.
2 Questo primo censimento fu fatto quando Quirino era governatore della Siria.
3 Tutti andavano a farsi registrare, ciascuno nella propria città.
4 Anche Giuseppe, che era della casa e della famiglia di Davide, dalla città di Nazaret e dalla Galilea si recò in Giudea nella città di Davide, chiamata Betlemme,
5 per farsi registrare insieme a Maria, sua sposa, che era incinta.
6 Proprio mentre si trovavano lì, venne il tempo per lei di partorire.
7 Mise al mondo il suo primogenito, lo avvolse in fasce e lo depose in una mangiatoia, poiché non c'era posto per loro nella locanda.
The differences in pronunciation are underlined in the following transcriptions; the velar [ŋ] is an allophone of /n/ and the long vowels are allophones of the short vowels, but are shown for clarity.
A rough transcription of the audio sample is:
2:1 [iŋ kwei ˈd͡ʒorni un deˈkreːto di ˈt͡ʃeːzare auˈɡusto ordiˈnaːva ke si faˈt͡ʃɛsse un t͡ʃensiˈmento di ˈtutta la ˈtɛrra
2ˈkwesto ˈpriːmo t͡ʃensiˈmento fu ˈfatto ˈkwando kwiˈriːno ˈe:ra ɡovernaˈtoːre ˈdella ˈsiːrja.
3ˈtutti anˈdaːvano a ˈfarsi red͡ʒisˈtraːre t͡ʃasˈkuːno ˈnella ˈprɔːprja t͡ʃitˈta
4ˈaŋke d͡ʒuˈzɛppe ke ˈe:ra ˈdella ˈkaːza e ˈdella faˈmiʎʎa di ˈdaːvide ˈdalla t͡ʃitˈta di ˈnadd͡zaret e ˈdalla ɡaliˈle:a si reˈkɔ in d͡ʒuˈde:a ˈnella t͡ʃitˈta di ˈdaːvide, kjaˈmaːta beˈtlɛmme
5per ˈfarsi red͡ʒisˈtraːre inˈsje:me a maˈriːa ˈswa ˈspɔːza, ke ˈeːra inˈt͡ʃinta
6ˈprɔːprjo ˈmentre si troˈvaːvano li ˈvɛnne il ˈtempo per lɛːi di partoˈriːre
7ˈmiːze al ˈmondo il swo primoˈd͡ʒeːnito, lo avˈvɔlse in ˈfaʃʃe e lo deˈpoːze in ˈuːna mand͡ʒaˈtɔːja poiˈke non ˈt͡ʃe:ra ˈpɔsto per ˈloːro ˈnella loˈkanda]
The Standard Italian pronunciation of the text is:
2:1 [iŋ kwei ˈd͡ʒorni un deˈkreːto di ˈt͡ʃeːzare auˈɡusto ordiˈnaːva ke ssi faˈt͡ʃesse un t͡ʃensiˈmento di ˈtutta la ˈtɛrra
2ˈkwesto ˈpriːmo t͡ʃensiˈmento fu fˈfatto ˈkwando kwiˈriːno ˈɛ:ra ɡovernaˈtoːre ˈdella ˈsiːrja.
3ˈtutti anˈdaːvano a fˈfarsi red͡ʒisˈtraːre t͡ʃasˈkuːno ˈnella ˈprɔːprja t͡ʃitˈta
4ˈaŋke d͡ʒuˈzɛppe ke ˈɛ:ra ˈdella ˈkaːsa e dˈdella faˈmiʎʎa di ˈdaːvide ˈdalla t͡ʃitˈta ddi ˈnadd͡zaret e dˈdalla ɡaliˈlɛ:a si reˈkɔ in d͡ʒuˈdɛ:a ˈnella t͡ʃitˈta ddi ˈdaːvide, kjaˈmaːta beˈtlɛmme
5per ˈfarsi red͡ʒisˈtraːre inˈsjɛ:me a mmaˈriːa ˈsuːa ˈspɔːza, ke ˈɛːra inˈt͡ʃinta
6ˈprɔːprjo ˈmentre si troˈvaːvano li ˈve:nne il ˈtɛmpo per lɛːi di partoˈriːre
7ˈmiːze al ˈmondo il suːo primoˈd͡ʒɛːnito, lo avˈvɔlse in ˈfaʃʃe e llo deˈpoːze in ˈuːna mand͡ʒaˈtoːja poiˈke non ˈt͡ʃɛ:ra ˈposto per ˈloːro ˈnella loˈkanda]
See also
- Italian alphabet
- Italian language
- Italian grammar
- Wikipedia help page for IPA for Italian - includes English approximations
- Italian pronunciation guide at Wiktionary
- Syntactic doubling
References
- ^ Hall (1944:77–78)
- ^ Hall (1944:78)
- ^ a b c Bertinetto & Loporcaro (2005:132)
- ^ a b Canepari (1992:62)
- ^ a b c Rogers & d'Arcangeli (2004:117)
- ^ a b c d Canepari (1992:68 and 75–76)
- ^ Canepari (1992:57, 84 and 88–89)
- ^ Bertinetto & Loporcaro (2005:133)
- ^ Canepari (1992:58 and 88–89)
- ^ Bertinetto & Loporcaro (2005:134)
- ^ Canepari (1992:57–59 and 88–89)
- ^ a b Bertinetto & Loporcaro (2005:134–135)
- ^ Canepari (1992:59)
- ^ Canepari (1992:58)
- ^ Ashby (2011:64): "(...) in a large number of Italian accents, there is considerable friction involved in the pronunciation of [ʎ], creating a voiced palatal lateral fricative (for which there is no established IPA symbol)."
- ^ a b c d Luciano Canepari, A Handbook of Pronunciation, chapter 3: «Italian».
- ^ http://www.dizionario.rai.it/poplemma.aspx?lid=30356&r=69940
- ^ http://www.dizionario.rai.it/poplemma.aspx?lid=30351&r=13567
- ^ a b Rogers & d'Arcangeli (2004:119)
- ^ Bertinetto & Loporcaro (2005:137)
- ^ Bertinetto & Loporcaro (2005:137–138)
- ^ Bertinetto & Loporcaro (2005:138)
- ^ [1]
- ^ [2]
- ^ [3]
- ^ [4]
- ^ Hall (1944:79)
- ^ Hall (1944:80)
- ^ Hall (1944:75)
- ^ Hall (1944:76)
- ^ Keren-Portnoy, Majorano & Vihman (2009:240)
- ^ a b c d e Zmarich & Bonifacio (2005:759)
- ^ Zmarich & Bonifacio (2005:760)
- ^ a b Majorano & D'Odorico (2011:53)
- ^ a b Fasolo, Majorano & D'Odorico (2006:86)
- ^ Majorano & D'Odorico (2011:58)
- ^ Doris Borrelli - Raddoppiamento Sintattico in Italian: A Synchronic and Diachronic ... -2002 Page 8 "Stress in Italian occurs most often on the penultimate syllable (paroxytones); it also occurs on the antepenultimate syllable (proparoxytones) ..."
- ^ D'imperio & Rosenthall (1999:5)
- ^ Majorano & D'Odorico (2011:61)
- ^ Cossu et al. (1988:10)
- ^ Cossu et al. (1988:11)
Bibliography
- Ashby, Patricia (2011), Understanding Phonetics, Understanding Language series, Routledge, ISBN 978-0340928271
- Bertinetto, Marco; Loporcaro, Michele (2005). "The sound pattern of Standard Italian, as compared with the varieties spoken in Florence, Milan and Rome" (PDF). Journal of the International Phonetic Association. 35 (2): 131–151. doi:10.1017/S0025100305002148.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Canepari, Luciano (1992), Il MªPi – Manuale di pronuncia italiana (in Italian), Bologna: Zanichelli, ISBN 88-08-24624-8
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - Cossu, Giuseppe; Shankweiler, Donald; Liberman, Isabelle Y.; Katz, Leonard; Tola, Giuseppe (1988). "Awareness of phonological segments and reading ability in Italian children". Applied Psycholinguistics. 9 (1): 1–16. doi:10.1017/S0142716400000424.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Costamagna, Lidia (2007). "The acquisition of Italian L2 affricates: The case of a Brazilian learner" (PDF). New Sounds: Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on the Acquisition of Second Language Speech. pp. 138–148.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - D'imperio, Maria Paola; Rosenthall, Sam (1999). "Phonetics and phonology of main stress in italian". Phonology 16 (1). pp. 1–28.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Fasolo, Mirco; Majorano, Marinella; D'Odorico, Laura (2006). "Babbling and first words in children with slow expressive development". Clinical Linguistics & Phonetics. 22 (2): 83–94. doi:10.1080/02699200701600015.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Hall, Robert A. Jr. (1944). "Italian phonemes and orthography". Italica. 21 (2). American Association of Teachers of Italian: 72–82. doi:10.2307/475860. JSTOR 475860.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Keren-Portnoy, Tamar; Majorano, Marinelloa; Vihman, Marilyn (2009). "From phonetics to phonology: The emergence of first words in Italian*". Journal of Child Language. 36 (2): 235–267. doi:10.1017/S0305000908008933. PMID 18789180.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Majorano, M.; D'Odorico, L. (2011). "The transition into ambient language: A longitudinal study of babbling and first word production of Italian children". First Language. 31 (1): 47–66. doi:10.1177/0142723709359239.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Rogers, Derek; d'Arcangeli, Luciana (2004). "Italian". Journal of the International Phonetic Association. 34 (1): 117–121. doi:10.1017/S0025100304001628.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Zmarich, Claudio; Bonifacio, Serena (2005). "Phonetic Inventories in Italian Children aged 18-27 months: a Longitudinal Study" (PDF). Interspeech. pp. 757–760.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
